HUP-T3
Cat.No.: CSC-C0359
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Ascites Metastasis
Morphology: epitheloid cells growing adherently in monolayers and clusters
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin +, cytokeratin-7 (+), cytokeratin-8 +, cytokeratin-17 -, cytokeratin-18 +, cytokeratin-19 +, desmin -, endothel -, EpCAM +, GFAP -, neurofilament -, v
HuP-T3 is a human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cell line established from the ascites of a 66-year-old male patient. It exhibits epithelial morphology and adherent growth characteristics. This model harbors the hallmark genetic alterations of PDAC, including KRAS, TP53 and a frameshift mutation in MSH6. In vivo, HuP-T3 cells form poorly differentiated adenocarcinomas with an invasive growth pattern, recapitulating the aggressiveness of clinical PDAC.
The molecular profile of this cell line, particularly its KRAS and TP53 alterations, are consistent with the genomic landscape of >90% of human PDAC cases, making it a translational model for studying therapeutic resistance, tumor-stroma interactions, and metastatic mechanisms. HuP-T3 is further characterized by its rapid proliferation in vitro and secretion of pro-tumorigenic factors (e.g., MMP-9, IL-8), which contribute to its application in drug screening and microenvironment studies.
ANP32E Downregulation Enhances the Susceptibility of PDAC Cells to Gemcitabine In Vitro
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a highly aggressive and fatal malignancy, although gemcitabine is administered as a single or combined therapeutic agent. Previous studies have demonstrated that ANP32E overexpression promoted PDAC cell proliferation. However, whether it affects treatment outcome and clinical prognosis is still unclear. In the present study, we aimed to determine whether ANP32E is negatively associated with the treatment outcome of gemcitabine.
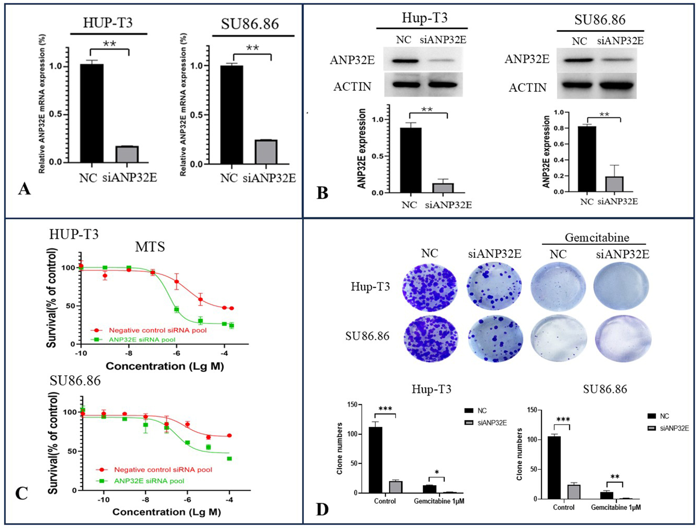
We downregulated ANP32E expression via specific siRNAs in two PDAC cell lines, HUP-T3 and SU86.86, followed by the detection of gemcitabine-induced cytotoxicity via MTS assays. As shown by the results of the qRT‒PCR (Fig. 1A) and Western blot (Fig. 1B) assays, ANP32E was efficiently knocked down in both cell lines. The MTS assay findings indicated that the downregulation of ANP32E significantly increased gemcitabine-induced cytotoxicity in Hup-T3 and SU86.86 cells (Fig. 1C). In addition, plate cloning experiments revealed that knocking down ANP32E effectively reduced the colony formation ability of PDAC cells and increased their sensitivity to gemcitabine (Fig. 1D).
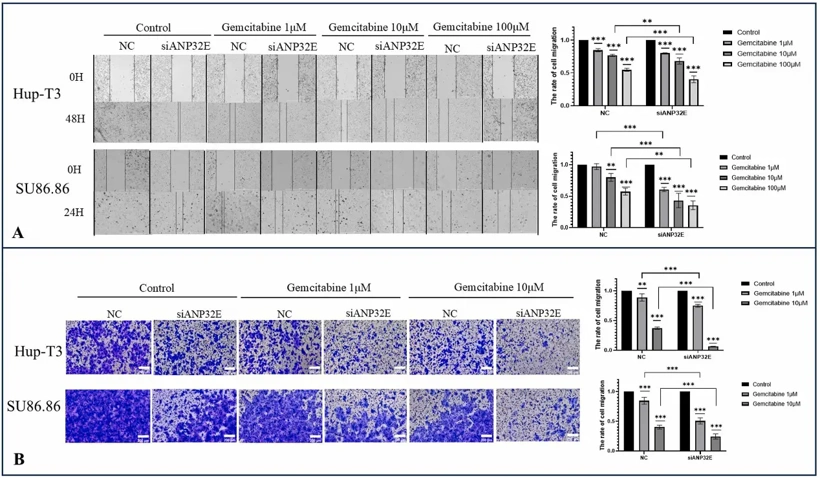
Owing to the migratory role of ANP32E in PDAC cells, we used a wound healing assay and a transwell migration assay to assess changes in the migration of PDAC cells after the downregulation of ANP32E. The results from the wound healing assay revealed that the migration of pancreatic cancer cells decreased after ANP32E was knocked down. The migration of PDAC cells diminished with increasing concentrations of the drug after the administration of gemcitabine at different concentrations. The antimigration effect was more obvious after the knockdown of ANP32E (Fig. 2A). Similarly, in the Transwell migration assay, downregulation of ANP32E expression in PDAC cells significantly reduced the migratory activity of PDAC cells and increased their sensitivity to gemcitabine (Fig. 2B).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells