PC-3M
Cat.No.: CSC-C9578L
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Bone Metastasis
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
vWA: 17
FGA: 24
Amelogenin: X
TH01: 6,7
TPOX: 8,9
CSF1P0: 11
D5S818: 13
D13S317: 11
D7S820: 8,11
Shipping Condition: Room Temperature
PC-3M is a highly metastatic human prostate cancer cell line subcloned from the parental PC-3 human prostate cancer cell line, which was derived from the bone metastasis of a grade IV prostatic adenocarcinoma patient. PC-3M cells were selected in vivo and in vitro for increased metastatic potential, and are characterized by higher motility, invasiveness, and tumorigenicity than their parental counterparts. PC-3M is a widely used experimental model for advanced, aggressive prostate cancer.
PC-3M cells are epithelial-like to spindle-shaped and grow as adherent monolayers under standard culture conditions, such as F-12K medium or RPMI-1640 medium, with fetal bovine serum. They exhibit rapid growth and are highly anchorage-dependent. PC-3M cells are androgen-independent with nonfunctional androgen receptor and thus display many of the clinical characteristics of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). The cells have multiple chromosomal aberrations and dysregulated pathways associated with cell proliferation, survival, and metastasis, such as the PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways.
PC-3M cells have a high invasive and migratory potential in vitro, and they form aggressive, metastatic tumors with propensity for lymph node and organ metastasis in xenograft models. The cells are therefore particularly useful for studies of prostate cancer metastasis, tumor progression, and drug resistance. It is commonly used for drug screening, evaluation of anti-metastatic drugs, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) studies, and investigation of the molecular mechanisms involved in advanced prostate cancer.
Knockdown of NEIL3 Inhibits the Proliferation of PCa Cells
Prostate cancer (PCa) is a common cancer globally. Nei endonuclease VIII-like 3 (NEIL3) is implicated in various cancers. Zhang's team investigated NEIL3's role in PCa, its association with prognosis, and its effects on cell proliferation, invasion, and migration via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.
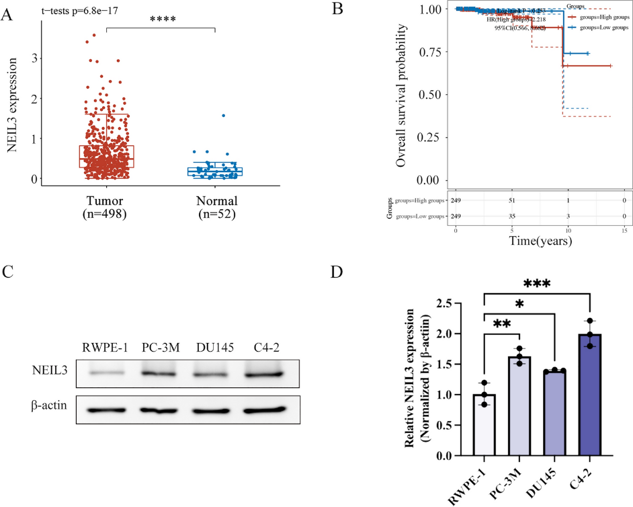
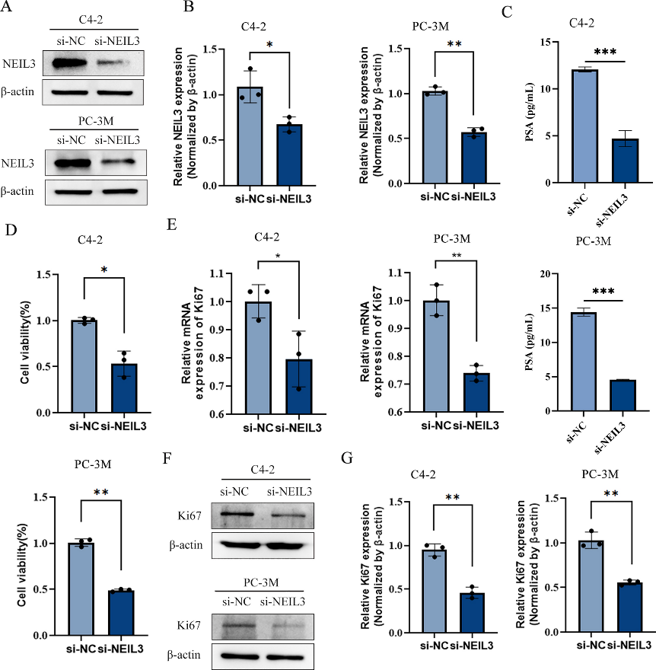
They analyzed the NEIL3 gene in 498 PCa tumor tissues and 52 adjacent non-tumor samples from the TCGA dataset (Fig. 1A). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that PCa patients with high NEIL3 levels had poorer overall survival (OS) (Fig. 1B). Western blot and qRT-PCR revealed higher NEIL3 protein (Fig. 1C) and mRNA (Fig. 1D) expression in PC-3M, DU145, and C4-2 cell lines compared to RWPE-1. Thus, NEIL3 upregulation is linked to shorter OS in PCa. Given the increased NEIL3 expression, they knocked it down using siRNA in C4-2 and PC-3M cells (Fig. 2A and B). ELISA showed that NEIL3 knockdown reduced prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels in these cells (Fig. 2C). CCK-8 assays indicated that NEIL3 knockdown significantly suppressed cell growth (Fig. 2D). Additionally, Ki67 expression, a proliferation marker, was decreased at both mRNA (Fig. 2E) and protein levels (Fig. 2F and G) in NEIL3-knockdown cells. These results suggest that NEIL3 knockdown inhibits PSA expression and PCa cell proliferation.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells