Hep 3B2.1-7
Cat.No.: CSC-C9187W
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Liver
Morphology: epithelial
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Hep 3B2.1‑7 is a fully characterized subclone of the Hep3B hepatocellular carcinoma line. It was isolated from the primary liver tumor of an 8‑year‑old African‑American male, and contains a full integration of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) genome. As such, Hep 3B2.1‑7 is among the few available human liver‑cancer models that express authentic viral antigens (HBsAg) and secrete high levels of α‑fetoprotein (AFP). Cytogenetically, the line is hyper‑diploid (≈60 chromosomes) with a highly unstable karyotype and loss of functional p53.
The line grows as an adherent, epithelial‑like monolayer in MEM or DMEM‑H supplemented with 10 % fetal bovine serum at 37 °C in a 5 % CO₂ atmosphere. Doubling time is 24-48 hours, and the cells are routinely passaged at a ratio of 1:2-1:4 once 80-90 % confluent. Standard media supplemented with 10 % DMSO is used for long‑term storage in liquid nitrogen.
Taken together, the HBV integration, high AFP production and p53 deficiency make Hep 3B2.1‑7 a flexible model to study HBV‑driven hepatocarcinogenesis, to screen antiviral and chemotherapeutic compounds, to perform gene‑function assays and to generate xenograft tumors in immunodeficient mice.
Identification and Characterization of Cell Lines HepG2, Hep3B217 and SNU387 as Models for Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Coronavirus Infection
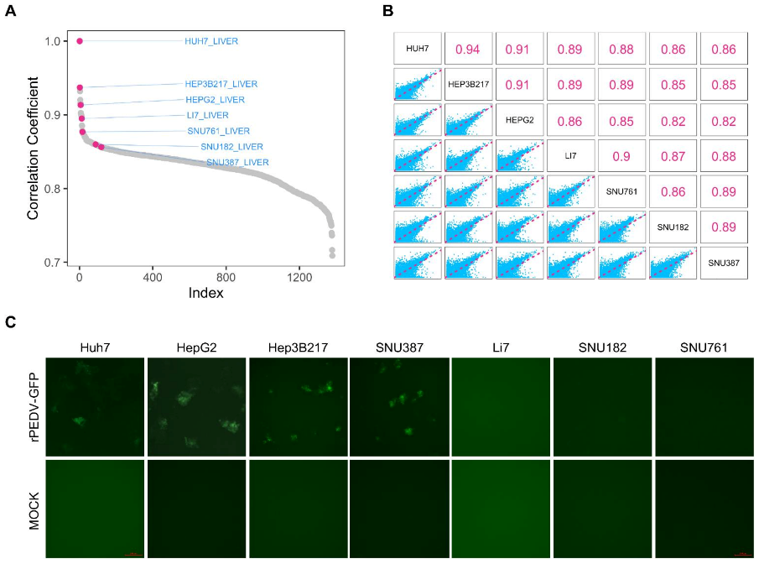
Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) induces acute diarrhea and dehydration in suckling piglets, resulting in a high mortality rate and huge economic losses to the swine industry. The identification and characterization of different cell lines are not only important for PEDV entry and replication studies, but also have guiding significance for the development of various types of biological pharmaceuticals against PEDV. The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia (CCLE) database contains mRNA-seq data for more than 1300 cell lines. Lv's team used Pearson's correlation coefficient to screen for cell lines with similar transcriptomes as Huh7, a previously established PEDV infection model. Six liver carcinoma cell lines, HepG2, Hep3B217, Li7, SNU182, SNU761 and SNU387, were selected. HepG2 and Hep3B217 had correlation coefficients of 0.91 and 0.90, respectively, with Huh7, and Li7, SNU182, SNU387 and SNU761 were below 0.85 (Fig. 1A). The correlation coefficients among these cell lines and Huh7 were also calculated (Fig. 1B). The six cell lines were then exposed to a reporter virus (rPEDV-EGFP) that expresses enhanced GFP (EGFP) during replication. The expression of EGFP was observed in HepG2, Hep3B217, SNU387, and Huh7 cells, but not in Li7, SNU182 or SNU761 cells (Fig. 1C). Taken together, these results indicate that HepG2, Hep3B217 and SNU387 support PEDV replication.
Expressions of EGFR Protein Have No Correspondence with Efficacy of Nimotuzumab
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) has rising incidence, high mortality, and recurrence rates, with unsatisfactory current treatments. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is important, but anti-EGFR agents have not shown ideal results in HCC.
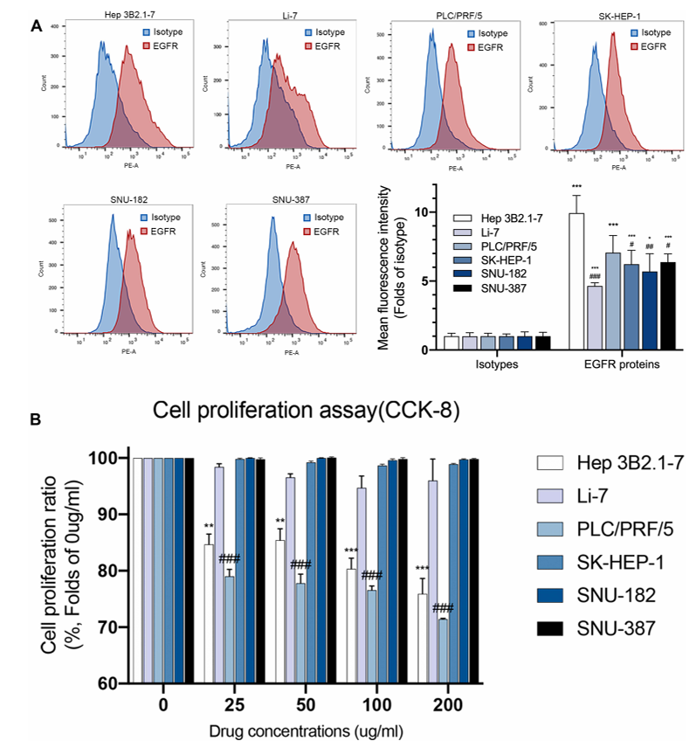
Wang et al. examined the efficacy of nimotuzumab and EGFR protein expression on the cell surface of six HCC cell lines (Hep 3B2.1-7, Li-7, PLC/PRF/5, SK-HEP-1, SNU-182, and SNU-387) by flow cytometry. Flow cytometry analysis (Fig. 2A) revealed that all six HCC cell lines expressed EGFR protein, and there were no significant differences among them. Hep 3B2.1-7 had the highest mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) value, and it was significantly higher than the MFI of other cell lines except PLC/PRF/5. PLC/PRF/5 expressed EGFR protein at a high level, and its MFI value was higher than that of the other four cell lines, but no significant difference was observed. The authors further evaluated the effect of nimotuzumab on HCC cell proliferation by CCK-8 assay. Cells were treated for 72 h with control or different concentrations of nimotuzumab. The results of the cell proliferation assay (Fig. 2B) indicated that nimotuzumab failed to inhibit cell proliferation of Li-7, SK-HEP-1, SNU-182, and SNU-387 cell lines. However, nimotuzumab inhibited the proliferation of Hep 3B2.1-7 and PLC/PRF/5 cell lines at all concentrations, and the corresponding proliferation rates were 75.92% and 71.43%, respectively, at 200 µg/mL of nimotuzumab. Although Hep 3B2.1-7 expressed EGFR protein at a high level, there was no significant difference in EGFR protein expression between PLC/PRF/5 and other resistant cell lines. Therefore, there was no obvious correlation between EGFR protein expression and nimotuzumab efficacy.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells