SET-2
Cat.No.: CSC-C0608
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Blood; Peripheral Blood
Morphology: mostly single cells in suspension, some cells grow loosely adherent, 1-3% giant cells
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: CD3 -, CD4 +, CD7 +, CD13 +, CD14 -, CD15 -, CD19 -, CD33 +, CD34 +, CD38 +, CD42 -, CD71 +, HLA-DR +
Viruses: PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HIV -, HTLV-I/II -, SMRV -
SET-2 is a human cell line derived from a 71-year-old Japanese female patient. The SET-2 cell line is an adult acute megakaryoblastic leukemia cell line from peripheral blood, and it is used for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) research. This cell line has the JAK2 V617F heterozygous mutation, which is a mutation that is commonly seen in myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) and causes abnormal cell proliferation and signal transduction. The SET-2 cell line also has the DNMT3A R882H mutation in DNA methyltransferase, a mutation that has been found in around 25% of patients with acute myeloid leukemia and causes abnormal methylation patterns and increased cell proliferation.
The SET-2 cell line is often used to study drugs that target the JAK2 V617F mutation, including JAK2 inhibitors. One study found that certain JAK2 inhibitors were able to suppress the proliferation of SET-2 cells by more than 50% and cause apoptosis. The SET-2 cell line can also be used to model the pathological mechanisms of myeloproliferative neoplasms to help researchers study the role that the JAK2 V617F mutation plays in the onset and progression of this condition.
Ruxolitinib Uptake by BM-Mscs and Antiproliferative Effects on Leukemic Stem Cells
Myelofibrosis (MF) is a chronic myeloproliferative disorder marked by bone marrow (BM) hyperplasia, fibrosis, and splenomegaly. Over 50% of patients carry the JAK2V617F mutation, driving uncontrolled cell proliferation. Ruxolitinib, a JAK1/2 inhibitor, can relieve inflammation in these patients but the crosstalk with BM-MSCs has not been evaluated so far, and MSCs could modulate the distribution of drugs. Marino et al. analyzed in vitro ruxolitinib uptake by MF patient-derived BM-MSCs and tested the impact of drug-treated MSCs and their conditioned media on leukemic cell proliferation.
The antiproliferative activity of CM from BM-MSCs treated with 5 μg/mL ruxolitinib for 24 h was evaluated on leukemic cells. Serial dilutions of ruxolitinib or CM were prepared and 2 × 104 SET-2 cells were added. After 7 days of incubation, cell proliferation was assessed by CCK-8 assay. The IC50 of the CM from BM-MSCs previously treated with ruxolitinib was significantly lower compared to ruxolitinib (57.3 ng/mL vs 74.2 ng/mL), while the IC10 was lower (10.1 ng/mL vs 19 ng/mL) and the IC90 was similar (353.1 ng/mL vs 289.1 ng/mL). This data suggests that the CM of ruxolitinib-treated BM-MSCs from MF patients exert stronger antiproliferative effects compared to ruxolitinib alone and further studies are needed to assess whether this response is mediated by the release of drug-loaded exosomes or by cytokine release (Fig. 1C).
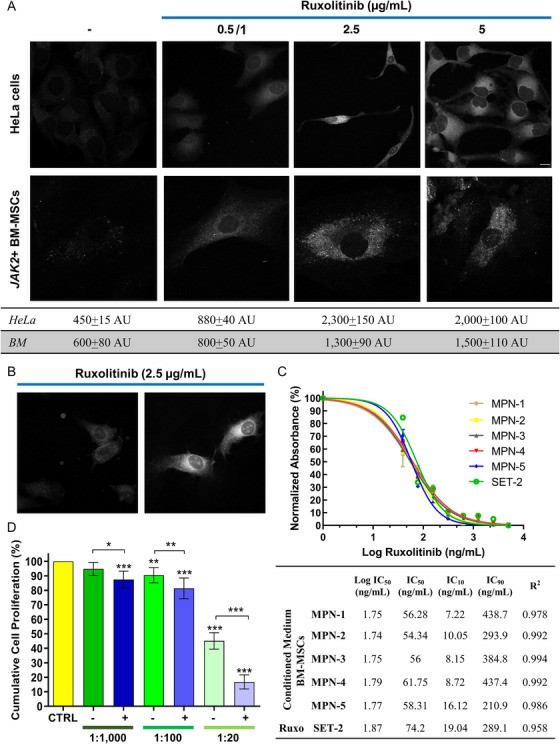 Fig. 1. Ruxolitinib uptake by BM-MSCs and antiproliferative effects on leukemic stem cells (Marino L, Charlier B, et al., 2020).
Fig. 1. Ruxolitinib uptake by BM-MSCs and antiproliferative effects on leukemic stem cells (Marino L, Charlier B, et al., 2020).
Identification of DNMT3AR882H and IDH2R140Q Neopeptides Using HLA Class I Peptidomics
DNA methyltransferase 3A (DNMT3A) and isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2 (IDH1/2) are epigenetic regulators mutated in 7–23% of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) (6). Struckman et al. assessed whether hotspot mutations in these two genes encode immunogenic neoantigens. They transduced five human B-lymphoblastoid cell lines expressing common HLA class I alleles with a minigene construct harboring DNMT3A or IDH1/2 mutations and used mass spectrometry to identify HLA-A01: 01-binding DNMT3AR882H and HLA-B07:02-binding IDH2R140Q peptides as candidate neoantigens (Table S2).
They next asked whether DNMT3AR882H and IDH2R140Q peptides are HLA class I-presented in AML. They used parallel reaction-monitoring mass spectrometry (PRM-MS) to assess HLA class I peptide eluates from AML cell lines and patient-derived AML samples (Fig. 1D). SET-2 is an AML cell line harboring a natural heterozygous DNMT3AR882H mutation, and K562-R140Q is a chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line into which homozygous IDH2R140Q mutations were introduced using gene editing technology. Sanger sequencing confirmed these mutations in these cell lines. PRM-MS analysis did not detect the 11mer YTDVSNMSHLA peptide in SET-2 transduced with HLA-A01: 01 or HLA-A01:01-positive patient-derived AML cells with a DNMT3AR882H mutation. YTDVSNMSHLA was detected, however, in SET-2 transduced with HLA-A*01:01 and the full-length DNMT3AR882H gene (Fig. 2C). YTDVSNMSH, the 9mer counterpart to YTDVSNMSHLA, was not detected in any HLA eluates.
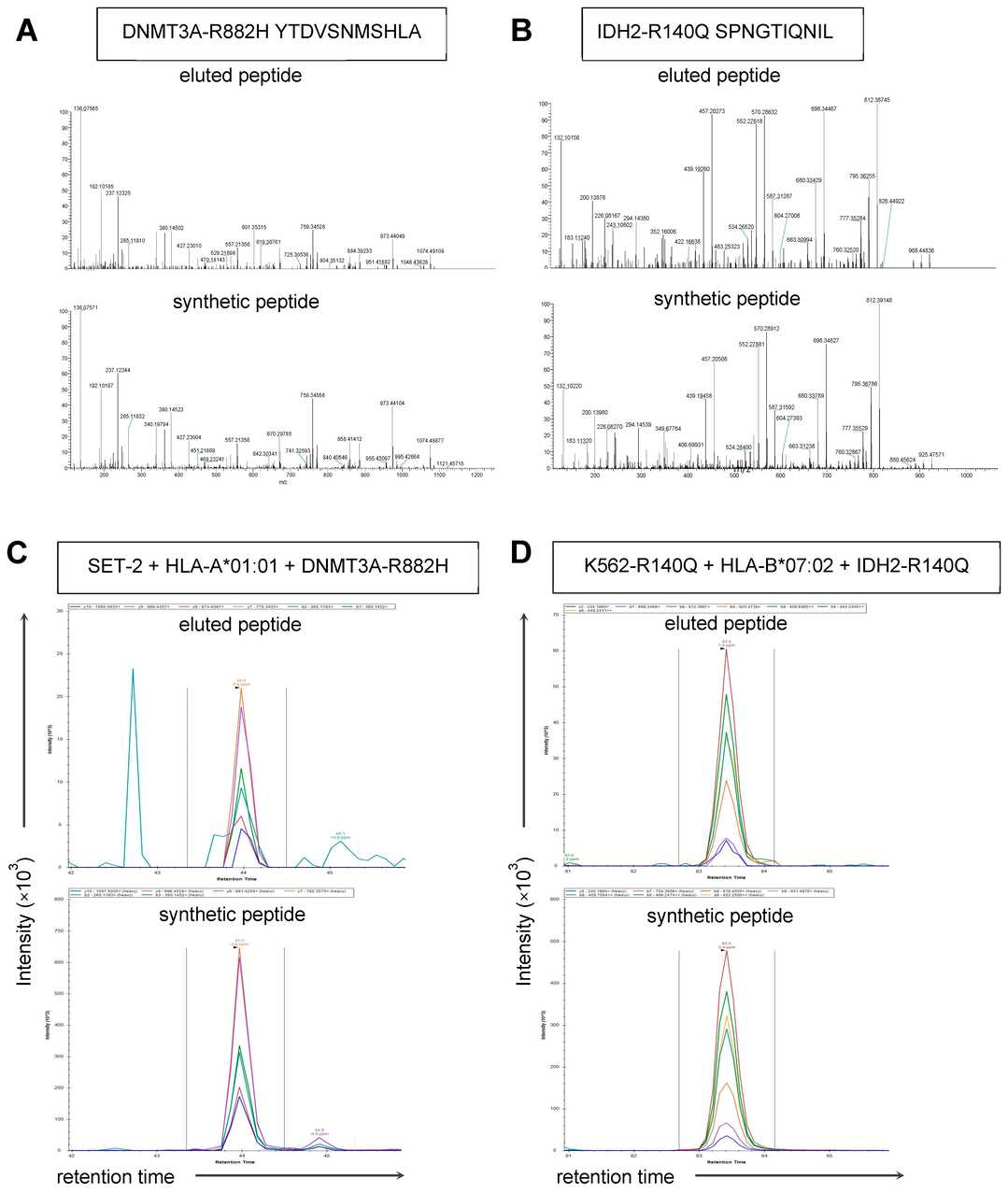 Fig. 2. Surface presentation of DNMT3A and IDH2 neopeptides assessed with HLA class I immunopeptidomics (Struckman NE, de Jong RCM, et al., 2024).
Fig. 2. Surface presentation of DNMT3A and IDH2 neopeptides assessed with HLA class I immunopeptidomics (Struckman NE, de Jong RCM, et al., 2024).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells





