SUP-M2
Cat.No.: CSC-C0518
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Cerebrospinal Fluid
Morphology: round cells growing singly or in clumps in suspension
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
- Documents
Immunology: CD2 +, CD3 -, CD4 +, CD13 -, CD14 -, CD19 -, CD21 -, CD25 +, CD30 +, CD34 -, CD71 +, HLA-DR +
Viruses: PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HIV -, HTLV-I/II -, SMRV -
SUP-M2 cells are a human cell line derived from the cerebrospinal fluid of a 5-year-old girl with refractory malignant histiocytosis. These cells are characterized by specific genetic and phenotypic features, making them an important model for studying a particular type of cancer known as anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL).
The SUP-M2 cell line is notable for carrying the characteristic translocation t (2; 5) (p23; q35). This translocation leads to the fusion of two genes, NPM1 and ALK, resulting in the formation of the NPM1-ALK fusion gene. The NPM1-ALK fusion gene is a hallmark genetic alteration in a subset of ALCL cases and plays a crucial role in the development and progression of this disease.
In addition to the genetic abnormality, SUP-M2 cells also express the CD30 antigen. CD30 is a cell surface marker that is commonly observed on ALCL cells. The presence of CD30 further defines SUP-M2 cells as anaplastic large-cell lymphoma and contributes to their phenotypic characteristics.
The SUP-M2 cell line has been widely used in research to investigate the biological and molecular aspects of ALCL, including the role of the NPM1-ALK fusion gene, cellular signaling pathways, therapeutic targets, and drug testing. By studying SUP-M2 cells, researchers aim to gain insights into the pathogenesis of ALCL and develop more effective treatment strategies for this type of lymphoma.
B7-H3 Redirected CAR-T Cells Control ALCLs In Vitro
B7 homolog 3 (B7-H3), also named CD276, is a member of the B7 family of immune regulatory proteins. B7-H3 CAR-T cells showed strong cytotoxicity and cytokine secretion against target ALCL cells (SUP-M2, SU-DHL-1, and Karpas 299) in vitro. Cytotoxicity was measured using two different approaches LDH release cytotoxic assay and luciferase-based assay in various E: T ratios. Increased cytotoxicity along with an increased E: T ratio was observed in B7-H3 CAR-T cells to target ALCL cell lines in both approaches. Furthermore, >60% specific lysis was reached when the E: T ratio was 5:1 for all targets in the LDH release cytotoxic assay (Fig. 1A).
To confirm this effect, stable expressing luciferase cell lines were generated from parental SUP-M2, Karpas299, and SU-DHL-1 cell lines as well as the performed luciferase-based assay. This was consistent with data from the LDH release cytotoxic assay, and B7-H3 CAR-T cells showed their potency in controlling SUP-M2, Karpas299, and SU-DHL-1 (Fig. 1B). The secreting of IL-2 and IFNγ was observed at a high level when B7-H3 T cells were co-cultured with ALCLs. In contrast, UTD and CD19 CAR-T control cells showed minimal secretion of both cytokines (Fig. 1C and D).
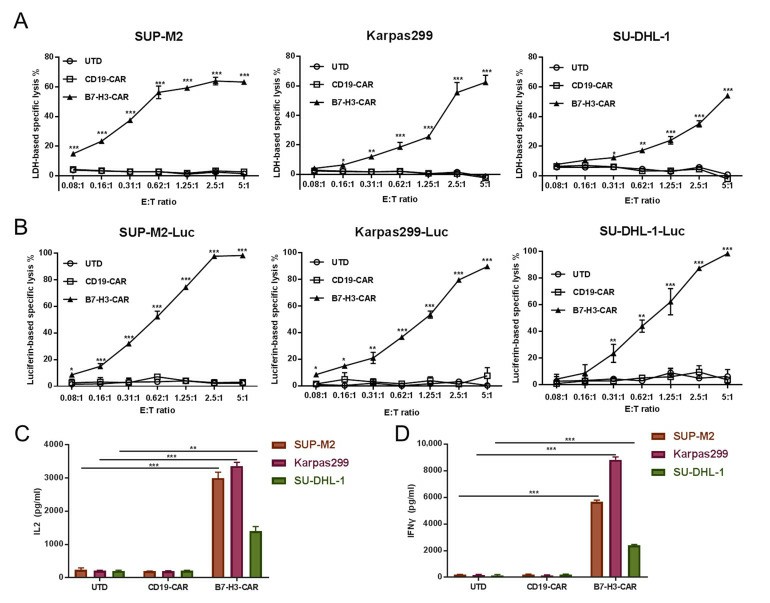 Fig. 1 B7-H3 T cell effects on B7-H3-expressing ALCL cells (SUP-M2, SU-DHL-1, and Karpas 299). (Slupianek A and Skorski T, 2004)
Fig. 1 B7-H3 T cell effects on B7-H3-expressing ALCL cells (SUP-M2, SU-DHL-1, and Karpas 299). (Slupianek A and Skorski T, 2004)
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells





