Immortalized Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells-SV40
Cat.No.: CSC-I2091Z
Species: homo sapiens
Morphology: Polygonal
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
free from contaminations (bacteria incl. mycoplasma, fungi, HIV, HAV, HBV, HCV, Parvo-B19) and cross-contaminations
Note: Never can cells be kept at -20°C.
Human nucleus pulposus cells originates from human lumbar disc nucleus pulposus tissue. The nucleus pulposus functions as the central part of the intervertebral disc which contains water-rich collagen fibers and proteoglycans that maintain elasticity and pressure buffering within the disc. The main role of nucleus pulposus cells involves generating and secreting extracellular matrix elements that consist of proteoglycans like aggrecan and collagens including type II collagen. Matrix components maintain the gel structure of the nucleus pulposus while also preserving the disc's mechanical properties. External stimuli including mechanical stress and inflammatory factors prompt nucleus pulposus cells to adjust their functions through multifaceted signaling pathways such as TGF-β/Smad and NF-κB.
Immortalized human nucleus pulposus cells-SV40 serve as crucial research tools in the investigation of intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD). Scientists can investigate molecular degeneration processes and locate possible treatment targets by creating simulated degenerative conditions that include inflammatory factor stimulation and mechanical stress loading.
Downregulation of hsa_circ_0059955 Induced Apoptosis of NP Cells
Low back pain, often caused by intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD), presents significant health and economic challenges globally. IVDD features decreased extracellular matrix and increased cell death. Recent studies highlight circRNAs' involvement in various diseases, including IVDD. However, the role of specific circRNAs like hsa_circ_0059955 in IVDD remains underexplored.
Kong's team identified hsa_circ_0059955 in immortalized human nucleus pulposus cells (NP) cells through a FISH assay and found its main location to be the cytoplasm (Fig. 1A). They used two shRNAs designated as hsa_circ_0059955 shRNA1 and hsa_circ_0059955 shRNA2 to reduce hsa_circ_0059955 expression in NP cells and found shRNA1 to be more effective (Fig. 1B), thus chosen for further experiments. The CCK-8 and Ki67 assays demonstrated that hsa_circ_0059955 reduction led to substantial inhibition of NP cell proliferation (Fig. 1C-E). JC-1 staining demonstrated that the downregulation led to a reduction in mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) (Fig. 2A) demonstrated that NP cell apoptosis rose due to higher Bax levels and increased cleaved caspase 3 and caspase 9 activity while Bcl-2 expression decreased (Fig 2B-H). Research shows that knocking down hsa_circ_0059955 expression triggers apoptosis in NP cells.
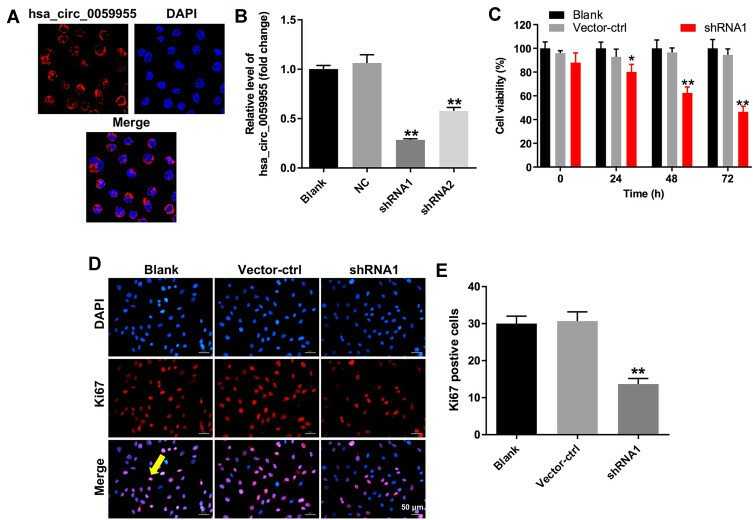 Fig. 1. Downregulation of hsa_circ_0059955 inhibited proliferation of NP cells (Kong DL, Gu R, et al., 2020).
Fig. 1. Downregulation of hsa_circ_0059955 inhibited proliferation of NP cells (Kong DL, Gu R, et al., 2020).
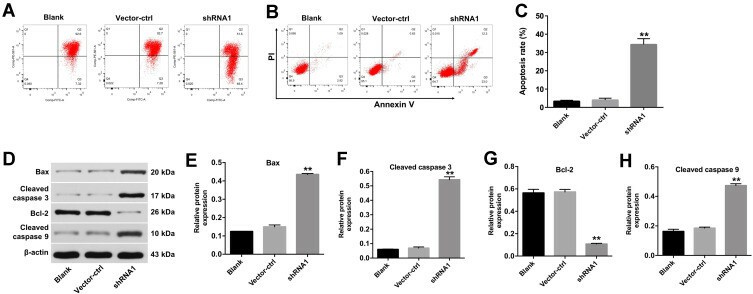 Fig. 2. Downregulation of hsa_circ_0059955 induced apoptosis of NP cells (Kong DL, Gu R, et al., 2020).
Fig. 2. Downregulation of hsa_circ_0059955 induced apoptosis of NP cells (Kong DL, Gu R, et al., 2020).
Evo Inhibits LPS-induced NPCs Apoptosis
IDD, linked to chronic back pain, lacks effective treatments. Nucleus pulposus cells regulate ECM components and are influenced by apoptosis and inflammation. Evo, with known protective effects, could impact these processes via SIRT1 and PI3K/Akt pathways.
The effect of Evo on immortalized human nucleus pulposus cells (NPCs) viability was detected. The results showed that Evo at 5, 10 and 20 μM had no significant effect on NPCs viability, but Evo at 40 μM caused damage on NPCs (Fig. 3A). Therefore, the maximum Evo concentration was 20 μM in the following experiments. Subsequently, CCK-8 assay (Fig. 3B) and TUNEL staining (Fig. 3C and D) showed significant apoptosis of NPCs induced by LPS. It should be noted that Evo enhanced NPCs viability in a concentration-dependent manner. In addition, caspase-3 activity and the expression levels of apoptosis-related proteins in NPCs were also assessed (Fig. 3E and F). Following LPS induction, caspase-3 activity was increased, Bax protein was significantly upregulated and Bcl-2 protein was downregulated, indicating that LPS induced apparent apoptosis. Similarly, this change also could be reversed by Evo.
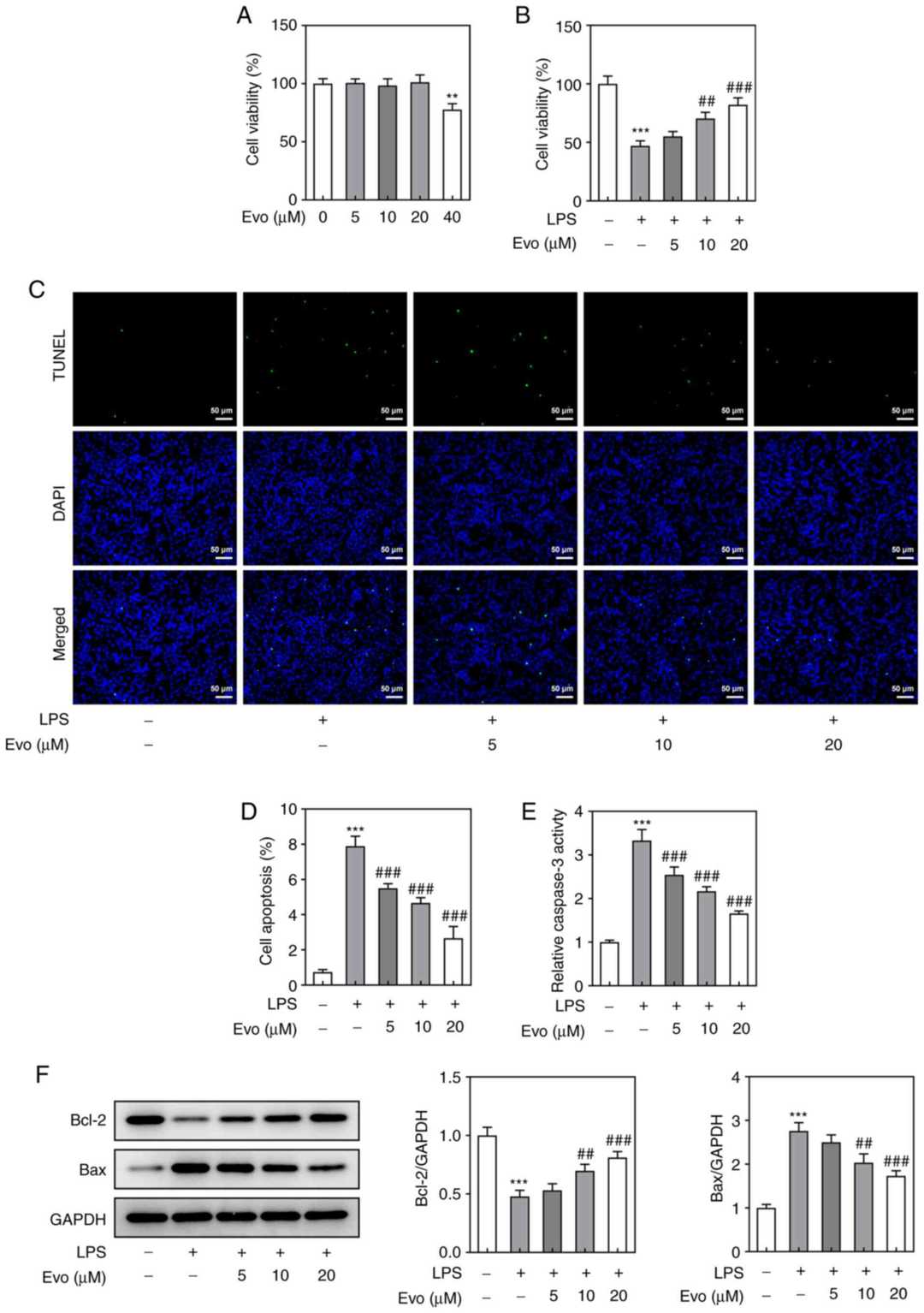 Fig. 3. Evo inhibits LPS-induced NPCs apoptosis (Kuai J and Zhang N, 2022).
Fig. 3. Evo inhibits LPS-induced NPCs apoptosis (Kuai J and Zhang N, 2022).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells