Immortalized Human Corneal Epithelial Cells-SV40
Cat.No.: CSC-I2318Z
Species: Human
Morphology: Epithelial morphology
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
- Documents
free from contaminations (bacteria incl. mycoplasma, fungi, HIV, HAV, HBV, HCV, Parvo-B19) and cross-contaminations
Note: Never can cells be kept at -20°C.
The corneal epithelium, a self-renewing, stratified epithelial sheet, constitutes the first line of defense against invading microorganisms. The homeostatic mechanisms regulating the normal physiological renewal of the epithelial sheet, involving proliferation, differentiation, and desquamation, are crucial for maintaining this intact barrier function. The underlying molecular interactions responsible for the balance and coordination of these processes, however, are still not well defined.
Cultured human corneal epithelial (HCE) cells could provide an efficient model for the study of cellular signaling and molecular pathways regulating normal corneal epithelial cell homeostasis. However, primary cultures of HCE cells can only be passaged a limited number of times before they undergo growth arrest and irreversible senescence.
In 1995, Araki-Sasaki et al. established a simian virus (SV)40-induced HCE cell line as an in vitro model for human corneal epithelial cells. Although several types of cell line currently exist for this specific epithelial cell type, the SV40-immortalized HCE cell line appears to be the one most favored and frequently used, possibly because it is free of infectious virus particles and is easy to maintain. The SV40-immortalized HCE cell line has historically been used for a range of studies, most of which are involved in drug development, elucidation of cellular signaling pathways,or molecular interactions maintaining homeostasis of normal corneal epithelial cells.
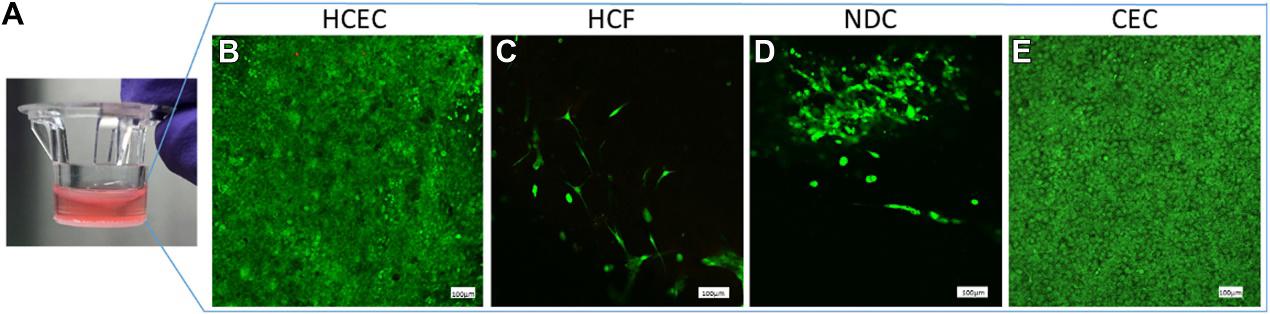
An In Vitro 3D Collagen-Based Corneal Construct Using Human Corneal Cell Lines
In vitro human corneal constructs were created using chemically crosslinked collagen and chondroitin sulfate extracellular matrix and seeded with 3 human corneal cell types (epithelial, stromal, and endothelial) together with neural cells. The neural cells were derived from hybrid neuroblastoma cells (NDC) and the other cells used from immortalized human corneal cell lines (HCEC, HCF, and CEC). To check the feasibility and characterize the constructs, cytotoxicity, cell proliferation, histology, and protein expression studies were performed.
The construct showed a typical appearance for different cellular layers, including healthy appearing, phenotypically differentiated neurons. The expected protein expression profiles for specific cell types within the construct were confirmed with western blotting.
The construct may be useful in evaluation of specific corneal disorders and in developing different corneal disease models. Additionally, the construct can be used in evaluating drug targeting and/or penetration to individual corneal layers, testing novel therapeutics for corneal diseases, and potentially reducing the necessity for animals in corneal research at the early stages of investigation.
![Western blot analysis of the expression of cell markers (MUC16 and cytokeratin 3 + 12 (A), Smooth muscle actin and ALDH3A1 (B), ZO-1 (C), and vimentin and β III tubulin (D) in corneal constructs were compared with positive control cell lines grown in monolayer cell culture (SV40-immortalized human corneal epithelial cells [HCEC], immortalized human corneal fibroblasts [HCF], telomerase-immortalized human corneal endothelial cells [CEC], or neuroblastoma cells [NDC], respectively).](/upload/images/immortalized-human-corneal-epithelial-cells-sv40-casestudy-2.jpg)
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells