OCI-Ly18
Cat.No.: CSC-C9228W
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Pleural Effusion
Morphology: small round cells
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
The OCI-Ly18 cell line is a well-characterized human B-cell lymphoma model, derived from a patient with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). It is classified within the activated B-cell-like (ABC) subtype, a molecular category associated with a poorer prognosis compared to the germinal center B-cell-like (GCB) subtype. This classification is functionally defined by its constitutive activation of the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway, a key driver of cell survival, proliferation, and resistance to apoptosis.
OCI-Ly18 harbors the genetic hallmarks of ABC-DLBCL, most notably a recurring mutation in the CD79B immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) and frequent co-occurrence of a mutation in the MYD88 adaptor protein (L265P variant). These mutations synergistically drive chronic active B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling and Toll-like receptor signaling, respectively, which converge to activate NF-κB. This makes OCI-Ly18 a genetically faithful in vitro representation of a clinically aggressive lymphoma subtype.
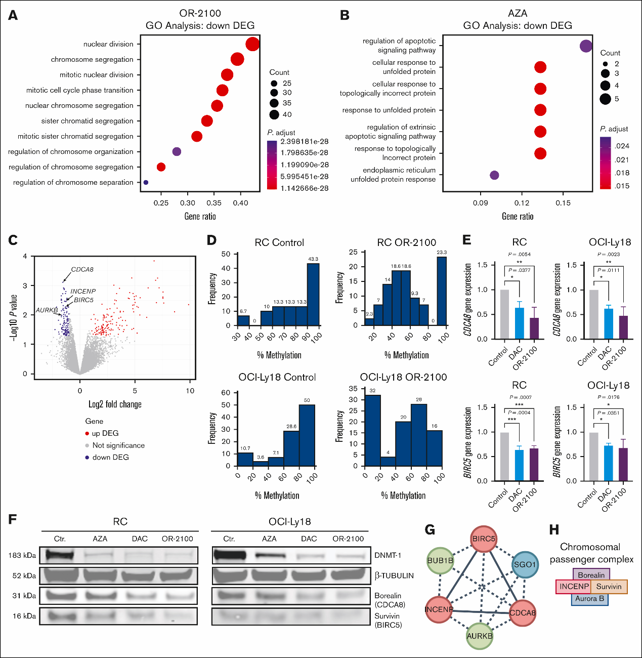
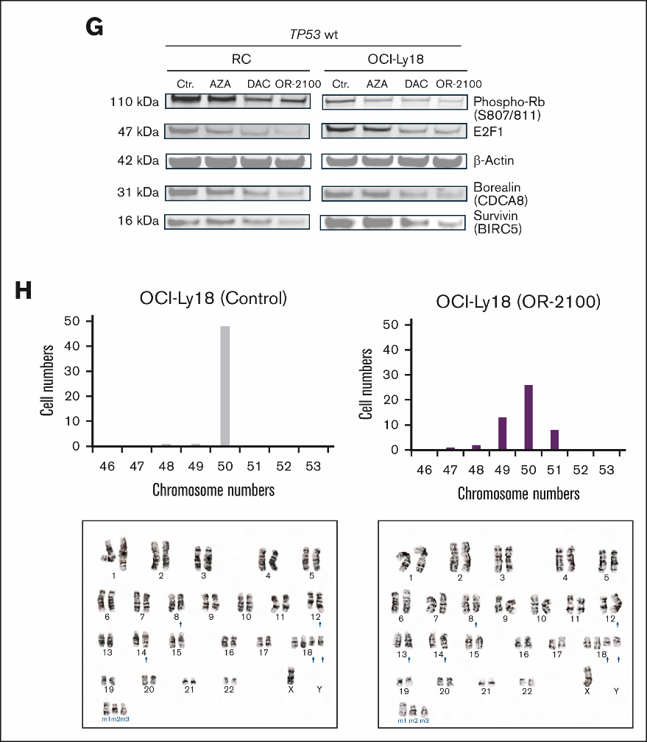
Decitabine Prodrug OR-2100 Induces Mitotic Perturbation for The Treatment of Double-Hit Lymphoma
Double-hit lymphoma (DHL), an aggressive B-cell lymphoma with a poor prognosis, harbors rearrangements of MYC and BCL2. The standard chemoimmunotherapy comprising R-CHOP (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) yields an unsatisfactory treatment response.
Hypomethylating agents increase the susceptibility to malignant lymphoma via the restoration of tumor suppressor genes. Decitabine not only inhibits DNA methylation but also causes mitotic disruption, which leads to antileukemia effects through the covalent binding of DNA methyltransferase 1 to DNA. Here, we investigated the efficacy and underlying mechanism of a decitabine prodrug (OR-2100) for the treatment of DHL.
OR-2100 alone or in combination with key anti-lymphoma drugs, including doxorubicin and vincristine, suppressed the in vitro proliferation of DHL cell lines, particularly those with wild-type TP53. OR-2100 induced downregulation of CDCA8 and BIRC5 (baculoviral IAP [inhibitor of apoptosis] repeat-containing 5), the knockdown of which suppressed the proliferation of DHL cell lines. Both OR-2100 treatment and CDCA8 knockdown led to mitotic perturbation, suggesting that the disruption of mitosis may underlie the antitumor mechanism of OR-2100 given that the efficacy of OR-2100 was dependent on the TP53 status and that CDCA8 and BIRC5 are downstream targets of the E2F1 pathway.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells