Immortalized Human Oral Keratinocytes
Cat.No.: CSC-I9230L
Species: homo sapiens
Source: Human Oral Mucosa
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
- Documents
Note: Never can cells be kept at -20 °C.
CIK-HT013 HT® Lenti-hTERT Immortalization Kit
CIK-HT003 HT® Lenti-SV40T Immortalization Kit
Immortalized Human Oral Keratinocytes (IHOKs) represent a pivotal in vitro model system engineered to overcome the significant limitations of primary oral keratinocytes. Primary cells, typically isolated from gingival, buccal, or palatal mucosa, have a finite replicative lifespan, undergo rapid terminal differentiation in culture, and exhibit substantial donor-to-donor variability due to age, health status, and anatomical site. These constraints hinder reproducible, long-term mechanistic studies. Immortalization, commonly achieved through the introduction of viral oncogenes (e.g., HPV16 E6/E7 or SV40 Large T antigen) or the catalytic subunit of human telomerase (hTERT), confers an extended, stable proliferative capacity while aiming to preserve the essential phenotypic and functional characteristics of their tissue of origin.
The defining advantage of well-validated IHOK lines is their provision of a genetically uniform, sustainable, and experimentally tractable human epithelial system that closely mimics the in vivo oral mucosal lining.
Cytotoxicity and Antifungal Effects of Combined Dexamethasone and Miconazole on Human Oral Keratinocytes and Gingival Fibroblasts
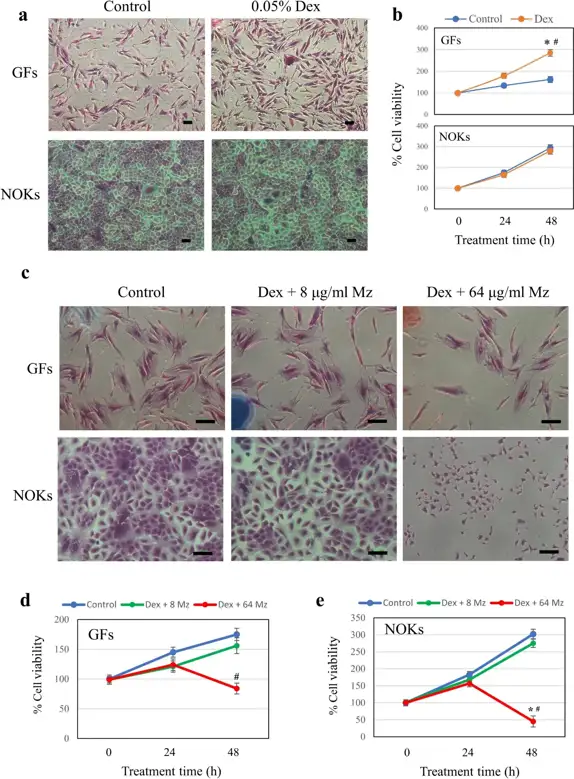
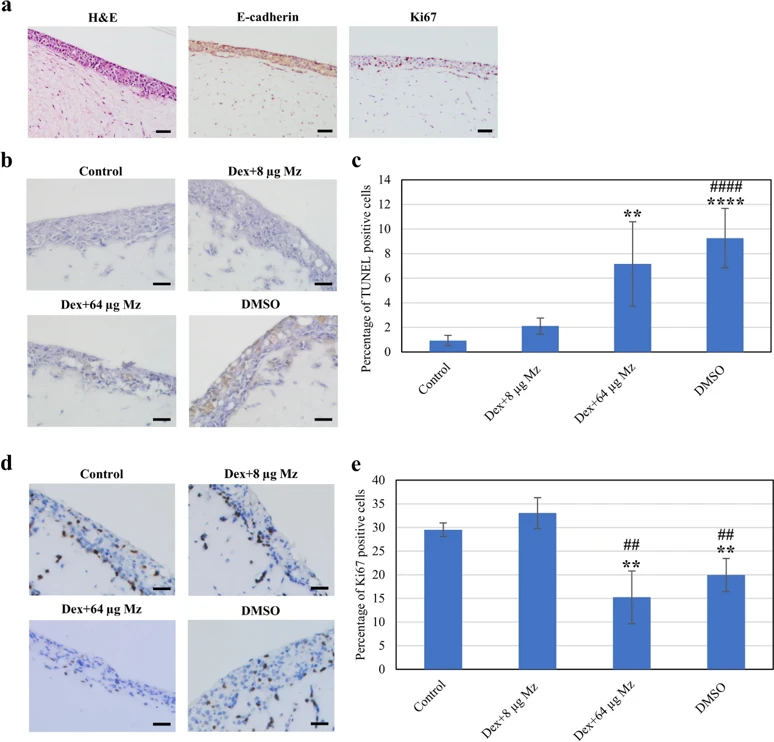
Oral lichen planus (OLP), a prevalent immune-mediated inflammatory condition, requires effective therapies. Topical corticosteroids, such as dexamethasone (Dex), are widely used for OLP treatment. However, they can predispose patients to secondary candidiasis, necessitating adjunctive therapy with antifungal agents like miconazole (Mz). Little is known about the cellular dynamics and toxicity of the combined use of dexamethasone and miconazole. This study examined the effect of dexamethasone on the antifungal activity of miconazole against Candida albicans and the effect of miconazole on the immunosuppressive activity of dexamethasone on human T cells. The cytotoxicity of dexamethasone alone and dexamethasone combined with miconazole on human oral keratinocytes (NOKs) and gingival fibroblasts (GFs) was also determined using both in vitro monolayer and Transwell co-culture models.
Dexamethasone did not affect miconazole's antifungal efficacy, and a single exposure of miconazole inhibited over 99% of C. albicans growth. In monolayer cultures, 0.05% dexamethasone was non-toxic to keratinocytes and fibroblasts, while miconazole exhibited dose-dependent cytotoxicity at high concentrations. Transwell co-culture models confirmed this dose-dependent cytotoxicity, with higher miconazole concentrations causing increased apoptosis. Dexamethasone significantly reduced T cell viability, activation, and proliferation, unaffected by miconazole co-treatment. In conclusion, when used in combination at optimal concentrations, miconazole's antifungal activity and dexamethasone's anti-T-cell proliferation activity are retained without cytotoxicity to human oral cells.
Immortalized Human Oral Keratinocytes-hTERT are oral keratinocyte cells derived from human sources that have been modified with the human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) gene. This modification allows the cells to go beyond 20 passages while retaining essential characteristics of primary oral keratinocytes.
Immortalized Human Oral Keratinocytes-hTERT are suitable for a wide range of applications, including:
Oral cancer research and carcinogenesis studies.
Oral biology and tissue engineering.
Wound healing and regenerative medicine.
Drug testing and toxicity assays relevant to oral tissues.
Studies on cell differentiation, signaling, and interactions in the oral epithelium.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells