OCI-LY-19
Cat.No.: CSC-C9229W
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Bone Marrow
Morphology: single round cells
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
The OCI-LY-19 cell line is a valuable model system for studying diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), a common and aggressive subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). This cell line was established in 1987 from the bone marrow of a 27-year-old woman with stage 4B DLBCL, at the time of relapse.
The availability of the OCI-LY-19 cell line has provided researchers with a valuable tool to investigate the molecular and cellular characteristics of DLBCL. As a model system derived from a patient at relapse, the OCI-LY-19 cells offer insights into the pathways and genetic alterations that may contribute to disease progression and treatment resistance. Researchers have utilized this cell line to elucidate key signaling cascades, identify potential therapeutic targets, and explore novel treatment approaches for DLBCL.
Combinations With BET Inhibitors and LRRK2 as a Novel Putative Target in Lymphoma
Inhibitors of the Bromo- and Extra-Terminal domain (BET) family proteins have strong preclinical antitumor activity in multiple tumor models, including lymphomas. The combination between LRRK2-IN-1 and birabresib was also evaluated using the efficacy and potency parameter (CIT) according to the MuSyC algorithm, showing additivity in efficacy and between additivity and synergism in the potency parameter in all the cell lines tested.
To uncover the importance of LRRK2 protein in the growth of GCB DLBCL cell lines (OCI-LY-19 and WSU-DLCL2), a silencing of LRRK2 by siRNAs was performed. LRRK2 silencing affected the cell growth causing a reduction in cell growth after 48 h of silencing (Fig. 1A-C). Total and phosphorylated GSK3β and AKT proteins were analyzed, due to their possible association with the function of LRRK2. LRRK2 silencing led to a downregulation of p-AKT (S473) and p-GSK3β (S9) levels (Fig. 2). The effect on cell proliferation after LRRK2 silencing was increased when LRRK2 siRNAs were combined with the BET inhibitor birabresib. There was a beneficial effect on the proliferation between LRRK2 silencing and birabresib treatment in OCI-LY-19 (48 h) (Fig. 2A). LRRK2 silencing was performed with four individual siRNAs present in the pool. A consistent reduction of proliferation compared to control siRNAs was increased when combined with birabresib (Fig. 2D).
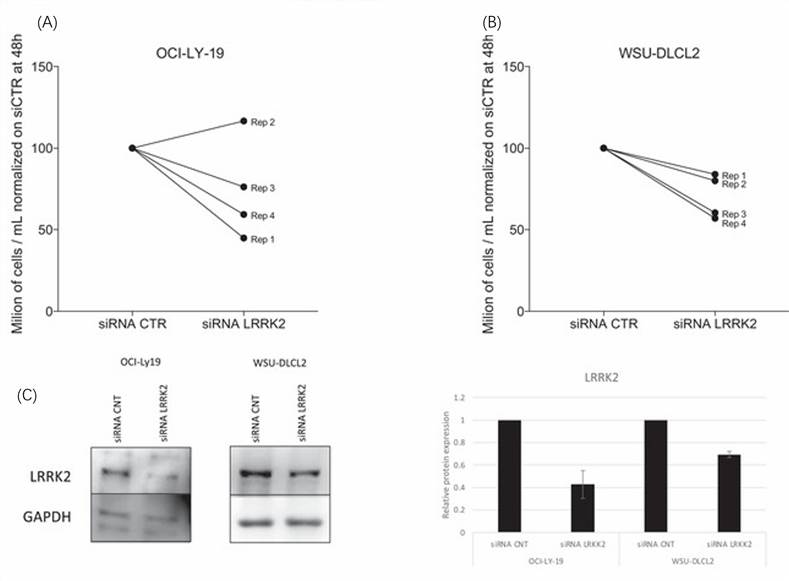 Fig. 1 LRRK2 is important for lymphoma cell lines (OCI-LY-19 and WSU-DLCL2). (Spriano F, et al., 2022)
Fig. 1 LRRK2 is important for lymphoma cell lines (OCI-LY-19 and WSU-DLCL2). (Spriano F, et al., 2022)
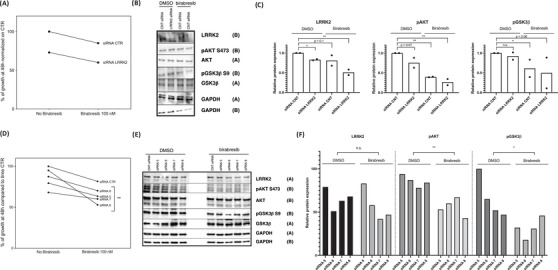 Fig. 2 Birabresib improves the LRRK2 silencing effect in OCI-LY-19. (Spriano F, et al., 2022)
Fig. 2 Birabresib improves the LRRK2 silencing effect in OCI-LY-19. (Spriano F, et al., 2022)
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells