DJM-1
Cat.No.: CSC-C6456J
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Skin
Morphology: epithelial-like
Culture Properties: Adherent cells
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Store in liquid nitrogen.
DJM-1 is a human adherent epithelial tumour cell line that was derived from an 87-year-old Japanese woman's skin lesion that was initially thought to be a malignant trichilemmal cyst/squamous carcinoma of the hair-follicle outer root sheath. Cell lines proliferation is marked by pronounced cell-surface laminin positivity and have an infinite lifespan under standard culture (MEM + 10% FBS, 37 °C, 5% CO₂). Cytogenetic studies found a modal chromosomal range of 39-89 and confirmed MSS status. The cell line has been used to functionally study tumour-stromal interactions: for example, 3-dimensional collagen gel cultures with added adipocytes inhibited proliferation (BrdU uptake) and promoted differentiation marker expression (e.g., involucrin, CK10). It has also been used as a model for the dermal-autoimmune interface in the same culture system, including BP180 (type XVII collagen) internalisation by anti-BP IgG. On a genomic scale, the cell line is part of large-scale pharmacogenomics resources (DepMap/CCLE) and carries homozygous SMAD4 p.Ser144Ter and heterozygous TP53 p.Gly266Val mutations, among other oncogenic alterations.
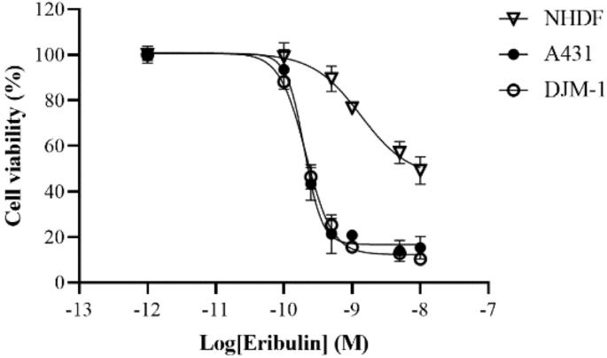
Eribulin Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Cell Death in cSCC Cell Lines
Advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) often fails to respond well to chemotherapy and radiotherapy. No preclinical studies have evaluated eribulin's effectiveness against cSCC. Hsu et al. investigated eribulin's antitumor effects using cSCC cell lines and a novel patient-derived xenograft (PDX) model.
Given eribulin's anti-tubulin activity, they tested its IC50 against two cSCC cell lines (A431 and DJM-1) and NHDFs (Fig. 1). After seeding, cells were treated with eribulin at various concentrations (0.001-10 nM) for 3 days. The IC50 values were similar for A431 (0.20 nM) and DJM-1 (0.21 nM), but much higher for NHDFs (1.34 nM). cSCC cells were ~7 times more sensitive than NHDFs. Since cSCC cells were highly sensitive to eribulin in vitro, they used flow cytometry to analyze DNA content and cell cycle effects. At 24 h post-treatment, A431 and DJM-1 cells showed increased subgroups in G2/M and sub-G0/G1 phases, but decreased in G0/G1 phase. NHDFs were unaffected (Fig. 2). Additionally, A431 cells had increased early apoptosis, while DJM-1 cells had increased late apoptosis. This indicates that eribulin induces apoptosis in A431 cells and cell death in DJM-1 cells, consistent with previous reports.

Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells