HO-1-u-1
Cat.No.: CSC-C6330J
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Salivary Gland
Morphology: epithelial-like
Culture Properties: Adherent cells
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Store in liquid nitrogen.
The HO-1-u-1 cell line is derived from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), a widespread malignant tumor that primarily occurs in the oral cavity, pharynx, larynx and skin of the neck region. The HO-1-u-1 cell line demonstrates classic squamous cell carcinoma characteristics by forming cellular clusters that resemble epithelial sheets under laboratory conditions. The cells exhibit tight junctions and microvilli-like features as well as multiple intercellular desmosomes.
HO-1-u-1 cell line serves as a common model for researchers testing permeability enhancers of lipophilic drugs in sublingual drug delivery studies. For example, scientific studies show that this cell line displays substantial reactions to different pH levels and osmotic pressures as well as penetration enhancers like sodium glycodeoxycholate making it an ideal model for sublingual drug delivery research. The HO-1-u-1 cell line displays squamous cell carcinoma properties making it a valuable resource to investigate gene expression and signaling pathways that are unique to squamous cell carcinoma. Studies indicate that the NFKB1 gene regulates HBp17/FGFBP1 expression via NF-κB signaling in this particular cell line. Additionally, researchers use the HO-1-u-1 cell line to evaluate the cytotoxicity of immunotoxins such as IT-Cmab and IT-Cetuximab. This particular cell line shows distinctive reactions to photodynamic therapy (PDT) and immunotoxins unlike any other HNSCC cell lines.
Cetuximab–Toxin Conjugate and NPe6 with Light Enhanced Cytotoxic Effects in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma In Vitro
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a cancer-targeted treatment that uses a photosensitizer (PS) and irradiation of a specific wavelength to exert cytotoxic effects. To enhance the antitumor effect against head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), Komatsu et al. developed a new phototherapy, intelligent targeted antibody phototherapy (iTAP). This treatment uses a combination of immunotoxin (IT) and a PS for PDT and light irradiation.
In this study, they newly investigate the iTAP targeting epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) which is widely used as a therapeutic target for HNSCC. First, Cmab and IT-Cmab showed dose-dependent cytotoxicity on SAS cells, which moderately express EGFR, with no significant difference in cytotoxicity between the two (p > 0.05) (Fig. 1a–d). The IC50 of IT-Cmab was about 0.07 nM in SAS (Fig. 1c). Both Cmab and IT-Cmab were ineffective in Sa3, HO-1-u-1, and HSQ-89 cells, likely due to insufficient internalization (Fig. 1a, b, d). Second, to enhance IT-Cmab's endosomal escape, they used NPe6 and its excitation wavelength to generate ROS, disrupting endosomes. The cytotoxicity of NPe6 varied among cell lines and with irradiation. No significant effect was observed in Sa3 (p > 0.05) (Fig. 2a), while significant differences appeared in HO-1-u-1 at 100 μM (p < 0.05) (Fig. 2b), SAS at 0.16 μM (p < 0.05) (Fig. 2c), and HSQ-89 at 20 and 100 μM (p < 0.05) (Fig. 2d). Maximum nonlethal NPe6 concentrations with irradiation were set at 20 μM for Sa3/HO-1-u-1, 0.8 μM for SAS, and 4 μM for HSQ-89 (Fig. 2a–d), which were used in subsequent assays.
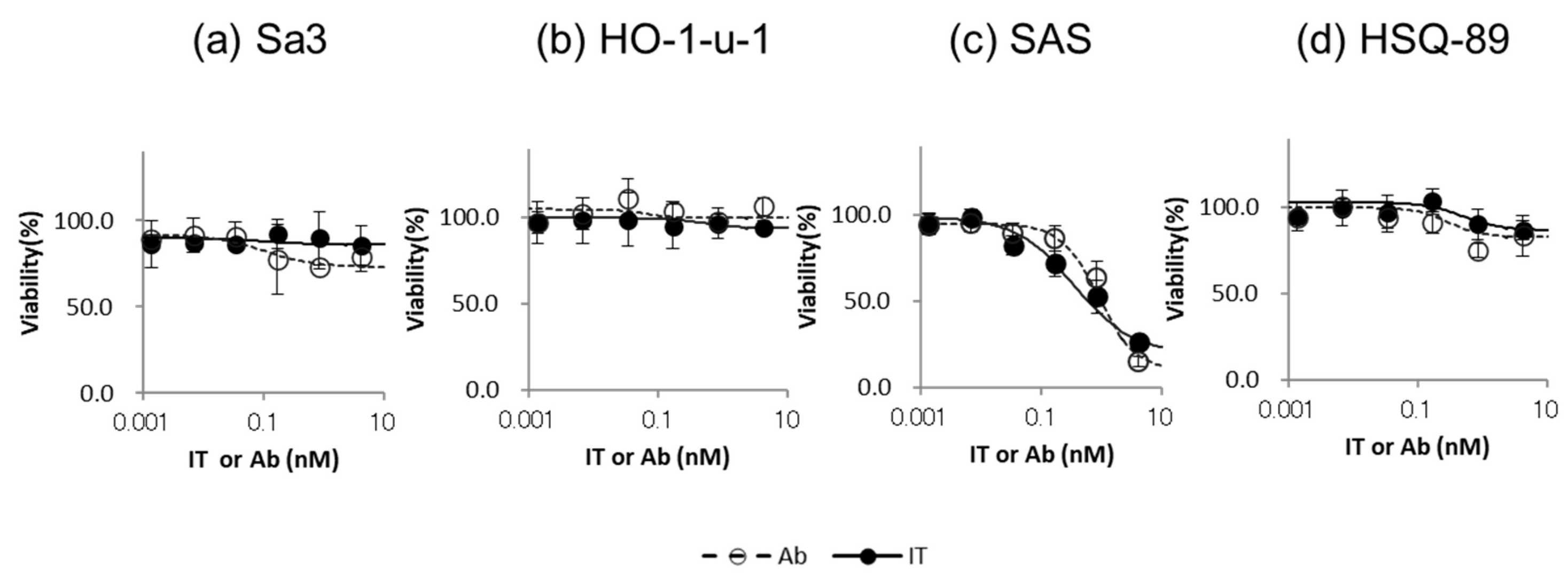 Fig. 1. Cytotoxicity of IT-Cmab or Cmab on each HNSCC cell line (Komatsu N, Kosai A, et al., 2024).
Fig. 1. Cytotoxicity of IT-Cmab or Cmab on each HNSCC cell line (Komatsu N, Kosai A, et al., 2024).
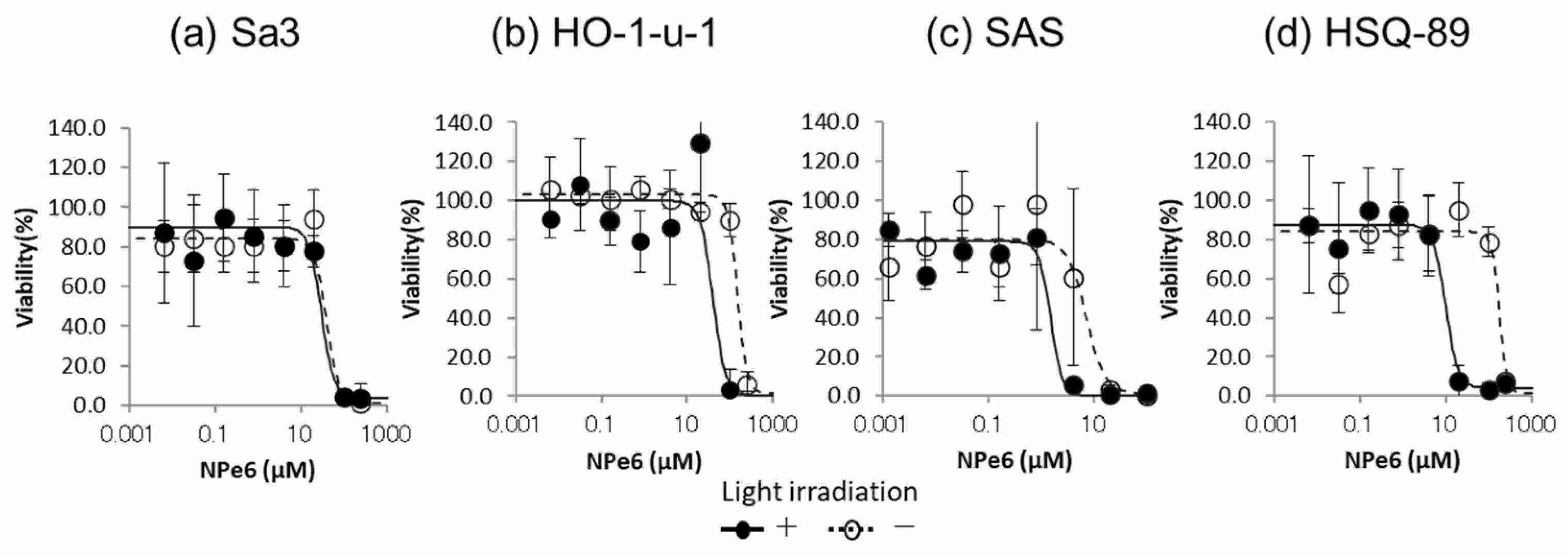 Fig. 2. Cytotoxicity of NPe6 and light irradiation on each HNSCC cell line (Komatsu N, Kosai A, et al., 2024).
Fig. 2. Cytotoxicity of NPe6 and light irradiation on each HNSCC cell line (Komatsu N, Kosai A, et al., 2024).
PTC124 Rescues Nonsense Mutation of Two Tumor Suppressor Genes NOTCH1 and FAT1 to Repress HNSCC Cell Proliferation
Nonsense mutations in tumor suppressor genes like NOTCH1 and FAT1 lead to premature stop codons, resulting in truncated, non-functional proteins. These mutations have a significant presence in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). PTC124 (Ataluren), a drug known to promote readthrough of such mutations, has potential in restoring the expression of these tumor suppressors. Wu's team explored the ability of PTC124 to rescue nonsense mutations in NOTCH1 and FAT1, thereby inhibiting HNSCC cell proliferation.
To test if PTC124 affects HES and YAP transactivation, they cloned firefly luciferase reporters with 2X NOTCH1/HES (CGTGGGAA) and 2X YAP1/TEAD (ACATTCCA) consensus sequences. Since PTC124 can stabilize luciferase, they washed cells three times before adding the lysis buffer to prevent interference. PTC124 activated the 2X NOTCH1/HES reporter in DOK cells (Fig. 3A) and repressed the 2X YAP1/TEAD reporter in HO-1-u-1 cells (Fig. 3B). PTC124's effect on growth inhibition in DOK cells was counteracted by the NOTCH inhibitor FLI-06 (Fig. 4A), while it reversed TT-10-driven growth in HO-1-u-1 cells (Fig. 4B). Therefore, PTC124 was able to rescue nonsense mutation of NOTCH1 and FAT1 to repress HNSCC cell proliferation.
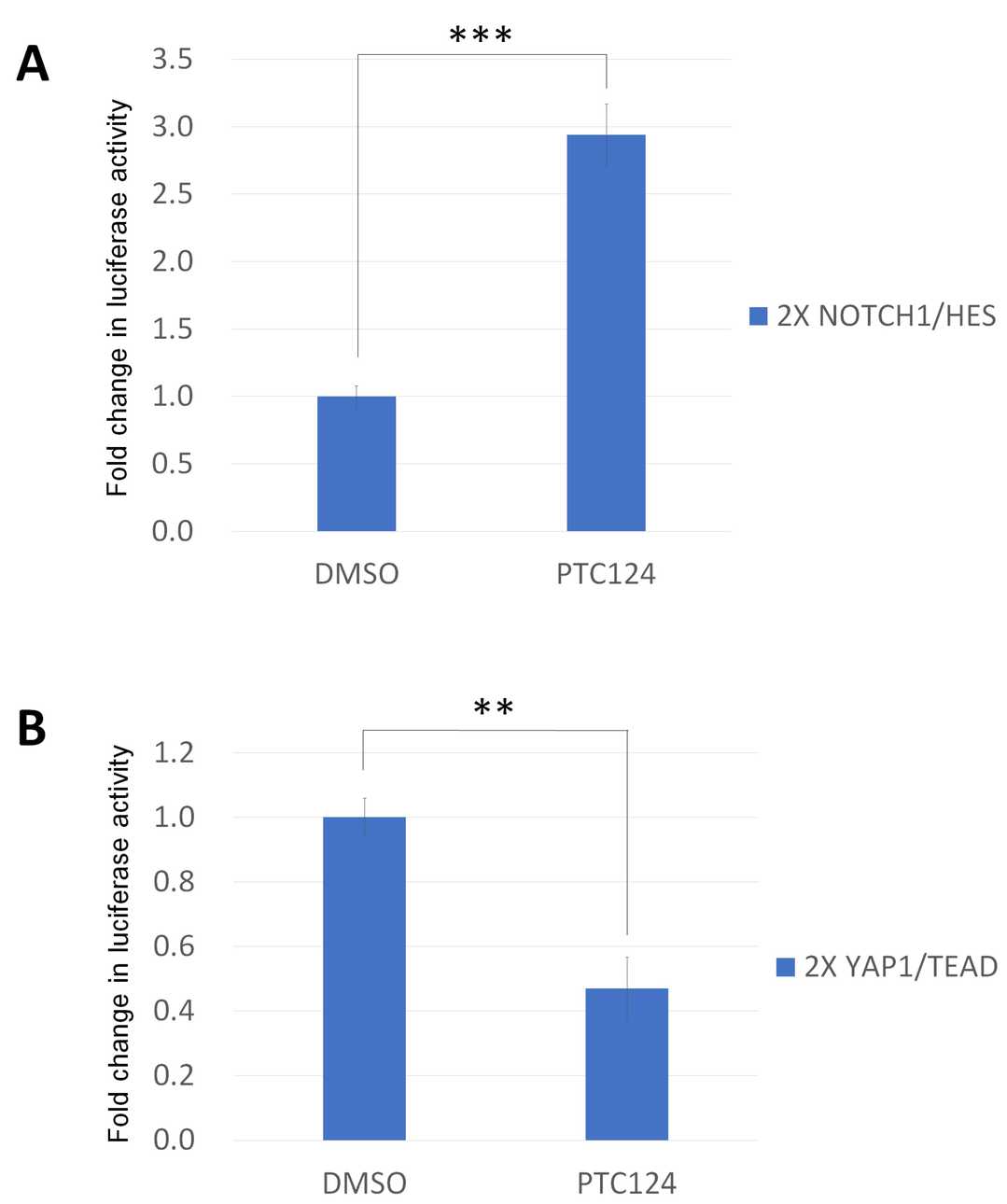 Fig. 3. PTC124 can moderate HES and TEAD transactivation function (Wu M-H, Lu R-Y, et al., 2022).
Fig. 3. PTC124 can moderate HES and TEAD transactivation function (Wu M-H, Lu R-Y, et al., 2022).
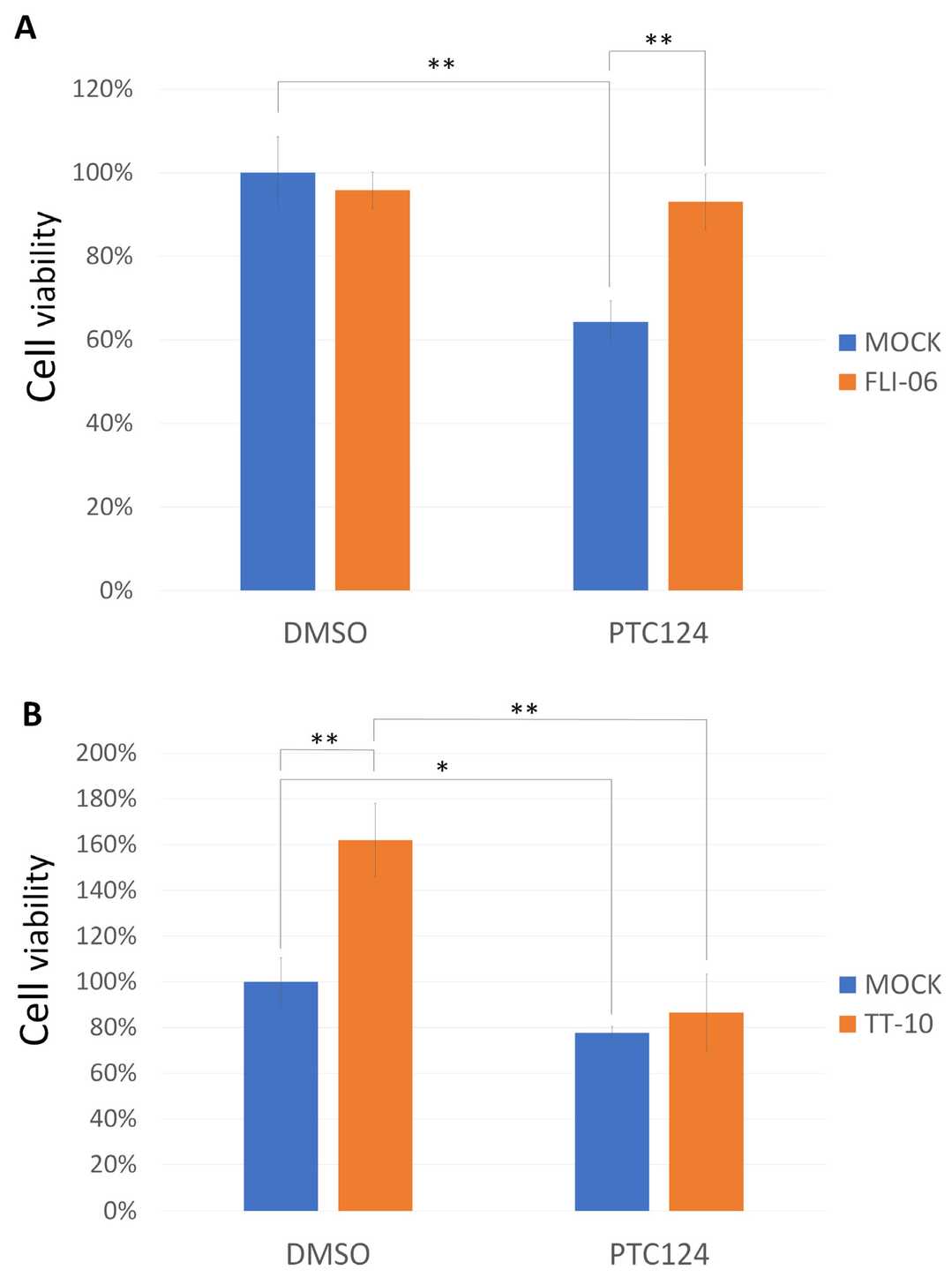 Fig. 4. PTC124 can control HNSCC cell growth in DOK and HO-1-u-1 cells (Wu M-H, Lu R-Y, et al., 2022).
Fig. 4. PTC124 can control HNSCC cell growth in DOK and HO-1-u-1 cells (Wu M-H, Lu R-Y, et al., 2022).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells