
K562/Adr
Cat.No.: CSC-C6619J
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Pleural Effusion
Morphology: Lymphocyte-like
Culture Properties: Suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Shipping: Dry Ice, Frozen
K562/Adr is an Adriamycin (doxorubicin) resistant subline of the human chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) cell line K562. The K562 cell line was isolated from the bone marrow of a patient with chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) in blast crisis, and K562/Adr was generated from K562 by stepwise or continuous exposure to Adriamycin, resulting in a stable, high-level multidrug resistant subline. Morphologically, K562/Adr cells are suspension-growing cells with round/oval morphology and prominent nuclei and nucleoli. These cells phenotypically resemble the parent cell line and display hematopoietic progenitor-like morphology.
K562/Adr cells display overexpression of P-glycoprotein (MDR1/ABCB1) efflux transporter. It has been used as an in vitro model of multidrug resistance (MDR) in leukemia, for studying the molecular mechanisms of chemoresistance, and for screening novel anti-cancer agents or MDR inhibitors. K562/Adr has been used to study the mechanisms and inhibition of drug transporters and apoptotic/survival signaling pathways in drug resistant leukemia, for screening of small molecules and drugs, and for gene silencing or editing of genes related to drug resistance.
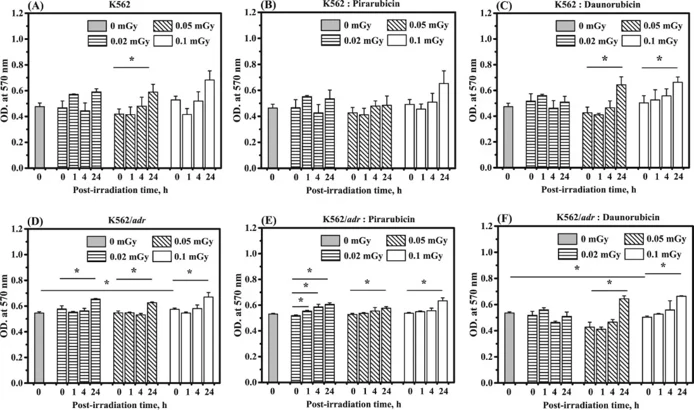
Effect of Low-Dose Radiation on the Kinetics of Pirarubicin and Daunorubicin Transport in K562 Cells and Drug Resistant K562/adr Cells
Low-dose radiation may affect drug transport kinetics. Here, Supawat et al. irradiated K562 and K562/adr cells with 137Cs gamma radiation at doses of 0, 0.02, 0.05, and 0.1 mGy and assessed cell viability and Pira/Dau transport kinetics at 0, 1, 4, and 24 hours post-irradiation.
Figure 1 A-F show the OD at 570 nm values in K562 and K562/adr cells collected at 0, 1, 4, and 24 h after in vitro exposure to various low doses of gamma radiation, followed by treatment with Pira and Dau. The OD at 570 nm indicates cell viability. At 0 h post-irradiation, significant changes in OD at 570 nm were observed in 0.1 mGy-irradiated K562/adr cells compared to non-irradiated K562/adr cells (Fig. 1D). Significant changes in OD at 570 nm were seen in irradiated K562/adr cells at 24 h post-irradiation compared to 0 h post-irradiation, while no significant changes were observed at 1 and 4 h post-irradiation (Fig. 1D). Significant changes in OD at 570 nm were also observed at 1, 4, and 24 h post-irradiation in 0.02 mGy-irradiated K562/adr cells treated with Pira compared to 0 h post-irradiation. Similarly, significant changes were seen at 24 h post-irradiation in 0.05 and 0.1 mGy-irradiated K562/adr cells treated with Pira compared to 0 h post-irradiation (Fig. 1E). At 0 h post-irradiation, significant changes in OD at 570 nm were observed in 0.1 mGy-irradiated K562/adr cells treated with Dau compared to non-irradiated K562 cells treated with Dau. Significant changes in OD at 570 nm were also seen at 24 h post-irradiation in 0.05 and 0.1 mGy-irradiated K562/adr cells treated with Dau compared to 0 h post-irradiation (Fig. 1F).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells





