Detroit 551
Cat.No.: CSC-C9370L
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Skin
Morphology: fibroblast
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
vWA: 18
FGA: 22,24
Amelogenin: X
TH01: 9,9.3
TPOX: 8
CSF1P0: 10,12
D5S818: 12,13
D13S317: 11,12
D7S820: 10,12
Detroit 551 is a cell line of immortalized human fetal skin fibroblasts. This cell line is derived from the skin tissue of a female fetus. Fibroblasts are important components of the skin and are involved in the physiological functions of the skin, such as secretion of extracellular matrix, skin repair, and other functions. In culture, Detroit 551 cells attach to the surface of culture vessels, distributing evenly when in good growth condition. Morphologically, they exhibit a typical fibroblast-like shape, appearing spindle-shaped or elongated, with a uniform size. Their morphology remains relatively stable across different culture stages without significant variation.
Detroit 551 cells are involved in skin-related physiological functions. They are used in the study of the tumor microenvironment and co-cultured with ovarian cancer cells to construct 3D spheroid models; in stem cell differentiation research, to explore the differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells into cardiomyocytes; and in the construction of skin models, as a source of dermal fibroblasts to construct 3D skin equivalents for use in skin research and cosmetics testing.
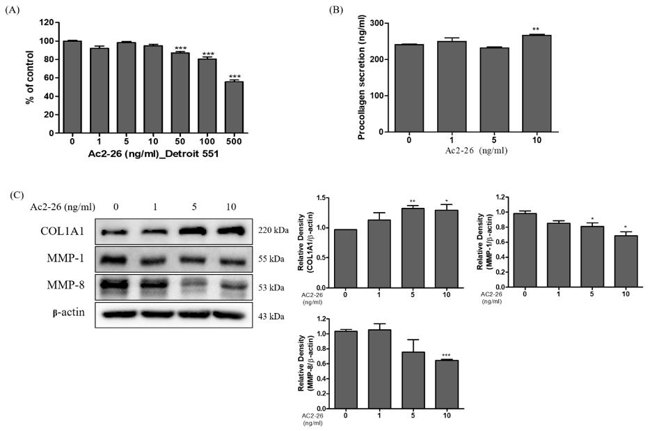
Expression of Collagen on Ac2-26 Treated Human Fibroblast Cells
Skin inflammation is a prevalent dermatological issue, and the anti-inflammatory responses of skin cells are crucial for combating these conditions. Annexin A1 (AnxA1) is a well-characterized endogenous anti-inflammatory mediator. However, the function of AnxA1 in skin keratinocytes and fibroblasts remains poorly understood. Kim et al. explored whether AnxA1 mimetic peptide Ac2-26 had anti-inflammatory and anti-wrinkle properties in human keratinocyte (HaCaT) and fibroblast (Detroit 551) cells.
They explored the effects of Ac2-26 on anti-wrinkle proteins in human fibroblast Detroit 551 cells. Cell viability assay (Fig. 1A) showed that there was no cytotoxic effect in 1, 5, and 10 ng/mL Ac2-26, and these doses were used for subsequent studies. As wrinkle formation is caused by low levels of collagen in the dermis, they next measured the secretion of procollagen, a precursor of collagen, in Ac2-26-treated Detroit 551 cells. The results (Fig. 1B) showed that Ac2-26 increased procollagen levels, and this implies that Ac2-26 induced collagen synthesis. Next, they measured the expression of collagenase proteins including MMP-1, MMP-8, and COL1A1. Figure 1C shows that Ac2-26 significantly inhibited MMP-1 and MMP-8, and increased COL1A1 levels. These results suggest that Ac2-26 promotes collagen synthesis and inhibits collagen degradation in Detroit 551 cells.
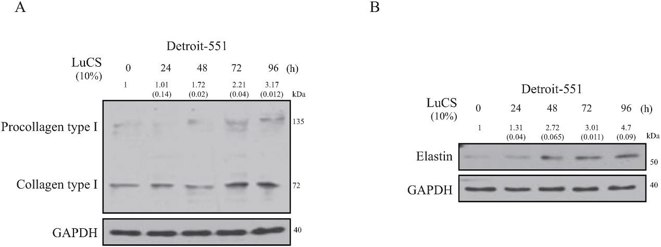
Effects of Luffa Cylindrica Stem Sap (LuCS) Treatment on Cellular Procollagen or Elastin Expression in Human Fibroblasts
Luffa cylindrica stem sap (LuCS) has been ethnopharmacologically used as a cosmetic ingredients to improve the facial condition in Asians, but there is no scientific proof about the advantages of LuCS as a supplement for skin elasticity inducer. Previously, Lee et al. have reported that the functional effects of LuCS on human skin are associated with regulating elastin and type I pro-collagen in human fibroblasts against intrinsic and extrinsic cues through the EGFR and PPARγ signaling. To further validate the effect of LuCS exposure on cellular elastin and collagen type I expression in human fibroblast, they performed Western blot analysis using LuCS treated Detroit-551 cells. Exposure to LuCS dose-dependently induced the expression of type I procollagen in Detroit-551 cells (Fig. 2A). LuCS treatment also significantly stimulated the expression of elastin in Detroit-551 cells in a dose-dependnet manner (Fig. 2B).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells