KMS-12-PE
Cat.No.: CSC-C0606
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Pleural Effusion
Morphology: small round cells growing singly or occasionally in small clumps in suspension
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
- Documents
Immunology: CD3 -, CD4 -, CD13 -, CD14 -, CD15 -, CD19 -, CD20 -, CD34 -, CD38 +, CD138 +, HLA-DR +
Viruses: PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HIV -, HTLV-I/II -, SMRV -
The KMS-12-PE cell line was derived in 1987 from the pleural effusion of a 64-year-old woman who had refractory, terminal multiple myeloma (Ig-non-producing) after undergoing combination chemotherapy. These cells are characterized by the presence of t (11: 14) (q13: q32) rearrangement. It is important to note that KMS-12-PE is described as the sister cell line of KMS-12-BM.
The KMS-12-PE cell line holds significance in multiple myeloma research, particularly due to its unique characteristics and origin from a refractory, terminal stage of the disease. These cells have been widely used to study the molecular mechanisms underlying multiple myeloma, including the impact of chromosomal rearrangements such as t (11: 14) (q13: q32). Additionally, the sister relationship to KMS-12-BM may provide comparative opportunities for researchers.
Furthermore, KMS-12-PE cells have been instrumental in testing potential therapeutic approaches and evaluating drug responses specifically in the context of refractory multiple myeloma, contributing to the advancement of treatment strategies for this challenging form of the disease.
Characterizations of KMS-12-PE Cell Lines
Most of the KMS-12-PE cells were small in size and round in shape with a few large distorted cells. Peroxidase, ASD-acetate esterase, and PAS staining were negative, and only the methyl-green-pyronine stain was positive in the cell lines. Ultrastructural, the cell lines revealed characteristic features of plasmacytoid cells, such as well-developed rough endoplasmic reticulum and ovoid eccentric nuclei with peripheral chromatin distribution (Fig. 1).
KMS-12-PE cells were positive for PCA-I, CD38, and OKT-9 (anti-transferrin receptor antibody). Representative karyotypes of KMS-12-PE and KMS-12-BM cells are shown in Fig. 2. Most of the metaphases of KMS-12-PE cells were hypodiploid, with the modal chromosome number being 41. In addition, all the metaphases of KMS-12-PE cells demonstrated a reciprocal chromosome translocation, t (9: 11) (q34; q13).
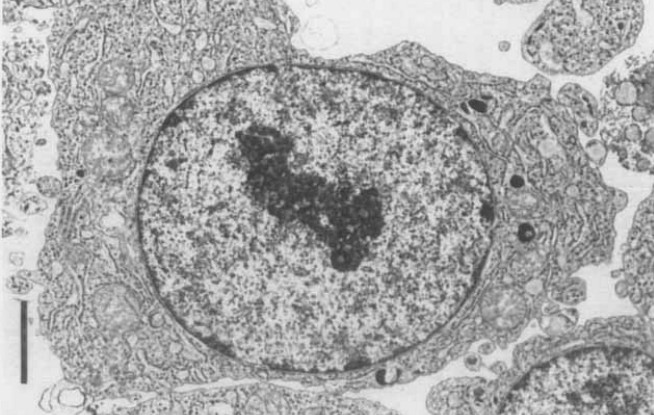 Fig. 1 Electron micrographs of KMS-12-PE cells. (Ohtsuki T, et al., 1989)
Fig. 1 Electron micrographs of KMS-12-PE cells. (Ohtsuki T, et al., 1989)
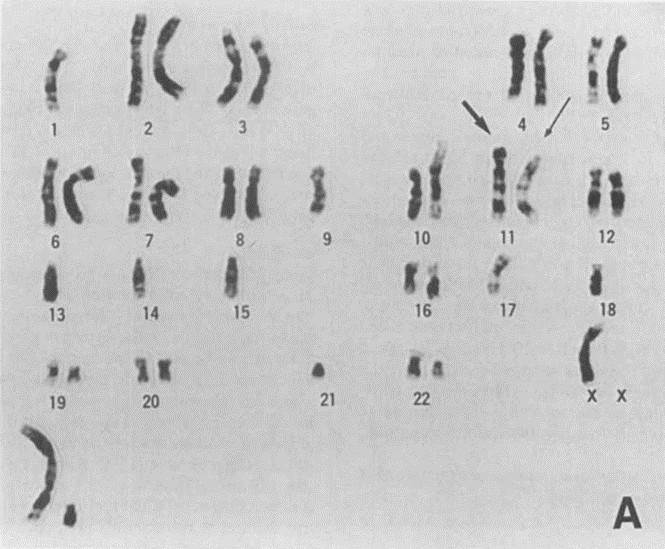 Fig. 2 Representative G-banded karyotypes of KMS-12-PE cells. (Ohtsuki T, et al., 1989)
Fig. 2 Representative G-banded karyotypes of KMS-12-PE cells. (Ohtsuki T, et al., 1989)
Chromothripsis in Treatment Resistance in Multiple Myeloma
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignant disease caused by an abnormal proliferation of plasma cells. Recently, the term chromothripsis has emerged, which is the massive but highly localized chromosomal rearrangement in response to a one-step catastrophic event. Many studies have shown an association of chromothripsis with the prognosis of several cancers.
The frequency of copy number alterations (CNAs) was analyzed, including mosaicism in 9 MM cell lines (U266, MM.1S, RPMI8226, KMS-11, KMS-12-BM, KMS-12-PE, KMS-28-BM, KMS-28-PE, and NCI-H929). Among them, chrs 1, 4, 5, 7, 8, and X were the sites with the most frequent CNAs in the MM cell lines (Fig. 3A). The chromosomes were divided into arms to confirm the trend of CNAs. According to the algorithm, if the copy number was 2.5 or more, it was considered an amplification, and if the copy number was 1.5 or less, it was considered a loss. Analysis of the tendency of CNAs showed that more CNAs were observed in the q arm than in the p arm (Fig. 3B and 3C).
Changes in CNAs were further analyzed in these cell lines by comparing CNAs after bortezomib (BTZ) treatment. Although the cell lines were derived from the same origin, the drug response between the two cell lines was different. In the case of KMS-12-BM, there was no difference in cell viability in the treatment group compared to the control, but in the case of KMS-12-PE, there was a sharp decrease in viability in the treatment group (Fig. 4).
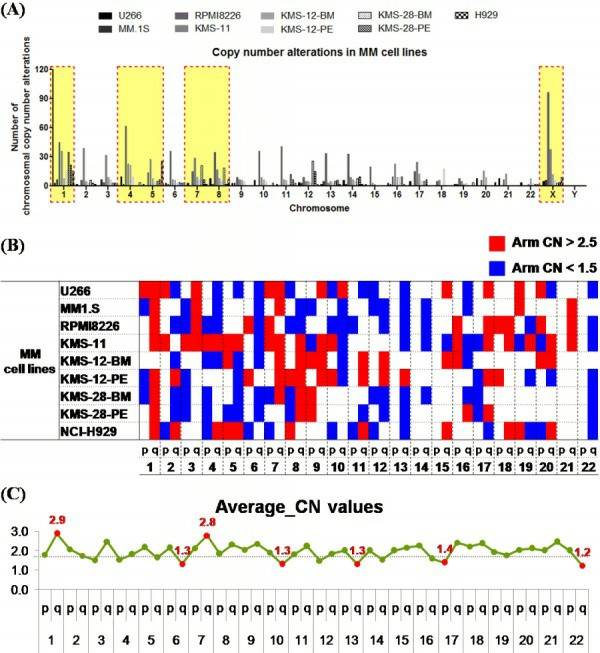 Fig. 3 Analysis of the frequency of copy number alterations in MM cell lines. (Lee KJ, et al., 2017)
Fig. 3 Analysis of the frequency of copy number alterations in MM cell lines. (Lee KJ, et al., 2017)
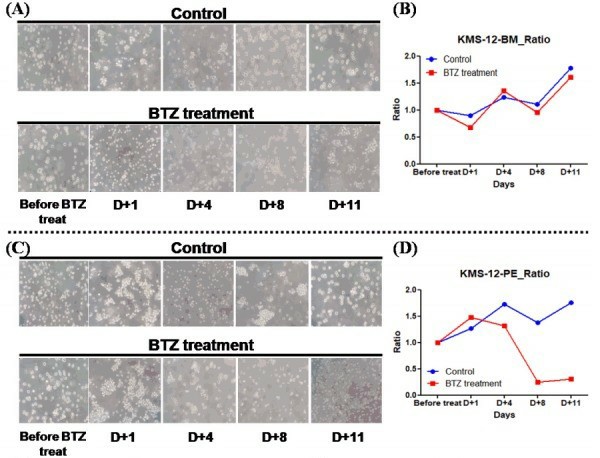 Fig. 4 Comparison of cell viability changes of KMS-12-BM and KMS-12-PE following treatment of bortezomib (BTZ). (Lee KJ, et al., 2017)
Fig. 4 Comparison of cell viability changes of KMS-12-BM and KMS-12-PE following treatment of bortezomib (BTZ). (Lee KJ, et al., 2017)
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells