YSCCC
Cat.No.: CSC-C6606J
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Ascites Metastasis
Morphology: Lymphocyte-like
Culture Properties: Suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Shipping: Dry Ice, Frozen
The YSCCC cell line, a human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) cell line, is derived from a patient's bile duct. YSCCC cells are unique in that their cultured form consists of both adherent and suspended cells, indicating a thick and repulsive glycocalyx that interferes with cell-substrate interactions. This characteristic makes YSCCC a suitable model system to study glycocalyx-mediated immune evasion in CCA. YSCCC cells have been shown to be resistant to the chemotherapeutic drug gemcitabine, and have also been used to perform gene expression analyses in order to identify which genes can be used to predict resistance to this drug. The thick glycocalyx of YSCCC cells, characterized by high MUC1 expression, poses a barrier to immune cell recognition and effective immunotherapy. Research has demonstrated that treating YSCCC cells with mucin-degrading enzymes like StcE and SmE can significantly reduce MUC1 levels on the cell surface, thereby enhancing cell adhesion and spreading. In summary, the YSCCC cell line is a useful in vitro model for studying the molecular mechanisms underlying CCA, screening for new therapeutic agents, and developing new immunotherapies.
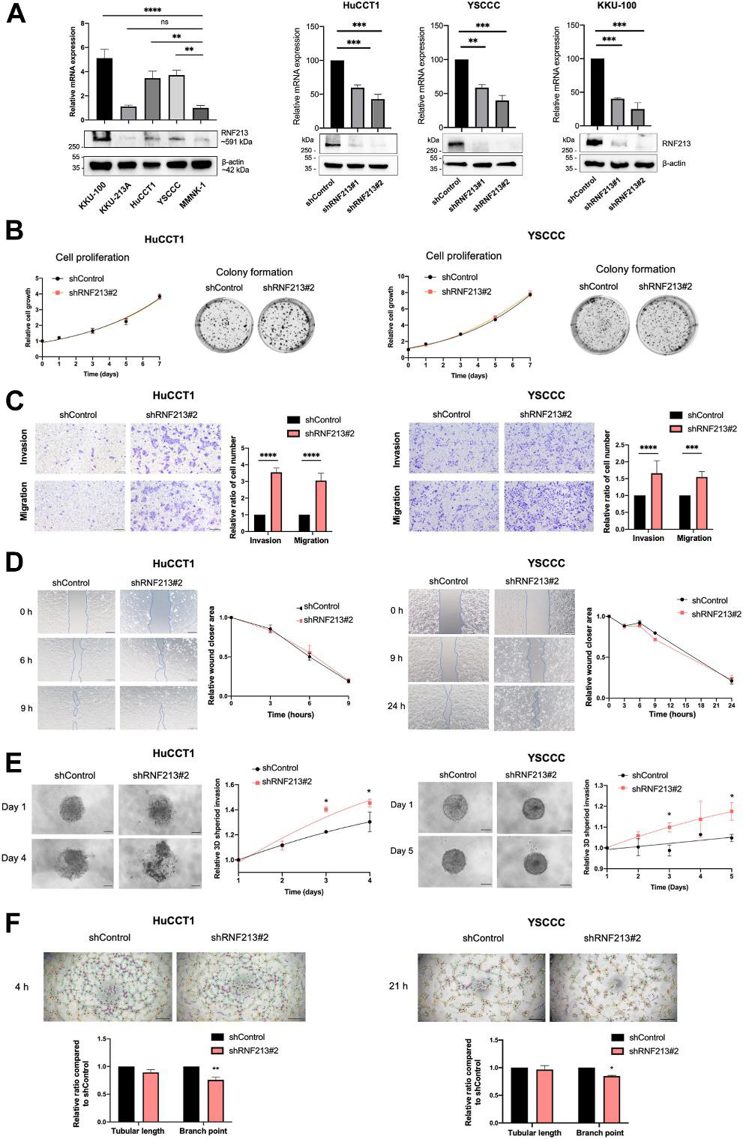
RNF213 Knockdown by shRNA Induces Cell Migration and Invasion in CCA Cell Lines
Intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct type (IPNB) is a rare subtype of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) in which cancer cells originate in the bile duct and then invade surrounding liver tissue, and therefore, is a suitable model for studying local invasion, the initial step of metastasis.
As shown in Fig. 1A, RNA-Seq data from the Human Protein Atlas database reveal that CCA cell lines have high RNF213 expression. RNA-Seq of 81 normal cell types indicates that cholangiocytes have moderate expression of RNF213, in the top one-third of all cell types. To investigate the role of RNF213 loss-of-function in ICC carcinogenesis, they first examined RNF213 expression and protein levels in CCA cell lines (KKU-100, KKU-213A, HuCCT1, YSCCC) and normal cholangiocytes (MMNK-1). RNF213 was significantly upregulated in KKU-100, HuCCT1, and YSCCC compared to MMNK-1 (Fig. 1A). Stable HuCCT1, YSCCC, and KKU-100 cells with shRNF213#1, shRNF213#2, and Control were generated using lentiviral transduction. shRNF213#2, which showed higher knockdown efficiency, was chosen for subsequent experiments (Fig. 1A). shRNF213#2 knockdown did not affect cell proliferation (Fig. 1B). The cell migration and invasion capacity of HuCCT1 and YSCCC were significantly increased upon shRNF213#2 knockdown (≥ 3.2- and ≥ 1.5-fold, respectively; Fig. 1C). No significant differences in wound closure rates were observed (Fig. 1D), but 3D spheroids of the shRNF213#2 knockdown group invaded Matrigel more than that of the control group (Fig. 1E). Last, shRNF213#2 knockdown significantly reduced branch point formations of tube-like structures in HuCCT1 and YSCCC cells (Fig. 1F).
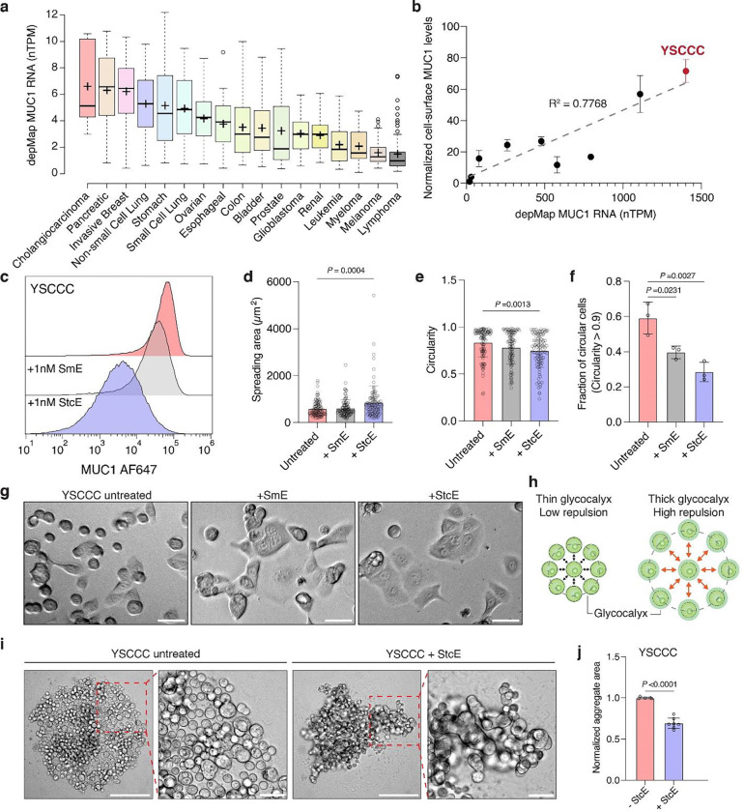
Cholangiocarcinoma Cell Line YSCCC Exhibits High MUC1 Surface Expression
The dense glycocalyx of cancer cells can hinder recognition by immune cells and effective immunotherapy. Park et al. profiled therapeutic agents that reduce the glycocalyx to aid anti-cancer immune responses, using Scanning Angle Interference Microscopy (SAIM). To this end, they developed a new membrane labeling strategy with leucine zipper pairs to define the glycocalyx boundary for its accurate measurement.
After establishing a method for membrane labeling, they surveyed various cancer cell lines to identify models for glycocalyx-mediated immune avoidance. Given that MUC1 levels are proportional to glycocalyx thickness, they queried DepMap data and determined that CCA has the highest MUC1 expression (Fig. 2a). Next, they measured MUC1 protein density on the cell surface using a MUC1-specific antibody and normalized the values to the SKBR3 cell line. Linear regression demonstrated high correlation between MUC1 protein and RNA expression (Fig. 2b). The YSCCC intrahepatic CCA cells had the highest MUC1 surface expression. The authors characterized the YSCCC cell line, which form both adherent and suspended cells in culture, which is indicative of a repulsive glycocalyx that prevents effective cell adhesion. To test this, they treated the YSCCC cells with low-dose mucin-digesting enzymes (StcE and SmE) overnight. Enzyme-treated cells had lower MUC1 levels (Fig. 2c) and increased adhesion and spreading compared to control cells (Fig. 2d-g), though SmE only showed a modest effect (Fig. 2e-g).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells