
BL-41
Cat.No.: CSC-C0305
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Morphology: single, round cells growing non-adherent in suspension
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: CD3 -, CD13 -, CD19 +, CD20 +, CD34 -, CD37 +, CD38 +, cyCD79a (+), CD138 +, HLA-DR +, sm/cyIgG -, sm/cyIgM +, sm/cykappa +, sm/cylambda -
Viruses: ELISA: rev
BL-41 is a B-lymphocyte cell line originating from peripheral blood or lymph node tissue of a patient with Burkitt lymphoma (BL), a highly aggressive form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and is frequently used as a Burkitt lymphoma model. Established from a 25-year-old Caucasian male, this cell line exhibits classic BL characteristics, including the MYC gene translocation t(8;14)(q24;q32), which leads to MYC protein overexpression and drives uncontrolled cell proliferation. Typically, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-negative, BL-41 serves as an ideal model for studying MYC-driven oncogenesis without interference from EBV-associated proteins. Additionally, the cell line has mutations in the ID3 and TP53 genes, which are involved in B-cell differentiation and may play a role in chemotherapy resistance.
BL-41 cells can be cultured in suspension and exhibit a lymphoblast-like morphology. They express high levels of B-cell markers (CD19, CD20, CD10) and have a rapid doubling time of about 24–36 hours in culture. As one of the well-established Burkitt lymphoma cell lines with known functional properties and a well-characterized genetic background, BL-41 cells are widely used in cancer biology research (MYC signaling, apoptosis mechanisms), anticancer drug screening (MTH1 inhibitors, BCL-2 inhibitors), as well as B-cell developmental disorders.
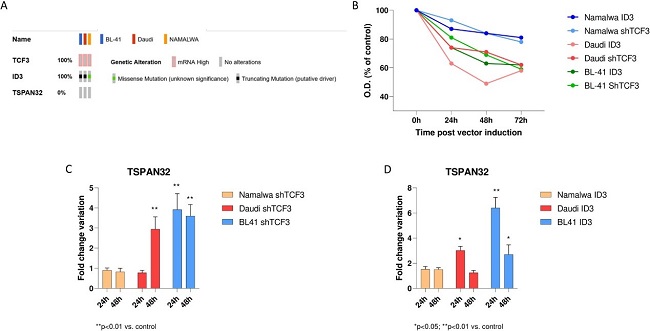
TCF3 and ID3 Regulate TSPAN32 Expression in Burkitt Lymphoma
Burkitt lymphoma (BL) is an aggressive B-cell lymphoma driven by MYC overexpression due to chromosomal translocations, with subtypes showing distinct clinical features. TSPAN32, a member of the tetraspanin family, is important in B-cell development. However, the expression and regulation of TSPAN32 in BL are not well understood. Scuderi et al. investigated the expression of TSPAN32 in BL subtypes and the mechanisms responsible for TSPAN32 dysregulation
They analyzed TSPAN32 expression in BL subtypes and found it was downregulated regardless of EBV status. In order to gain an understanding of the mechanisms that may be responsible for the regulation of TSPAN32 expression, the authors explored the role of TCF3 and ID3 in three BL cell lines (Namalwa, Daudi, and BL41). ID3 mutations (truncating) were found in both Daudi and BL41 cells (Fig. 1A). Both TCF3 knockdown and ectopic induction of functional ID3 decreased proliferation, with the most significant decrease in Daudi and BL41 cells (Fig. 2B). Using PCR, they confirmed a decrease in TCF3 (64.6%) and an increase in ID3 (31.1%). They also found that knockdown of TCF3 and overexpression of ID3 had no effect on TSPAN32 in Namalwa cells (Fig. 1C and D).
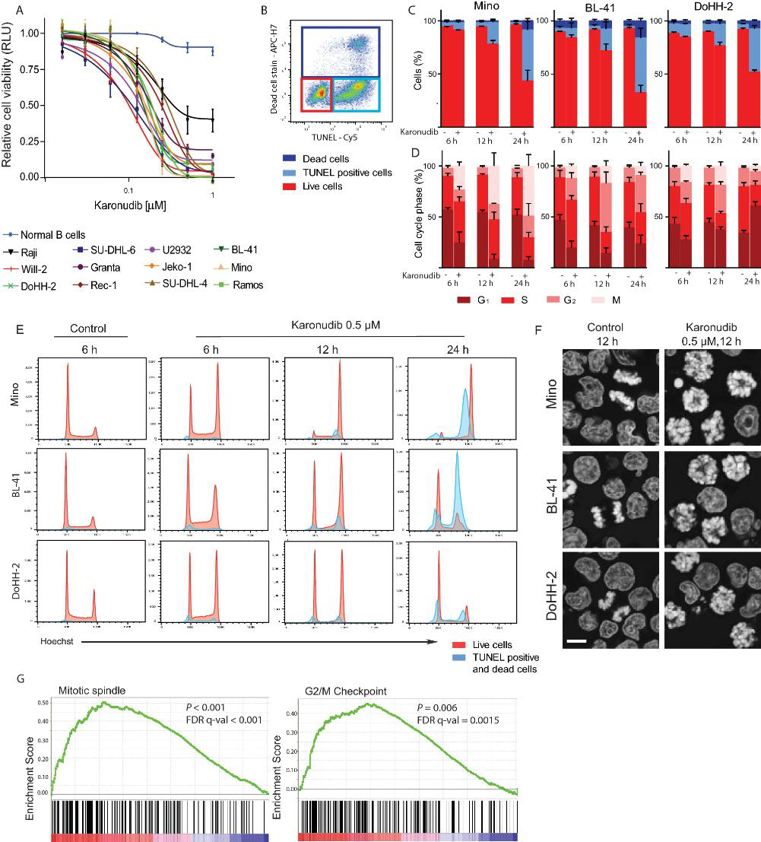
Karonudib Has Potent Anti-Tumor Effects in Preclinical Models of B-Cell Lymphoma
Despite advances in chemo-immunotherapy, relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphomas (e.g., DLBCL, Burkitt lymphoma, and mantle cell lymphoma) remain a major clinical challenge. MTH1, an enzyme preventing oxidized DNA damage, is upregulated in these cancers, making it a promising therapeutic target. In this regard, Oksvold et al. evaluated the preclinical characteristics of karonudib (TH1579) to assess its potential as a treatment for B-cell lymphoma as an MTH1 inhibitor.
Viability, DNA damage (incorporation of 8-oxo-dGTP), and cell cycle arrest were assessed in vitro. Cell viability staining and TUNEL assays indicated that karonudib treatment led to high levels of apoptotic cells (>50% at 24 h), with little evidence of necrosis in three karonudib-sensitive lymphoma cell lines (Fig. 2B, C). In cell cycle experiments, G2/M arrest was induced as early as 6–12 h after treatment, and this effect was prolonged until 24 h in Mino cells, in contrast to DoHH-2 cells, which instead shifted into G1 arrest (Fig. 2D, E). Apoptosis was induced from G2/M in TP53-mutant lines (Mino, BL-41) but also from G1 in TP53-wild-type DoHH-2 (Fig. 2E). Microscopy studies indicated that this arrest was prometaphase due to failure of spindle assembly, as evidenced by monopolar spindles and the absence of anaphase cells (Fig. 2F). No significant increase in ɣH2AX was observed, which indicated that the cell cycle arrest was not due to replication stress. Differential expression and gene set enrichment analyses were also performed, which indicated dysregulation of "mitotic spindle" and "G2/M arrest" gene sets (Fig. 2G), which was in agreement with the flow cytometry studies.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells





