U-373 MG
Cat.No.: CSC-C9745L
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Brain
Morphology: epithelial
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Tumorigenecity: Yes, in nude mice; Grade III astrocytomas are formed
Isoenzyme: PGM3,1;PGM1,1;ES-D,1;G6PD,B;AK-1,1;GLO-1,1
Histopathology: glioblastoma; astrocytoma
vWA: 16,18
FGA: 21,25
Amelogenin: X,Y
TH01: 9.3
TPOX: 8
CSF1P0: 11,12
D5S818: 11,12
D13S317: 10,11
D7S820: 10,12
Shipping Condition: Room Temperature
U-373 MG is a human astrocytoma-derived cell line and one of the most commonly used models of high-grade glioma in vitro. The cell line was originally reported to have been derived from the malignant astrocytoma of a 61-year-old female patient, but many commercially available stocks of U-373 MG cells were later found to be actually closely related to or actually derived from the U-251 MG cell line. In any case, U-373 MG cells have the typical biology and molecular features of malignant astrocytomas, with morphologically typical adherent growth of heterogeneous populations of polygonal or spindle tumor cells with hyperchromatic, prominent nuclei, and abundant, pale cytoplasm. In particular, U-373 MG cells retain high expression of astrocytic markers like GFAP and S100β, and also frequently display dysregulated signaling pathways commonly implicated in glioma biology like NF-κB, JAK/STAT, PI3K/AKT, and MAPK/ERK.
Functionally, U-373 MG cells have been reported to have high invasiveness, increased cytokine secretion, increased apoptosis resistance, and moderate chemoradiation resistance, making it particularly useful for recapitulating these properties in vitro. In particular, because U-373 MG cells are highly responsive to inflammatory stimuli and secrete cytokines like IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1, they have been used as an in vitro model of neuroinflammation. In general, U-373 MG cells are used for a variety of applications, like modeling glioma biology, screening drug efficacy, studying signaling pathways, and CRISPR-mediated genetic perturbations or RNA interference.
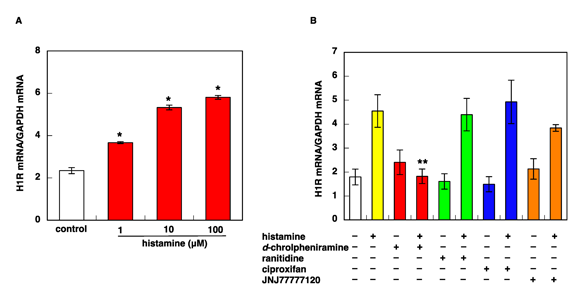
Histamine-Induced Upregulation of H1R Gene Expression is Mediated by H1R Activation, and PKCα Is Involved in its Signaling Pathway in U-373 MG Cells
The histamine H1 receptor (H1R) is a histamine target in the nervous system and peripheral tissues. Protein kinase Cδ (PKCδ) signaling plays a role in histamine-induced H1R gene upregulation in HeLa cells. Histamine also upregulates H1R gene expression in U-373 MG cells, but the underlying molecular signaling remains unclear.
Mizuguchi et al. previously reported that histamine upregulates H1R gene expression via H1R activation, and that PKCδ/Hsp90/ERK signaling was involved. In this study, histamine upregulated H1R gene expression in a dose-dependent manner in U-373 MG cells (Fig. 1A). This upregulation was inhibited by the H1R antagonist d-chlorpheniramine but not by H2R, H3R, or H4R antagonists (Fig. 1B). This indicates that histamine-induced H1R gene upregulation in U-373 MG cells is H1R-mediated, similar to HeLa cells. Histamine-induced H1R gene upregulation was suppressed by the pan-PKC inhibitor Ro-31-8220. H1R exists in an equilibrium between active and inactive forms, with constitutive signaling even without histamine. Ro-31-8220 (10 μM) suppressed H1R gene upregulation below control levels, indicating inhibition of H1R's constitutive activity, with PKC signaling as the primary pathway for H1R-activated H1R gene expression in U-373 MG cells. PKCα/βI inhibitor Go6976 also suppressed the histamine-induced H1R gene upregulation. Because 10 μM Go6976 had the same effect as 1 μM, 1 μM is enough to inhibit H1R gene expression. The PKCβ inhibitor Ly333531 (10 μM) showed no inhibition, consistent with the report that U-373 MG cells do not express PKCβ. Therefore, the effect of Go6976 is due to PKCα inhibition. The fact that 10 μM Go6976 could not show further suppression implies that the other PKC isoforms is involved in U-373 MG cells.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells