SEM
Cat.No.: CSC-C0554
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Blood; Peripheral Blood
Morphology: round to polygonal single rather small cells in suspension
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: CD3-, CD4-, CD11b-, CD13+, CD14-, CD15+, CD19+, CD33+, CD34-, cyCD68-, HLA-DR+, sm/cyIgG-, sm/cyIgM-, sm/cykappa-, sm/cylamda-
Viruses: PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HIV -, HTLV-I/II -, S
The establishment of the SEM cell line in 1990 provided researchers with a valuable in vitro model system to investigate the unique biology and molecular pathogenesis of this specific subtype of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Before the availability of the SEM cell line, researchers had limited access to primary samples from patients with the t(4;11) translocation, which hindered the progress of research in this area.
By utilizing the SEM cell line, researchers have been able to elucidate the underlying mechanisms by which the MLL-AFF1 fusion protein drives leukemogenesis, including its effects on gene expression, epigenetic regulation, and cellular signaling pathways. This knowledge has been crucial for the development of targeted therapies and personalized treatment approaches for patients with MLL-rearranged ALL.
Furthermore, the SEM cell line has been extensively characterized, with its genomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic profiles being well-documented. This comprehensive characterization has allowed researchers to identify potential therapeutic targets and test the efficacy of various drug candidates in a clinically relevant in vitro model system.
The ALL Cell Line SEM With t(4;11) Chromosomal Rearrangement
A cell line, designated SEM, was established from the peripheral blood of a 5-year-old girl in relapse with t(4;11) ALL. During the first 8 months of culture, SK-HEP-1 hepatoma culture supernatant appeared necessary for the growth of SEM cells. During the first 8 months of culture, the doubling time of SEM cells was 7-10 d. After this period, the growth of SEM cells increased and the cell doubling time was approximately 48 h. Then SK-HEP-1 culture supernatant was omitted from the culture medium. The cell line has been propagated for more than 2 years in IMDM containing 10% FCS. SEM cell line was growing as single cell suspension and was found to be free of mycoplasma contamination and Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen.
SEM cells showed a lymphoblastic morphology with cell nuclei exhibiting one or more prominent nucleoli. Cells were pleomorphic in size and had cytoplasmic vacuolations (Fig. 1). Cytochemical staining of SEM cells revealed negativity for peroxidase. Sudan black, non-specific esterase activity and PAS reaction following staining results of the lymphoblasts of the patient. SEM cells were positive for TdT activity. Cytogenetic analysis of the SEM cell line was performed 5 and 10 months after the beginning of the culture. A t(4;11)(q21;q23), deletion of the short arm of chromosome 7 del(7)(p15), and deletion of the long arm of chromosome 13 del(13)(q12) were found as clonal karyotypic abnormalities (Fig. 2). Cytogenetic analysis of the leukemic cells from the patient's peripheral blood revealed identical cytogenetic abnormalities.
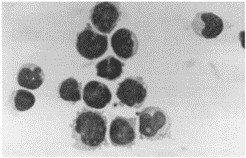 Fig. 1 Photomicrograph of SEM cells stained with Pappenheim's stain. (Greil J, et al., 1994)
Fig. 1 Photomicrograph of SEM cells stained with Pappenheim's stain. (Greil J, et al., 1994)
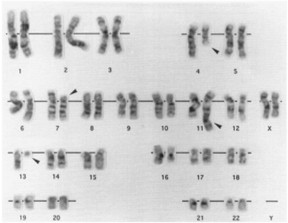 Fig. 2 A representative karyotype of SEM cell line after GTG banding. (Greil J, et al., 1994)
Fig. 2 A representative karyotype of SEM cell line after GTG banding. (Greil J, et al., 1994)
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells





