TALL-1
Cat.No.: CSC-C0530
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Bone Marrow
Morphology: single cells growing in suspension
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: CD2 +, CD3 +, CD4 +, CD5 +, CD6 +, CD7 +, CD8 +, CD13 -, CD19 -, CD34 -, TCRalpha/beta (+), TCRgamma/delta -
TALL‑1 was established from the bone marrow of a 28-year-old male patient with lymphosarcoma (T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia or T-ALL) in the leukemic phase. These cells are non-adherent lymphoblast-like cells growing in suspension. They exhibit both spherical and rod-shaped morphologies under standard culture conditions (RPMI-1640 with 10-15% FBS). The population doubling time is 50-70 hours and maximal cell density is about 2.5 × 106 cells/mL. TALL‑1 cells are immunophenotypically characterized by expression of several T-cell markers including CD2, cytoplasmic CD3, CD4, CD7, and CD8, but do not express the myeloid (CD13), B-cell (CD19), or stem‑cell antigen (CD34).
Genomic profiling reveals oncogenic mutations, including NRAS G12D and TP53 variants, and a frameshift mutation in PHF6, making TALL‑1 a genetically representative model of T-ALL. Functionally, TALL‑1 recapitulates critical aspects of T-ALL pathobiology, including deregulated signaling pathways (e.g., NOTCH1, RAS) and apoptosis susceptibility. It has been used to understand mechanistic aspects of T-ALL pathobiology, for example, mitochondrial potassium channel modulation of mitochondrial reactive-oxygen-species (ROS) generation and ROS-mediated therapy sensitization. TALL‑1 has also been used in drug screening assays, to understand molecular drivers of oncogenesis and to validate therapies. TALL‑1 is included in multiple large-scale genomic dependency datasets such as the Cancer Dependency Map and the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia. TALL‑1 is a robust and well-characterized T-ALL model commonly used in both basic and translational leukemia research.
KLF4 Induced T-Cell Differentiation in TALL-1 Cells
Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) has oncogenic or tumor-suppressive functions depending on cancer types. KLF4 is silenced by promoter methylation in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL), and its induction suppresses T-ALL cell proliferation. Noura et al. examined KLF4 functions in T-ALL cell differentiation and evaluated APTO-253 as a therapeutic compound.
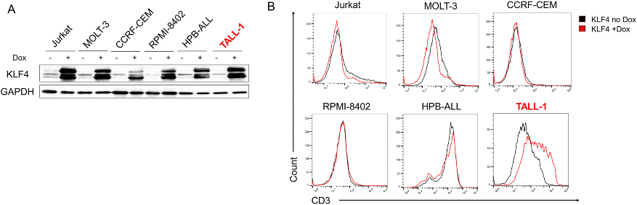
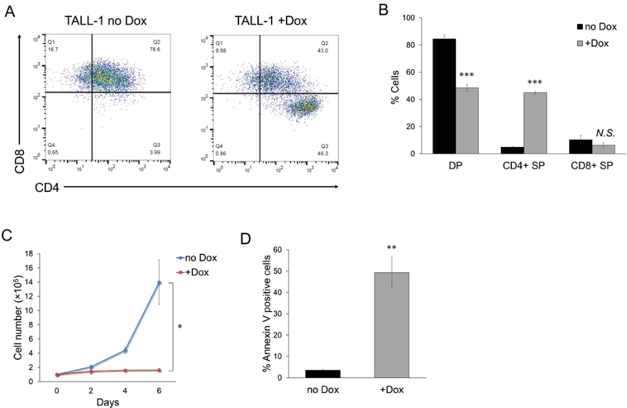
To test if KLF4 induces T-cell differentiation in T-ALL cell lines, Noura et al. lentivirally transduced a Doxycycline (Dox)-inducible KLF4 expression vector in six T-ALL cell lines (Jurkat, MOLT-3, CCRF-CEM, RPMI-8402, HPB-ALL, and TALL-1), and established Dox-inducible (Di)-KLF4 T-ALL cell lines. KLF4 expression was induced by 3 μM Dox (Fig. 1A). They first evaluated CD3 surface expression, a pan-T-cell marker. CD3 expression increased only in Dox-treated Di-KLF4/TALL-1 cells (Fig. 1B). Thus, they focused on TALL-1 cells, a CD4/CD8 double-positive (DP) cell line and found that KLF4 overexpression significantly decreased the DP cell population and increased the CD4 single-positive (SP) cell population (Fig. 2A, B). In contrast, KLF4 overexpression also slightly increased CD4 SP cell population in HPB-ALL, another DP cell line, but to a lesser extent than TALL-1. KLF4 overexpression inhibited TALL-1 cell proliferation and induced apoptosis (Fig. 2C, D). These findings suggest that KLF4 shows an anti-leukemic effect on TALL-1 cells through the induction of T-cell differentiation and subsequent apoptosis.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells