CWR22-RV1
Cat.No.: CSC-C9097W
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Prostate
Morphology: epitheloid
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
CWR22-RV1 is a human prostate cancer cell line. It was originally obtained from a bone metastasis of a patient with hormone-sensitive prostate cancer, but serial passaging in castrated nude mice made it an androgen-independent cell line that is commonly used to study CRPC. The cells have epithelial morphology and are adherent upon growth. RV1 expresses wild-type AR that is constitutively active and retains the ability to secrete PSA. Compared to the parental CWR22, RV1 is resistant to conventional anti-androgen therapies but retains AR signaling, so it is used to study mechanisms of escape from AR signaling.
In research applications, RV1 is widely used to study metabolic reprogramming in CRPC, drug resistance mechanisms, and the development of novel targeted therapies—particularly those involving polyamine and methionine metabolic pathways. It is a unique cell line since other androgen-independent prostate cancer cell lines such as LNCaP (androgen-sensitive) and PC-3 (AR-negative) leave a research gap for androgen-independent but AR-positive prostate cancer that RV1 fills.
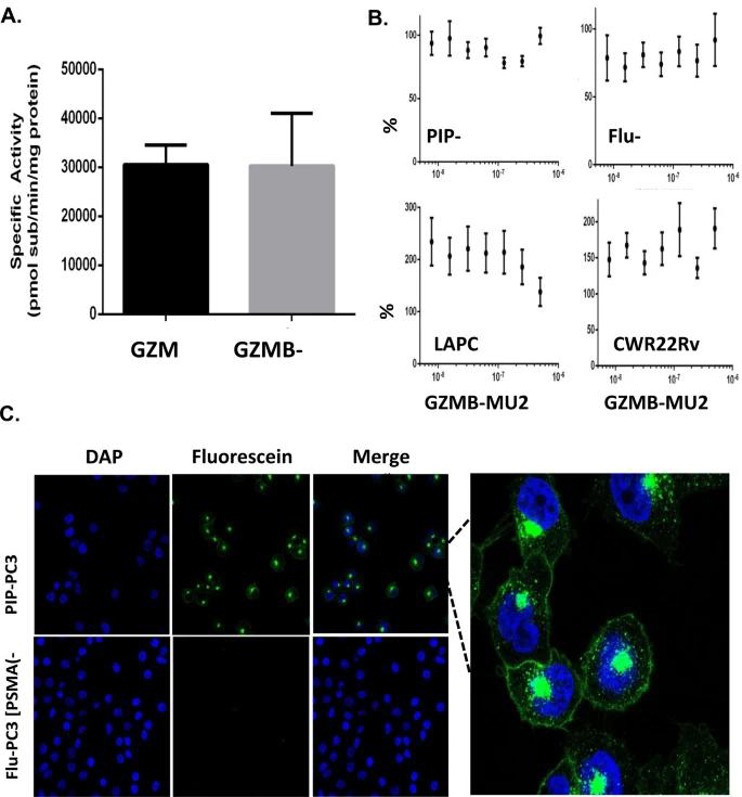
Cytotoxicity and Uptake of GZMB-MU2
Prostate cancer is a slowly growing malignancy that expresses high levels of PSMA. Protein toxins exert their cytotoxicity in a proliferation-independent manner and are non-tumor specific. In order to evaluate the potential for selective delivery, Rogers et al. conjugated a urea-based PSMA-inhibitor to two cytotoxic proteins, human Granzyme B (GZMB) and a cysteine-containing fragment of the pseudomonas exotoxin A gene (PE35). The complex GZMB-MU2 was tested for cytotoxicity against PSMA expressing prostate cancer cell lines (PIP-PC3, LNCaP, CWR22Rv1) and control (Flu-PC3) cells. GZMB-MU2 demonstrated no impact on cell proliferation, morphology or survival when tested at concentrations up to 300 nM (Fig. 1B). To investigate whether the lack of toxicity was due to poor internalization, fluorescein-tagged GZMB-MU2 was incubated with PIP-PC3 and Flu-PC3 cells for 2 h. Confocal microscopy demonstrated punctate fluorescein staining in PIP-PC3 cells localized near the nucleus and membrane, but not in Flu-PC3 cells (Fig. 1C). Treatment with endosome-disrupting agents (HIV TAT peptides, chloroquine) did not enhance cytotoxicity, although chloroquine alone produced significant toxicity. Low cytosolic delivery or SERPIN-mediated inactivation of GZMB may account for lack of apoptosis.
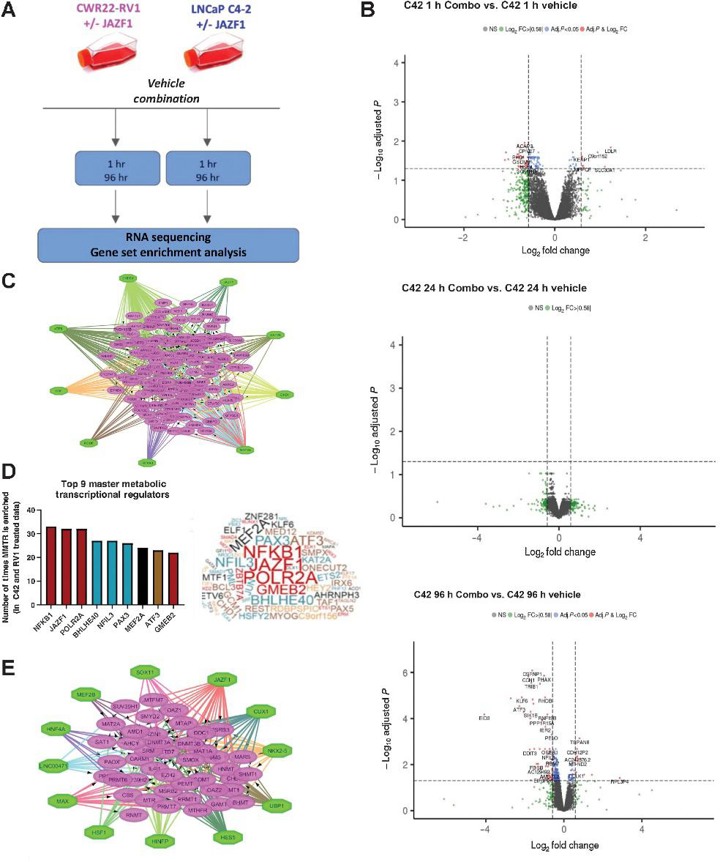
In Vitro RNA-Seq Data Highlights JAZF1 as a Modulator of Response to Polyamine-Targeted Therapies
Metabolic dysregulation plays a critical role in diseases like prostate cancer, where targeting specific pathways (e.g., polyamine biosynthesis and methionine cycle) has shown therapeutic potential. However, the master metabolic transcriptional regulators (MMTRs) controlling these pathways and their impact on treatment response remain unclear. Rosario et al. aimed to identify novel MMTRs influencing prostate cancer's sensitivity to polyamine- and methionine-targeted therapies, focusing on JAZF1 as a key regulator.
A gene signature of treatment-naïve prostate tumors was used to predict intrinsic nonresponse to polyamine-targeted therapy, and this nonresponse was associated with the dysregulation of metabolic pathways (e.g., downregulation of polyamine biosynthesis). Patient-derived ex vivo samples and TCGA tumor data were interrogated to identify 82 DEGs that stratified responders and nonresponders, and metabolic profiling of tumors from each group identified the downregulation of polyamine synthesis in resistant tumors. To identify key MMTRs of treatment sensitivity, they intersected MMTRs of the 82 response-related genes with those found to regulate adaptive responses to therapy. As shown previously, BENSpm + MTDIA treatment of prostate cancer cell lines (LNCaP, C4-2, CWR22-RV1) results in progressive cytotoxicity over 4-12 days. To study adaptive mechanisms to therapy before cell death (8-12 day timepoints), they treated RV1 and C4-2 cells with vehicle, single agents, or combination therapy for 1h, 24h, and 48h/96h (Fig. 2A). RNA-seq showed a cyclical transcriptional response to therapy with initial dysregulation (1h), transcriptional stabilization (24h), and point of irreversible dysregulation (48h/96h; Fig. 2B). MMTR analysis of DEGs showed JAZF1 to be a shared regulator of polyamine/methionine pathways as well as response to therapy with binding motifs in ODC1, MAT2A, PAOX, and SAT1 (Fig. 2C-E).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells