Immortalized Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells
Cat.No.: CSC-I9355Z
Species: homo sapiens
Morphology: Polygonal
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
- Documents
CIK-HT003 HT® Lenti-SV40T Immortalization Kit
Note: Never can cells be kept at -20 °C.
Immortalized Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells (HBMECs) are a commonly utilized in vitro model for studying blood-brain barrier (BBB) cell and molecular biology. The immortalization of human brain microvessel-derived HBMECs utilizes methods including the SV40 large T antigen to promote their extended growth and division capabilities. Morphologically, HBMECs display the characteristic cobblestone-like monolayer typical of microvascular endothelium and express hallmark endothelial markers including CD31, VE-cadherin, vWF, and eNOS. Importantly, they form tight junction structures-such as ZO-1, claudin-5, and occludin-that are essential for modeling the barrier properties of the BBB.
Immortalized HBMECs have been used to study a wide range of BBB cellular and molecular biology properties, such as selective molecular transport, expression of efflux transporters like P-gp and BCRP, inflammatory responses, for example, induction of adhesion molecules such as ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 upon stimulation with inflammatory cytokines. This, along with their physiological relevance, has made them a commonly used model for various applications, including drug permeability assays, neuroinflammation, CNS infection, neurovascular unit, and oxygen-glucose deprivation to mimic ischemia. They are also used in more complex systems, for example in co-culture or microfluidic "BBB-on-a-chip" systems.
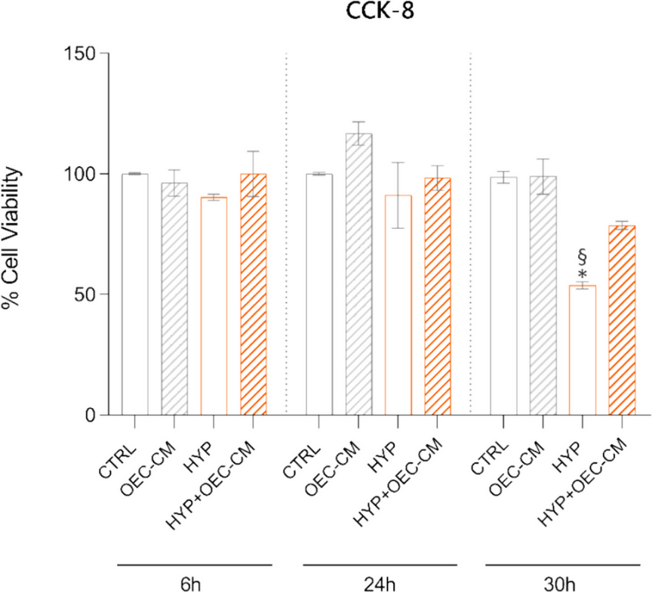
Effect of OEC-CM on HBMEC Viability under Normoxic or Hypoxic Conditions
Hypoxia compromises the blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity and induces inflammation. Olfactory ensheathing cells (OECs) have neuroregenerative and anti-inflammatory properties. Agafonova et al. investigated the modulatory effects of OEC-conditioned medium (OEC-CM) on human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMECs) under hypoxia.
The effect of OEC-CM treatment on the proliferation and viability of HBMECs was assessed using the CCK-8 assay under both normoxic and hypoxic conditions at different time points (6 h, 24 h, and 30 h) (Fig. 1). At the 6 h and 24 h time points, the viability of HBMECs under hypoxic conditions (HYP) in their basal medium closely resembled that of cells in normoxia (CTRL). However, a notable decrease in viability was observed at the 30 h time point. Incubation with OEC-CM under hypoxic conditions (HYP + OEC-CM) at 6 h and 24 h exhibited results comparable to their respective controls in hypoxia, while at 30 h, the viability increased by 1.46-fold compared to the corresponding hypoxic control. Results indicate a significant impact of OEC-CM treatment on HBMEC viability, particularly under long-term hypoxic conditions.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells
