Immortalized Human Cord Blood Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (cbMSC-hTERT)
Cat.No.: CSC-I9207L
Species: Homo sapiens
Source: Umbilical cord blood
Morphology: Fibroblast-like
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Note: Never can cells be kept at -20 °C.
CIK-HT013 HT® Lenti-hTERT Immortalization Kit
2) TRAP assay was performed to determine the telomerase activity;
3) Flow cytometry was used to detect surface markers such as CD29, CD73, CD105, CD44 and HLA-ABC;
4) G-banding was used for karyotype analysis;
5) Tumuorigenicity assay was performed to evaluate the cells’ tumorigenic potential.
Immortalized human cord‑blood mesenchymal stromal cells (cbMSC‑hTERT) are an extensively characterized, hTERT‑transduced MSC line with an origin in neonatal umbilical cord blood. Parental cells are extracted from the blood component of the umbilical cord, a fetal tissue that naturally harbors large quantities of primitive mesenchymal progenitors. Subsequent retroviral transduction with human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) confers the cells with unlimited proliferative capacity. The classic MSC phenotype is retained, including plastic adherence, fibroblast‑like morphology, and immunophenotype characterized by expression of CD29, CD44, CD73, CD90, CD105 and HLA‑ABC with lack of hematopoietic markers CD14, CD34 and CD45.
The line features a doubling time of ~24 h and can be passaged to >20 generations without evidence of senescence. Karyotype analysis and comparative genomic hybridization analysis have demonstrated stability of the genome. In vivo tumorigenicity assays in immunodeficient mice have not demonstrated evidence of malignant transformation and the line is considered a non‑tumorigenic, BSL‑2 research tool. Functionally, cbMSC‑hTERT demonstrates vigorous trilineage differentiation capacity to form mineralized matrix in osteogenic differentiation, lipid droplets in adipogenic differentiation, and proteoglycan rich matrix in chondrogenic differentiation culture conditions.
Due to its capacity for infinite expansion, stable phenotype, and non‑tumorigenic safety profile, cbMSC‑hTERT is a broadly useful tool for studies in basic MSC biology, tissue‑engineering scaffold seeding, high‑throughput drug screens, disease model construction, and in vivo cell tracking studies (e.g., RFP‑labelled derivatives in traumatic brain injury or multiple sclerosis models).
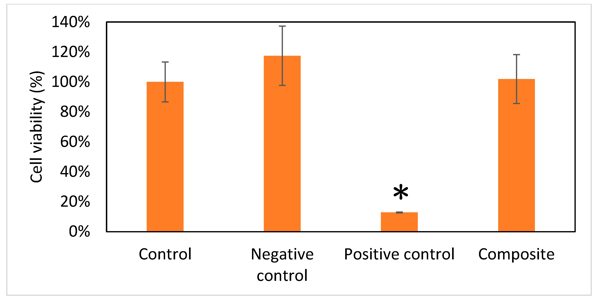
Cell Viability of Stromal Cell-Derived Factor-1 Contained in Gelatin/Hyaluronate Copolymer Mixed with Hydroxyapatite
Bone defects from orthopedic trauma are difficult to manage. Here, Chang's team fabricated a Gel/HA copolymer with HAP and SDF-1 to enhance bone regeneration. Cell viability and proliferation were assessed using WST-1 assays. Target cbMSC-hTERT cells were treated with different media extracts. In the positive control group, 0.2 g/mL zinc diethyldithiocarbamate was added; in the negative control group, 0.2 g/mL aluminum oxide was used. The composite group received 0.2 g/mL Gel/HA-HAP. Untreated controls were set at 100% viability. Figure 1 shows that cbMSC-hTERT cell growth was unaffected in the Gel/HA-HAP and negative control groups, while the positive control group showed significant viability reduction. ANOVA revealed significant differences only in the positive control group compared to the other three groups.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells