CAL-29
Cat.No.: CSC-C0524
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Bladder
Morphology: adherent epitheloid cells growing as monolayers
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin +, cytokeratin-7 -, cytokeratin-8 +, cytokeratin-17 +, cytokeratin-18 +, cytokeratin-19 +, desmin -, endothel -, EpCAM +, GFAP -, neurofilament -, vimentin -
Viruses: PCR:
CAL-29 is a cell line of urothelial carcinoma of the bladder, isolated from an 80-year-old female patient with muscle-invasive bladder cancer (T2 stage, MIBC). The MIBC subtype of bladder cancer is the most common form of this cancer, which is also very heterogeneous and aggressive. Under laboratory conditions, CAL-29 cells exhibit normal epithelial cell structure. Researchers use this cell line as a platform for testing and confirming the effectiveness of potential anti-cancer medications. For instance, hemocyanin and its functional units (FUs) from mollusks have demonstrated significant anti-tumor activity against CAL-29 cells, with better efficacy than that of the conventional chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin. Dihydroanthraquinone compounds extracted from stem bark of Kigelia africana also showed cytotoxicity against CAL-29 cells. CAL-29 cells are also used to study molecular mechanisms of bladder cancer. A study reported the interaction between the WWOX gene and the AP-2α and AP-2γ transcription factors, and the regulatory role of the LINC01137/miR-186-5p/WWOX axis in bladder cancer, by using the stable lentiviral transduction of CAL-29 cells and the high-throughput sequencing technology. The cell line is also applied in basic biological studies, such as cell metabolism and signaling pathways. For example, the metabolomics analysis has been used to profile the metabolic response of CAL-29 cells with different drug treatment.
Cell Line-Based Human Bladder Organoids with Bladder-like Self-Organization—A New Standardized Approach in Bladder Cancer Research
Bladder cancer therapy development is limited by the lack of robust in vitro models that replicate tumor complexity. While patient-derived organoids show promise, they suffer from low establishment rates and inconsistent reproducibility.
Berndt-Paetz et al. employed a standardized approach using ultra-low attachment plates to generate organoids from four human BCa cell lines (RT-4, RT-112, T-24 and CAL-29), co-cultured with bladder fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells. After only 24 h, uniform spheroids form spontaneously and were able to further develop over 7 days (Fig. 1a). RT-112 organoids on day 4, 5 and 7 are shown as an example. The formation from day 1 to 4 is shown in Figure 2. Organoids were then fixed, processed and evaluated by HE staining. After 4 days, all cultures already have distinct structures, defined by a peripheral layer and inner organoid core. In RT-4, RT-112, and CAL-29, the outer layer forms a compact border. In contrast, the outer cells of the T-24 organoids are more loosely arranged (Fig. 1b). Organoids reached a size between 650 and 1000 µm in diameter after 96 h, without any sign of central necrosis. Overall, organoid size decreased with increasing tumor grade (Fig. 1c and d). The only exception was RT-4, which did not develop a clearly defined structure. In all cell lines except RT-4, the spheroids completely lost their structural integrity by day 7 (Fig. 2). Thus, the authors selected 4-day-old organoids for the following analysis.
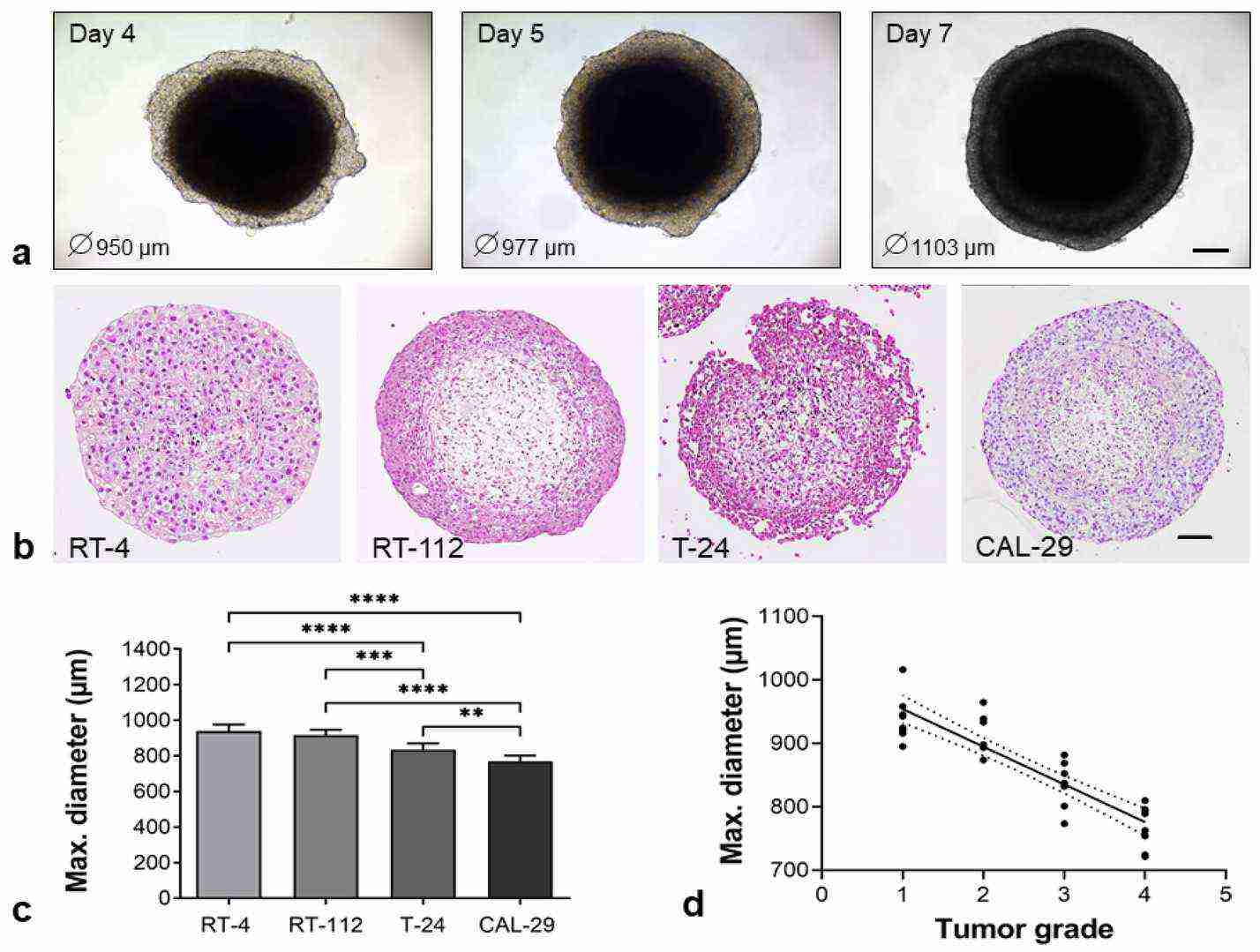 Fig. 1. Spontaneous formation of heterogeneous, compact BCa organoids. BCa cells (RT-4, RT-112, T-24, CAL-29) were co-cultured with hBF and hBSMC in an ULA plate (Berndt-Paetz M, Han S, et al., 2023).
Fig. 1. Spontaneous formation of heterogeneous, compact BCa organoids. BCa cells (RT-4, RT-112, T-24, CAL-29) were co-cultured with hBF and hBSMC in an ULA plate (Berndt-Paetz M, Han S, et al., 2023).
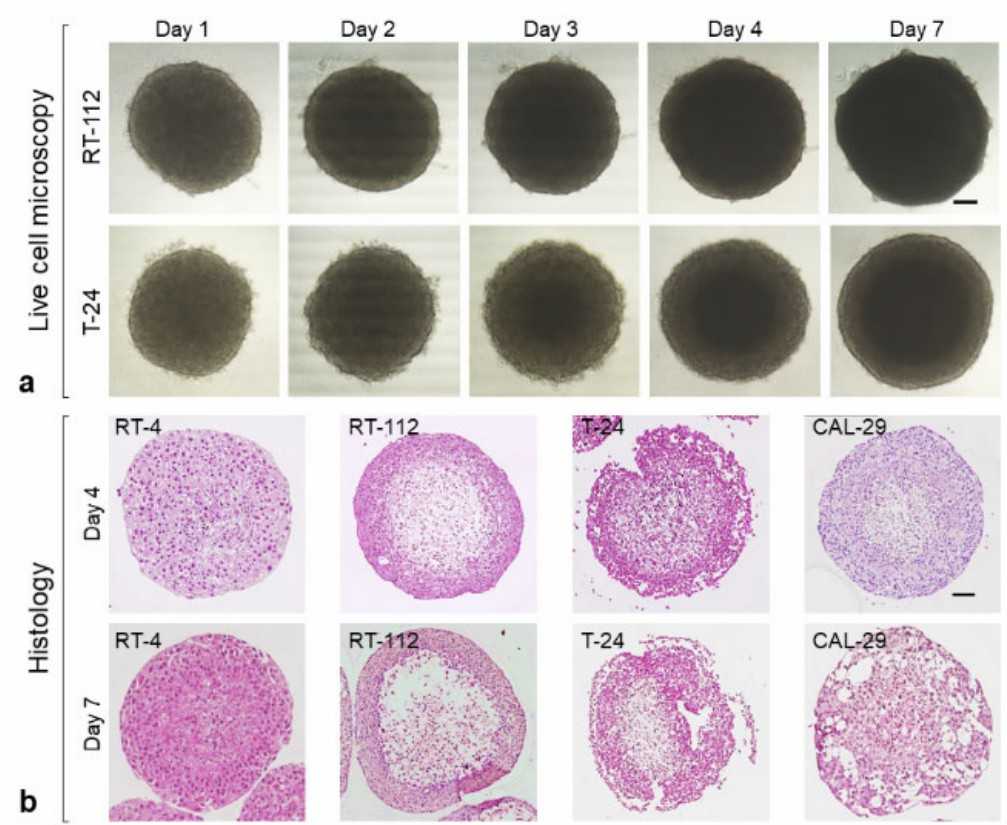 Fig. 2. Live cell observation and histology of BCa organoids (Berndt-Paetz M, Han S, et al., 2023).
Fig. 2. Live cell observation and histology of BCa organoids (Berndt-Paetz M, Han S, et al., 2023).
Production of Saponins from In Vitro Cultures of Astragalus Glycyphyllos and Their Antineoplastic Activity
Natural production of saponins from Astragalus glycyphyllos is not sufficient and its environment-friendly collecting is not sustainable. In vitro plant cultures may serve as a platform for regular and relatively high-yield production of secondary bioactive compounds. In the current study, callus, shoot and suspension cultures of A. glycyphyllos were established using different media and culture conditions optimized to these types of cultures. Content of saponins was determined using LC-MS and cytotoxicity of saponin-rich fractions obtained from the shoot culture were assessed towards a range of human cancer cell lines.
Antineoplastic activity of saponin-containing fractions 1–3 (wild-grown) and 4–6 (in vitro cultures) was determined towards various human tumor cell lines using MTT assay (Fig. 3). In all cases tumor growth was dose-dependently inhibited. The fractions 4–6 showed a more prominent cytotoxic activity against all cell lines tested based on the IC50 values. This fraction was particularly effective against lymphoma cell lines MJ and HUT-78 (IC50: 74.5 and 77.8 µg/mL). Fraction 1–3 was more variable and cells of T-24 bladder carcinoma were the least sensitive (IC50: 168.4 µg/mL), and HUT-78 the most sensitive (IC50: 87.6 µg/mL). However, the CAL-29 bladder cells, also expressing MDR1 (gp170), were more sensitive than T-24 cells, and MDR1 level in CAL-29 is significantly higher.
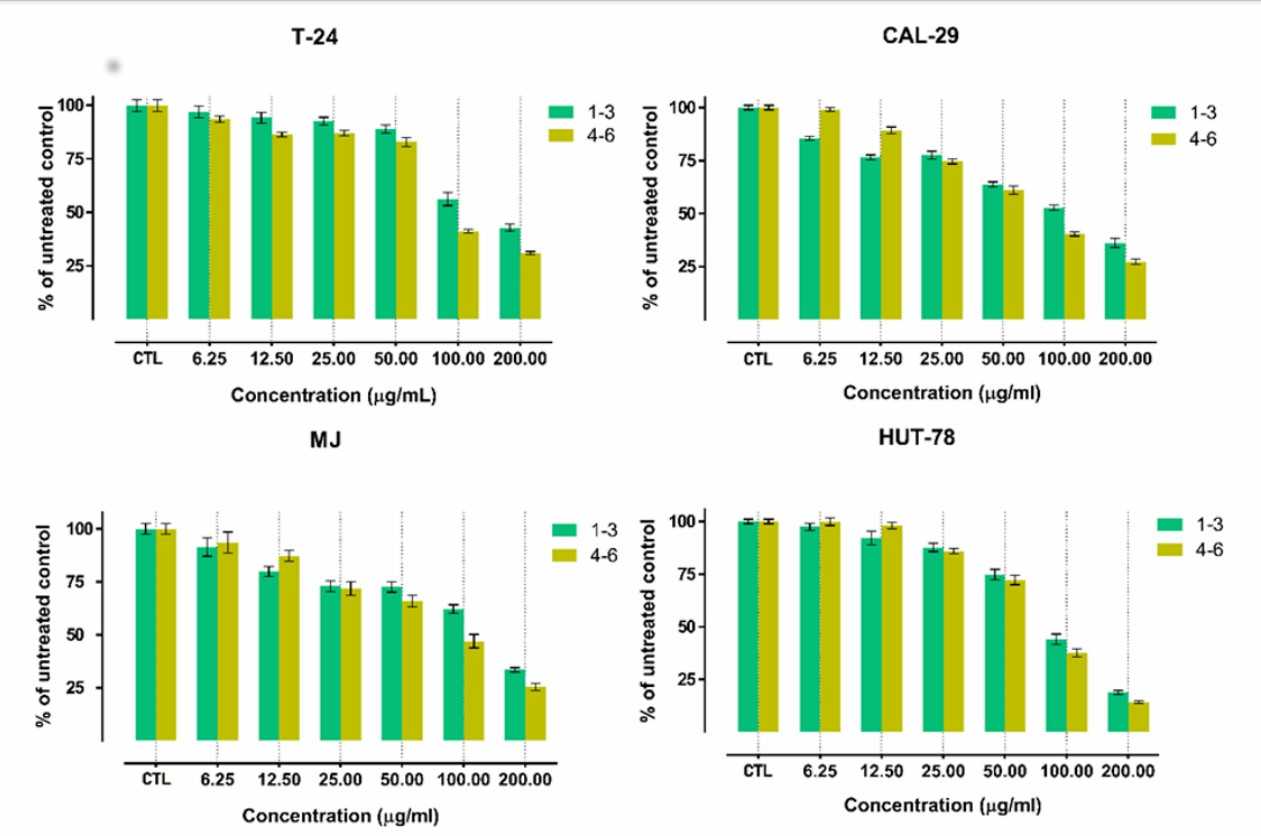 Fig. 3. Viability of T-24, CAL-29, MJ and HUT-78 cells following 72 h exposure to various concentrations of fractions 1-3 and 4-6 (Shkondrov A, Krasteva I, et al., 2019).
Fig. 3. Viability of T-24, CAL-29, MJ and HUT-78 cells following 72 h exposure to various concentrations of fractions 1-3 and 4-6 (Shkondrov A, Krasteva I, et al., 2019).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells