UM-SCC-14C
Cat.No.: CSC-C8961H
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Oral Cavity
Morphology: epithelial
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
CSF1PO: 10
D13S317: 12
D16S539: 12
D5S818: 11,14
D7S820: 9,10
THO1: 6,8
TPOX: 8
vWA: 14,18
D3S1358: 15
D21S11: 29
D18S51: 15
Penta E: 7
Penta D: 12,16
D8S1179: 8,13
FGA: 20,21
UM-SCC-14C is a human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) cell line originally derived from a recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity from a male patient. It is one of a set of HNSCC cell lines known as the University of Michigan Squamous Cell Carcinoma (UM-SCC) series that are commonly used to study the biological and molecular diversity of head and neck cancers.
Morphologically, UM-SCC-14C cells have an epithelial-like, polygonal appearance and are adherent, growing as a monolayer with strong cell-cell adhesion. The cells can be readily propagated and proliferate vigorously when maintained in standard culture conditions, usually DMEM containing fetal bovine serum. At the molecular level, UM-SCC-14C cells retain a number of key features of HNSCC, including alterations in tumor suppressor and cell cycle regulatory pathways that are common in oral squamous cell carcinoma. The cell line is commonly used to study signaling pathways in tumor progression, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and therapeutic resistance. The cells are also used as a model to study novel targeted therapies, radiosensitizers and combination treatment strategies for head and neck cancer.
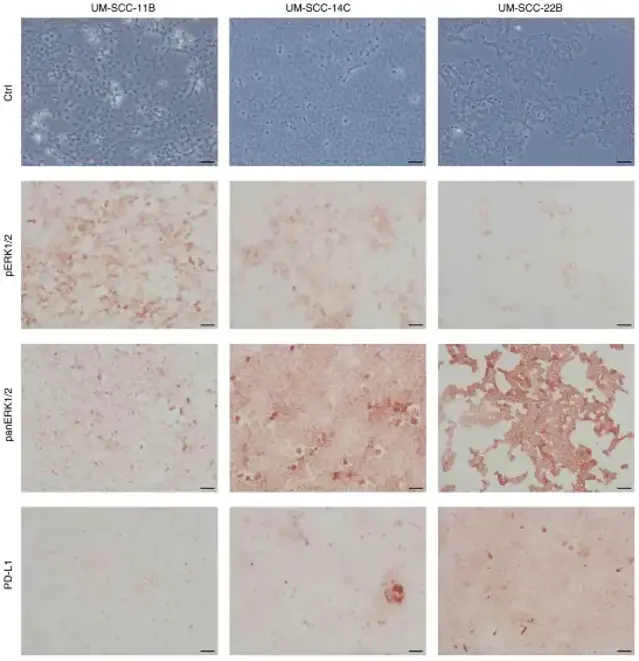
Modulation of PD‑L1 Expression by Standard Therapy in Head and Neck Cancer Cell Lines and Exosomes
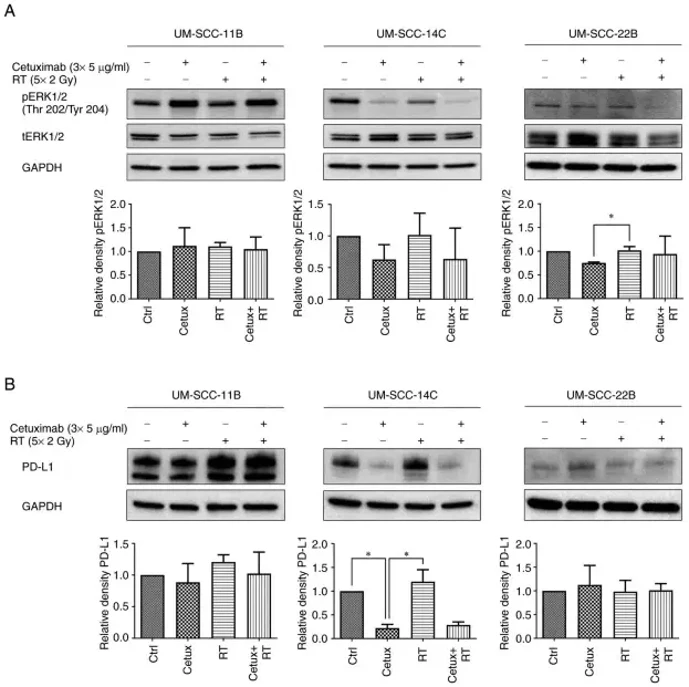
Checkpoint inhibitors (CPI) have offered a new therapeutic opportunity to patients with advanced HNSCC. However, the responses to CPIs are not yet fully predictable. PD-L1 is a key biomarker and target in immunotherapy and is expressed by tumor cells as well as exosomes, which suppress immune responses. Affolter et al. aimed to determine how PD-L1 expression is modulated by different standard therapies in HNSCC cell lines (UM-SCC-11B, UM-SCC-14C, UM-SCC-22B) and in their exosomes.
Immunohistochemistry revealed varied baseline expression levels of pERK1/2, panERK1/2, and PD-L1 across the three cell lines. UM-SCC-11B showed the highest pERK1/2 levels, while UM-SCC-22B had the highest PD-L1 and panERK1/2 levels (Fig. 1). The study adopted a fractionated radiotherapy (RT) scheme (5×2 Gy per week) with Cetux, mimicking clinical conditions. Cetux/EGFR blockade dramatically reduced basal pERK1/2 expression only in UM-SCC-14C, and to a lesser extent in UM-SCC-11B and UM-SCC-22B. In contrast, EGFR blockade did not prevent the post-radiogenic ERK1/2 activation in any cell lines, even though EGFR is a key component of the Ras-RAF-MEK-ERK pathway (Fig. 2).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells