Immortalized Mouse WildType Aortic Endothelial Cells (iMAEC-WT)
Cat.No.: CSC-I9358L
Species: Mus musculus
Source: Heart
Morphology: Elongated
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Note: Never can cells be kept at -20 °C.
CIK-HT003 HT® Lenti-SV40T Immortalization Kit
2) Characterization by Dil-Ac-LDL staining and immunostaining
The immortalized mouse wildtype aortic endothelial cells (iMAEC-WT) cell line was immortalized using a retroviral method involving the polyoma middle T antigen. This technique allows cells to keep their stable proliferative ability in vitro while maintaining essential endothelial properties. The iMAEC-WT cells have a spindle shape which matches more with mouse aortic endothelial cells under high shear stress conditions in vivo than with human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). Cells show alignment with flow direction when subjected to unidirectional laminar shear (LS) but this behavior does not occur under oscillatory shear stress (OS) or static conditions. LS conditions elevate KLF2 and eNOS protein levels while OS conditions result in distinct gene and miRNA expression patterns. Under OS conditions iMAEC-WT cells show strong tube formation and migration skills which matches the behavior seen in primary cultured endothelial cells such as HUVEC.
The iMAEC-WT cell line represents an essential research tool for exploring endothelial cell functions in vascular health and disease. The sensitivity of iMAEC-WT cells to shear stress renders them an ideal model for studying vascular conditions such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular inflammation. Researchers have created multiple gene knockout iMAEC lines including iMAEC-cav1 and iMAEC-eNOS to examine the specific roles of genes in endothelial cell functions besides the wild-type line.
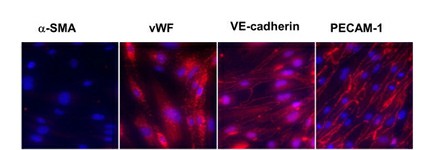 Fig. 1. Characterization of iMAEC-WT lines by immunostaining (Ni CW, Kumar S, et al., 2014).
Fig. 1. Characterization of iMAEC-WT lines by immunostaining (Ni CW, Kumar S, et al., 2014).
Synthetic LXR and RXR Agonists, but Not Endogenous LXR and RXR Agonists, Increase ABCA1 Protein Expression in iMAEC
Atherosclerosis, leading to heart attacks and strokes, involves arterial cholesterol buildup. Statins lack effectiveness in directly reducing arterial cholesterol. Recent studies suggest targeting endothelial cell cholesterol with LXR/RXR agonists might benefit treatment, as they boost ABCA1 expression and enhance cholesterol efflux. Huang's team tests synthetic and endogenous LXR/RXR agonists on immortalized mouse aortic endothelial cells (iMAEC).
The researchers chose 22?-hydroxycholesterol and 9-cis-retinoic acid as natural activators of LXR and RXR because these compounds increase ABCA1 mRNA levels within endothelial cells. The synthetic LXR agonist GW3965 was selected for its function in increasing ABCA1 levels and promoting cholesterol efflux while T0901317 operates as an LXR agonist but also targets pregnane X receptors. SR11237 was selected as the synthetic RXR agonist for its specificity. Their findings demonstrated that 22?-hydroxycholesterol or 9-cis-retinoic acid alone failed to increase ABCA1 protein in iMAECs, but GW3965 or SR11237 alone significantly increased it (Fig. 1A–D). This suggests synthetic LXR or RXR agonists alone effectively upregulate ABCA1 protein, unlike their endogenous counterparts.
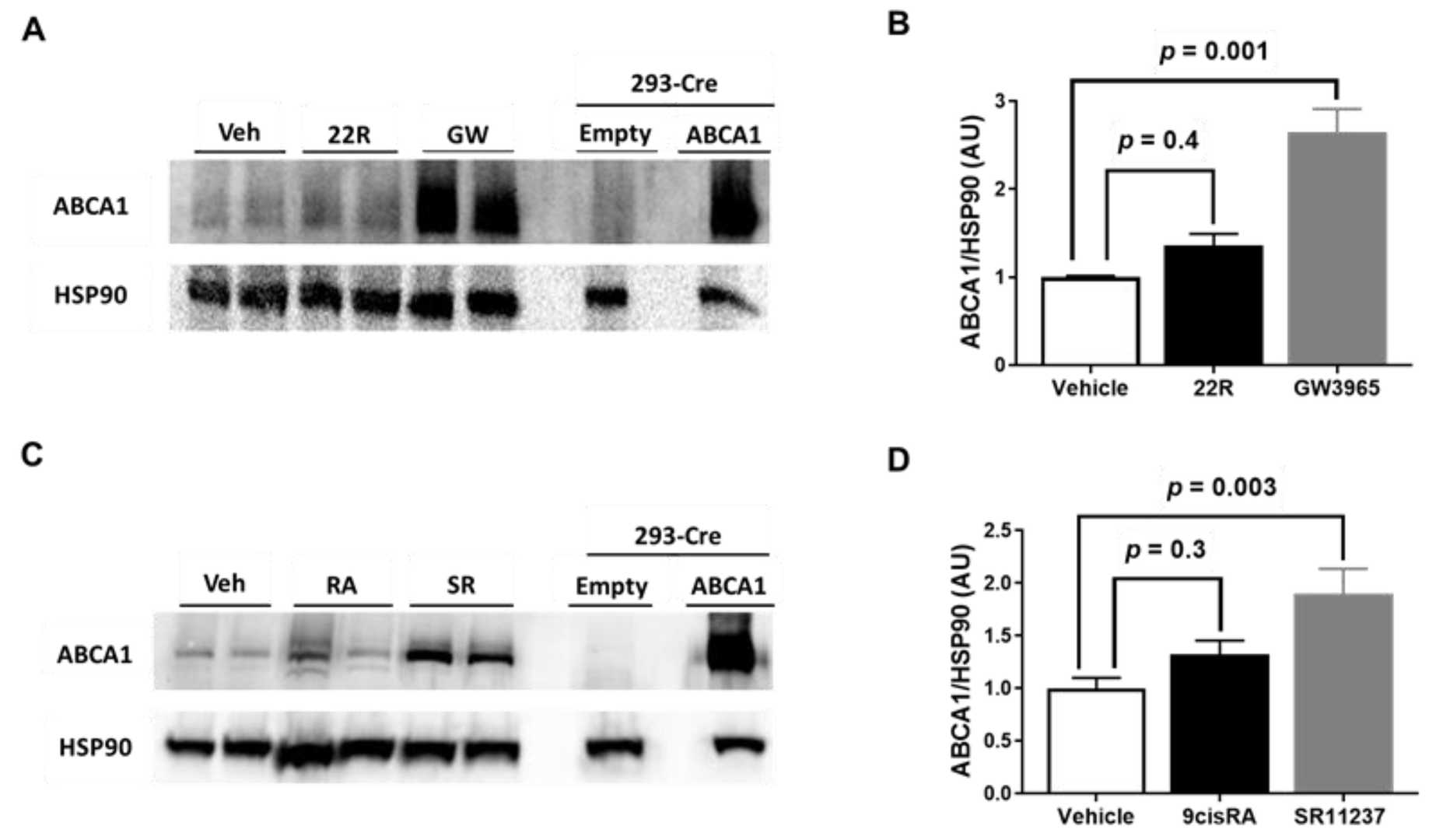 Fig. 1. Effect of LXR and RXR agonist treatment on ABCA1 protein expression in immortalized mouse aortic endothelial cells (iMAEC) (Huang K, Jo H, et al., 2021).
Fig. 1. Effect of LXR and RXR agonist treatment on ABCA1 protein expression in immortalized mouse aortic endothelial cells (iMAEC) (Huang K, Jo H, et al., 2021).
LPS-Challenged iMAECs Exhibit Robust Plasmid DNA Transfection Efficiency
Cholesterol and inflammation lead to atherosclerosis which commonly affects endothelial cells making them a significant focus for researchers. The functions of miR-33a-3p in biological processes have yet to be defined even though miR-33a is recognized for its role in managing cholesterol levels. Through plasmid transfection, Huang's team reduced miR-33a-3p levels in cultured iMAECs to investigate if miR-33a-3p inhibition boosts cholesterol efflux by increasing ABCA1 expression in pro-inflammatory endothelial cells.
To determine if miR-33a-3p inhibition can upregulate ABCA1 protein in pro-inflammatory endothelium, they first confirmed successful transfection of pA3p into these cells. Transfecting immortalized cell lines faces challenges, especially when inflammation affects transfection efficiency. We used endpoint RT-PCR to verify transgenic transcripts in LPS-challenged iMAECs transfected with pA3p or pScr (Fig. 2A). Flow cytometry evaluated transfection efficiency, showing high efficiency with both plasmids (Fig. 2B and C). miR-33a-3p expression was significantly reduced in LPS-challenged iMAECs transfected with pA3p compared to pScr (Fig. 2D). These results confirm that pA3p effectively inhibits miR-33a-3p in cultured pro-inflammatory endothelial cells.
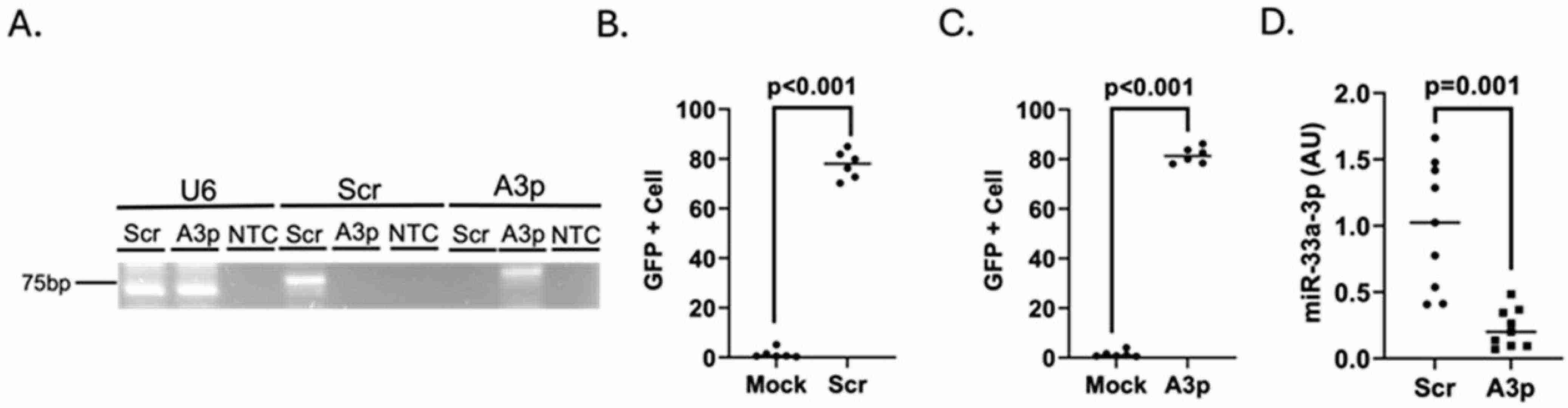 Fig. 2. Transfecting pro-inflammatory endothelial cells with pA3p decreases miR-33a-3p expression (Huang K, Pokhrel A, et al., 2025).
Fig. 2. Transfecting pro-inflammatory endothelial cells with pA3p decreases miR-33a-3p expression (Huang K, Pokhrel A, et al., 2025).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells
