IGR-39
Cat.No.: CSC-C0344
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Skin
Morphology: adherent epithelial-like cells growing in monolayers
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin -, desmin -, endothel -, GFAP -, HMB-45 -, neurofilament -, vimentin +
IGR‑39 is a human melanoma cell line established from primary amelanotic melanoma of the left thigh from a 26‑year‑old male patient. IGR‑39 cells are adherent cells that grow in DMEM medium supplemented with 15 % fetal bovine serum and typically reach confluency in 3-4 days (≈doubling time: 30-36 h). Morphologically, IGR‑39 cells have an epithelial‑like, moderately large cells with large nuclei and a tetrapentaploid karyotype with some chromosomal rearrangements in common, including der(1q;12)(p13;q11) and der(16)(p13;q23). On a molecular level, IGR‑39 cells have high integrin α/β expression, high MMP‑9 compared to MMP‑2, and a unique sialyltransferase signature (SIAT3, SIAT4C, SIAT1) that impacts adhesion, extracellular matrix degradation, and glycosylation. When compared with the matched metastatic IGR‑37 cell line, IGR‑39 is used to study primary‑tumor biology and progression to metastasis.
This cell line is used in melanoma research for the study of cell migration, integrin signaling, and protease expression, as well as preclinical testing of a range of targeted therapeutics including small‑molecule inhibitors and oncolytic viruses (HSV‑1 d106S, T‑VEC).
The Synthesis of 2'-Hydroxychalcones under Ball Mill Conditions and Their Antimelanoma Activities
Chalcones are polyphenols with wide-spectrum pharmacological activity. A library of 2'-hydroxychalcone derivatives was synthesized by a simple one-step mechanochemical process under ball mill conditions by Claisen-Schmidt condensation. The biological activity of 17 compounds was evaluated against Plasmodium falciparum, Leishmania donovani and IGR-39 melanoma cell lines.
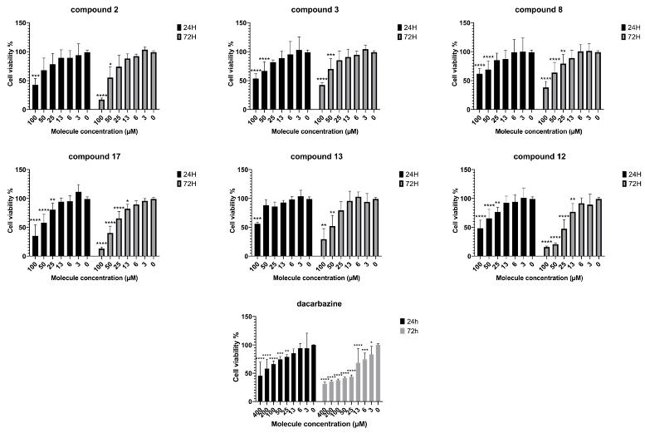
Chalcones were tested by MTT assay for the effect on viability and proliferation of the IGR-39 human melanoma cell line. The effect was evaluated after 24 h and 72 h of incubation with various concentrations (3.125 to 100 µM) for each chalcone compound and dacarbazine (3.125 to 400 µM) - a chemotherapy drug used for melanoma treatment. Six out of 17 tested compounds (2, 3, 8, 12, 13, and 17) showed activity on melanoma cell viability (Fig. 1). After 24 h, chalcones were more effective than dacarbazine: at 100 µM concentration they inhibited cell viability in the range of 39-65% versus 34% for dacarbazine. After 72 h of incubation, the most potent compounds were chalcones 12, 13 and 17 with IC50 values 24.7, 51.5 and 38.3 µM, respectively. The most active compound 12 (IC50 = 24.7 µM) had activity almost identical to dacarbazine (IC50 = 25.0 µM).
Antimelanoma Effect of Novel 1,2,3-Triazole Linked Chromene Hybrids
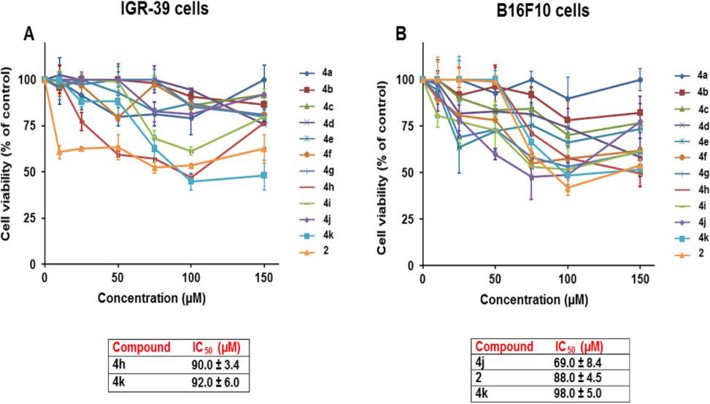
Hajlaoui et al. presented an efficient microwave-assisted synthesis of novel 1,4-disubstituted triazole derivatives under a copper(I) catalyst. The compounds' structures were confirmed by spectroscopic data (HRMS, NMR). They assessed the compounds' pharmacological activities in vitro, focusing on their effects on murine (B16F10) and human (IGR-39) melanoma cell lines and anti-α-amylase activity.
Cell viability was tested using the MTT assay with increasing concentrations of the compounds. The synthesized compounds showed different activities against the two cancer cell lines (Fig. 2). Compound 4k was effective against both cell lines, while compounds 2 and 4j were active against the B16-F10 cell line, and compound 4h was active against the IGR39 cell line. The active compounds were fluorinated and hydroxylated derivatives, while chlorinated and nitro compounds (4a, 4b, 4c, 4d, and 4e) were mostly inactive against both cell lines. Chromene-triazole derivatives 4h and 4k were active against the IGR39 cell line with IC5~~0 values of 90.0 ± 3.4 µM and 92.0 ± 6.0 µM, respectively (Fig. 2A). This suggests that attaching 2-Et-Ph and 2-OH-5-Me-Ph to the triazole ring enhances activity against human melanoma (IGR39) cells. Comparing compounds 4g (inactive) and 4h (90.0 ± 3.4 µM), the cytotoxic activity seems related to the ethyl group's position, with C-2 being more favorable. Comparing compounds 4i (inactive) and 4k (92.0 ± 6.0 µM), the methyl position and the presence of a hydroxyl group on the aryl moiety affect cytotoxic activity. Notably, the IGR39 cell line is highly drug-resistant, and few agents show activity against it.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells