Immortalized Human Oviductal Cells (OE-E6/E7)
Cat.No.: CSC-I9284L
Species: Homo sapiens
Source: Fallopian tube
Morphology: Epithelial
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Note: Never can cells be kept at -20 °C.
CIK-HT003 HT® Lenti-SV40T Immortalization Kit
2) Western blot preformed to detect presence of CK19 and estrogen receptors.
OE-E6/E7 is a cell line of Human Oviductal Epithelial Cells (OE). Human Oviductal Epithelial Cells were first obtained from a patient during surgery for the removal of uterine fibroids, and the cell line immortalized through the introduction of HPV 16 E6/E7 genes. The oviduct is part of the female reproductive system that is used to transport eggs and is where sperm travel to fertilize them.
OE-E6/E7 is a human cell line that maintains many of the functions and characteristics of the epithelial cells that line the oviduct. The OE-E6/E7 cell line can secrete various kinds of glycoproteins, which can be useful for embryo development, like human oviduct-specific glycoprotein, commonly known as oviductin, which can support embryo development in an in vitro environment. The cell line is capable of expressing estrogen receptor α (ERα) and estrogen receptor β (ERβ), and so it can be activated by estrogen. These properties make the OE-E6/E7 cell line a stable in vitro model for researching oviduct functions, embryo development, and the pathomechanisms of related diseases.
Human Sperm DNA Damage has an Effect on Immunological Interaction Between Spermatozoa and Fallopian Tube
Toll-like receptors are crucial for the immune interaction of spermatozoa with the fallopian tube, influencing ovulation, sperm capacitation, fertilization, and pregnancy. Zandieh et al. examined how sperm with high DNA fragmentation (high DF) affects the expression of toll-like receptors, adaptor molecules, and cytokines in the human fallopian tube cell line (OE-E6/E7), compared to normal sperm.
Semen samples were collected from 10 infertile males with high DF (>20%) and 10 healthy donors with DF 1-3%. After preparation, samples were co-cultured with OE-E6/E7 cells. TUNEL results divided samples into high (20-25%) and low DF groups (1-3%). Figure 1 presents images of positive (A) and negative (B) controls and a sample with fragmented DNA spermatozoa (C). Only complete spermatozoa were considered; heads without tails were excluded. Prior research revealed that OE-E6/E7 expresses TLR1-6 at mRNA and protein levels. Figure 2 displays TLR1-6 gene expression profiles in OE-E6/E7 cells with high and low DF groups. TLR1-6 genes showed significantly higher expression with high DF sperm. Adaptor molecule expression was also significantly higher in the high DF group, except in the TRAM pathway (Fig. 3).
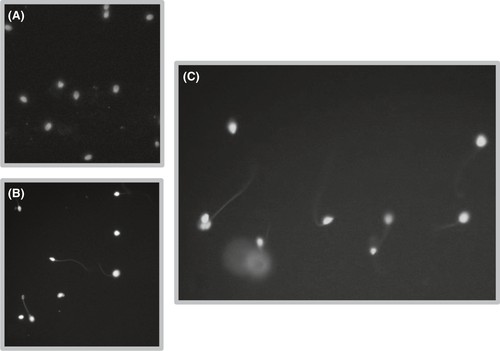 Fig. 1. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) dUTP Nick-End Labeling (TUNEL) assay (Zandieh Z, Ashrafi M, et al., 2019).
Fig. 1. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) dUTP Nick-End Labeling (TUNEL) assay (Zandieh Z, Ashrafi M, et al., 2019).
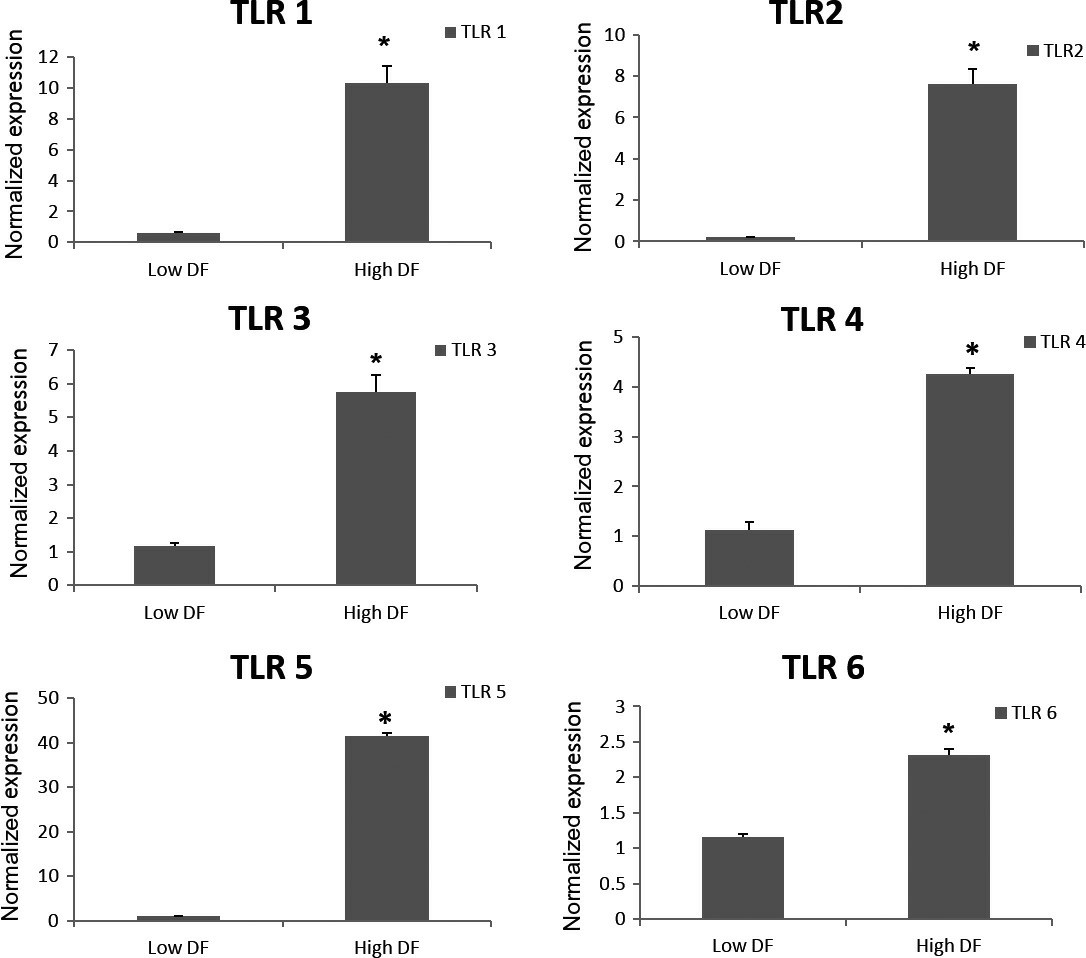 Fig. 2. The mean relative expression of TLR genes 1-6 in OE-E6/E7 cells co-cultured with high and low DF groups (Zandieh Z, Ashrafi M, et al., 2019).
Fig. 2. The mean relative expression of TLR genes 1-6 in OE-E6/E7 cells co-cultured with high and low DF groups (Zandieh Z, Ashrafi M, et al., 2019).
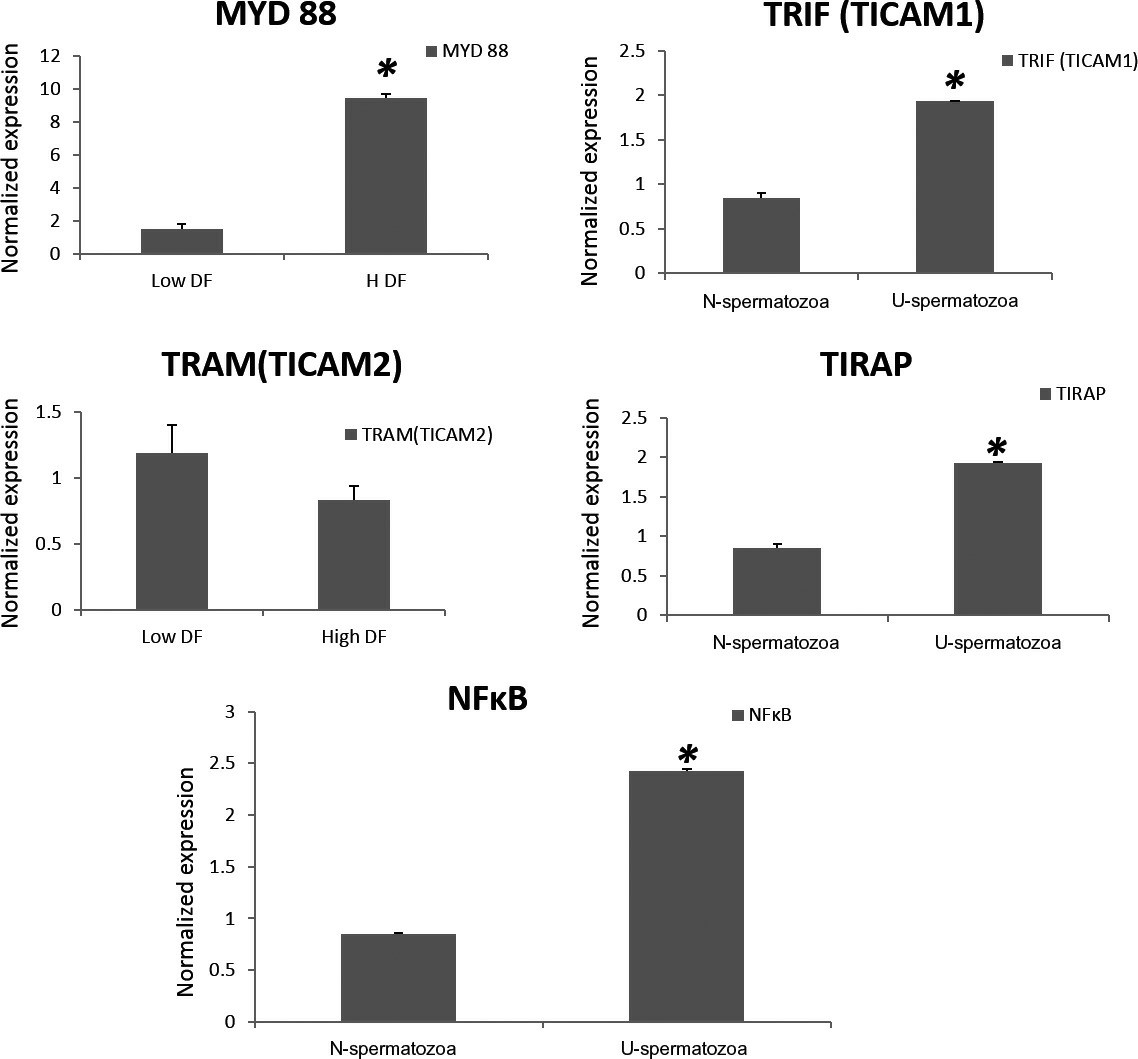 Fig. 3. The mean relative expression of adaptor molecules MyD88, TIRAP, TRIF (TICAM 1), TRAM (TICAM 2) in high DNA fragmentation (DF) and low DF groups (Zandieh Z, Ashrafi M, et al., 2019).
Fig. 3. The mean relative expression of adaptor molecules MyD88, TIRAP, TRIF (TICAM 1), TRAM (TICAM 2) in high DNA fragmentation (DF) and low DF groups (Zandieh Z, Ashrafi M, et al., 2019).
Effect of LNG on Fallopian Tube Epithelium Receptivity
Previous study of Li's team indicated that emergency contraception, including levonorgestrel and progesterone, could lead to ectopic pregnancy following contraception failure. However, their understanding of the effects of levonorgestrel and progesterone on oviductal physiology is limited.
To determine whether LNG affects the receptivity of the fallopian tubal epithelium, they subjected the tubal epithelial cell line OE-E6/E7 to different doses of LNG and P4 and detected the expression of various receptive markers, including LIF, STAT3, IGFBP1, ITGB3, MUC1, and ACVR1B, through qRT-PCR and western blot analyses. However, the expression of these receptive markers did not show any significant changes following the administration of LNG or P4, regardless of the dose (Fig. 4). Furthermore, they performed JAr spheroid-fallopian tubal epithelial cell attachment assays. Spheroids of approximately 60–150 μm were produced from JAr cells and allowed to attach to a monolayer of OE-E6/E7 cells (Fig. 5a) that had been previously treated with different doses of LNG and P4, and the percentages of attached JAr spheroids did not show any significant differences among the groups (Fig. 5c-d).
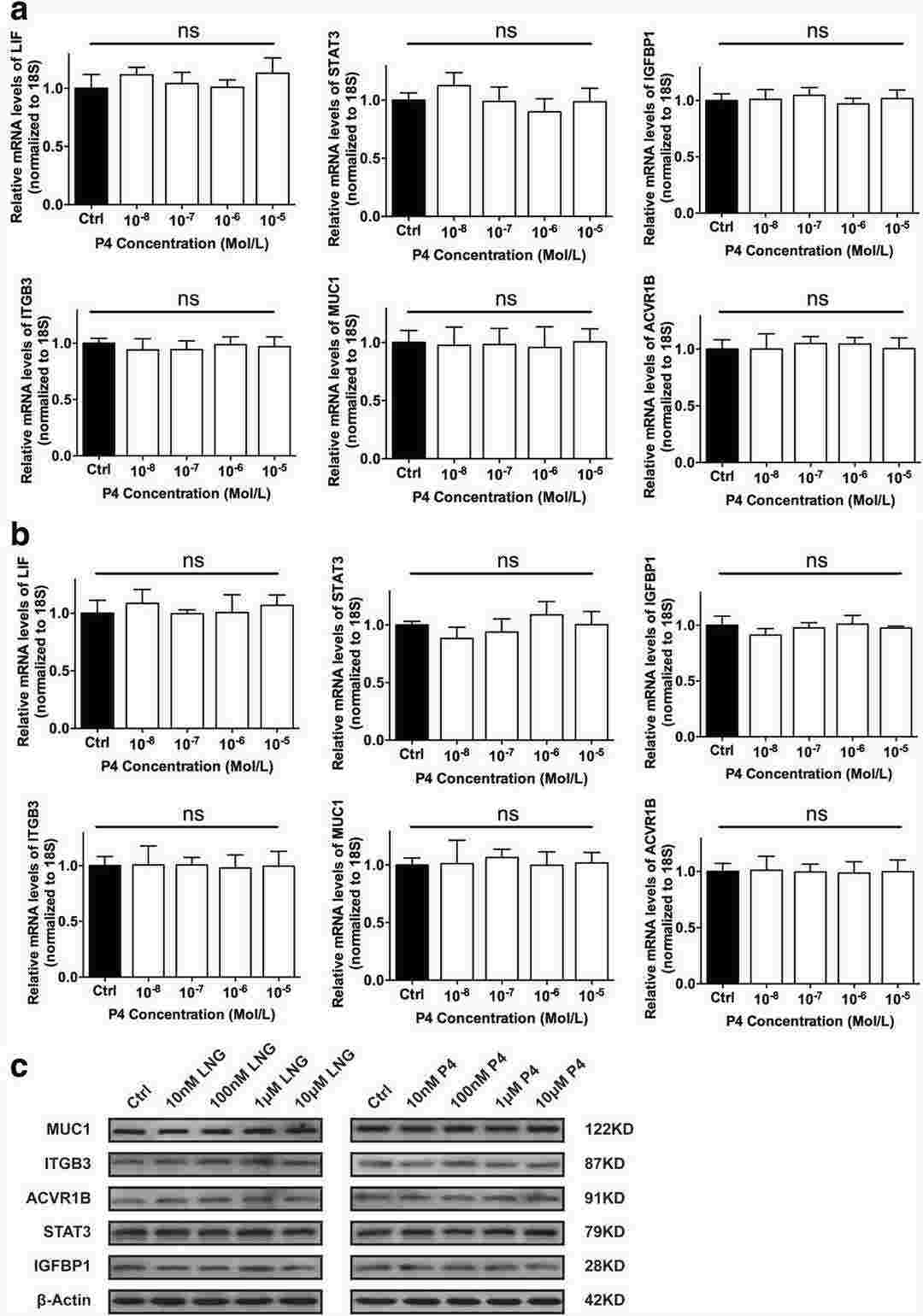 Fig. 4. Effects of different concentrations of LNG and P4 on the expression of receptivity markers in the fallopian tubes (Li C, Zhang HY, et al., 2018).
Fig. 4. Effects of different concentrations of LNG and P4 on the expression of receptivity markers in the fallopian tubes (Li C, Zhang HY, et al., 2018).
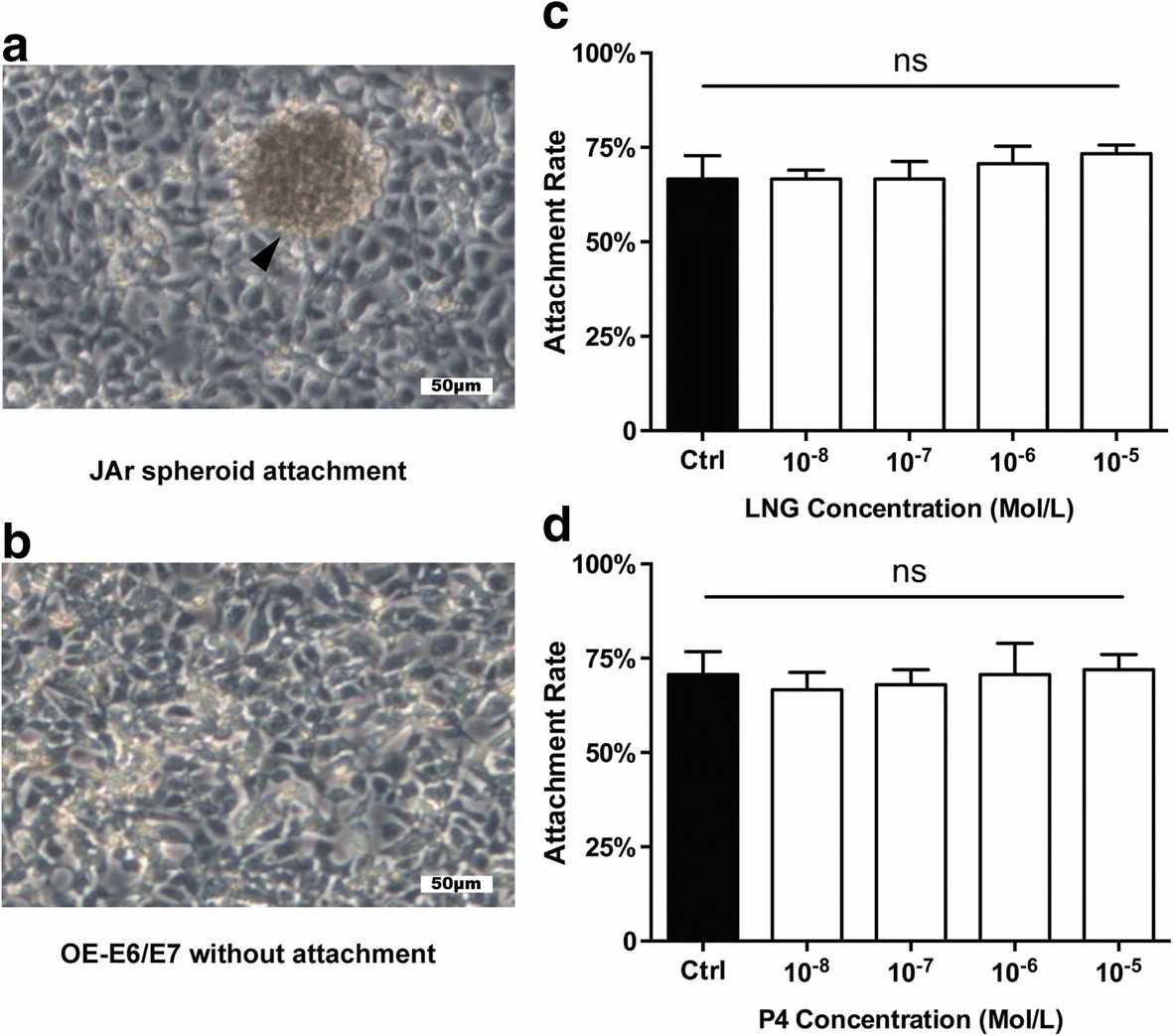 Fig. 5. Effects of different concentrations of LNG and P4 on JAr spheroid- fallopian tubal attachment rates (Li C, Zhang HY, et al., 2018).
Fig. 5. Effects of different concentrations of LNG and P4 on JAr spheroid- fallopian tubal attachment rates (Li C, Zhang HY, et al., 2018).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells