C4-2
Cat.No.: CSC-C7107J
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Lymph Node Metastasis
Morphology: Epithelial
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
The C4-2 cell line is a seminal, androgen-independent human prostate cancer model derived through the in vivo selection and subsequent culture of a bone metastasis from a tumor initially formed by its parental line, LNCaP, in a castrated mouse. This in vivo derivation process endowed C4-2 with a markedly more aggressive phenotype, including the ability to form tumors in intact and castrated mice and a pronounced propensity for osteoblastic bone metastasis-the most common and debilitating site of prostate cancer spread.
C4-2 cells retain expression of the androgen receptor (AR) and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) but proliferate robustly in the absence of androgens, mimicking the clinical transition to castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). It serves as the premier paired model (with LNCaP) to investigate the molecular mechanisms driving the transition from androgen-dependent to androgen-independent growth. As a model of advanced CRPC, C4-2 is essential for preclinical testing of next-generation AR pathway inhibitors (e.g., enzalutamide, abiraterone), AR-targeting degraders, and agents targeting bone metastasis (e.g., radium-223, bisphosphonates). It is also used to study resistance mechanisms to these therapies. C4-2 cells exhibit a strong tropism for bone and induce characteristic osteoblastic lesions in animal models. This makes them an indispensable tool for studying the vicious cycle of tumor-stromal interactions in the bone microenvironment, including crosstalk with osteoblasts and osteoclasts.
Cytotoxicity and Cell Cycle Changes in Prostate Cancer Cells After Treatment With PSMA-Targeting Radioligand [212Pb]Pb-AB001
Targeted alpha therapy holds promise for treating advanced prostate cancer, but the interplay between prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) expression, p53 status, and downstream cell fate remains poorly defined. This study evaluates the cytotoxic and cell cycle effects of the alpha-emitting radioligand [212Pb]Pb-AB001 in prostate cancer cell lines with differing PSMA expression and p53 status: C4-2 (PSMA+/TP53-wild-type) and PC-3 PIP (PSMA+++/ TP53-null).
[212Pb]Pb-AB001 significantly inhibited proliferation and clonogenic survival in both cell lines in an activity-dependent manner. At 95% clonogenic inhibition, both cell lines exhibited G2-phase arrest, S-phase suppression and reduced mitotic entry on day 1. At higher activities, PC-3 PIP cells showed polyploidy, and features consistent with mitotic catastrophe and senescence. Cytotoxicity was more pronounced in C4-2 3D spheroid models than in 2D monolayers, suggesting contribution of crossfire and bystander effects. Total cell-bound activity, rather than added activity, better predicted radiotoxicity in both TP53-wild-type and TP53-null cell lines, indicating that its therapeutic effect is primarily governed by PSMA-mediated uptake rather than p53 status. These results support the therapeutic potential of [212Pb]Pb-AB001 across cells with varying TP53 status and suggest that combining [212Pb]Pb-AB001 with DNA repair or checkpoint inhibitors may enhance treatment efficacy.
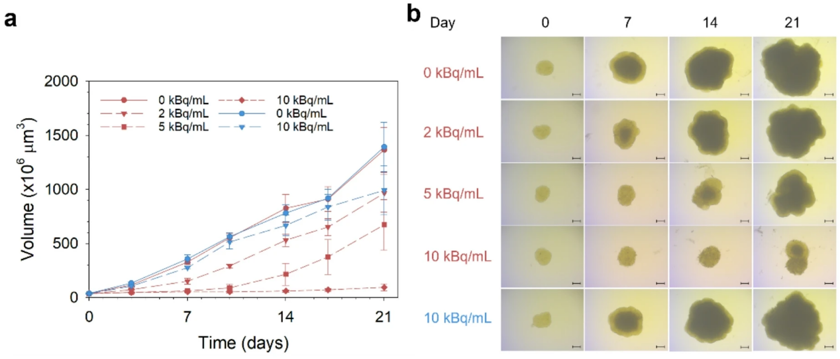
![Cell-cycle phase distribution of C4-2 and PC-3 PIP cells after treatment with [212Pb]Pb-AB001 for 1 h (both cell lines) or 4 h (C4-2 only).](/upload/images/c4-2-casestudy-2.webp)
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells