NRK-52E
Cat.No.: CSC-C2041
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Source: Kidney
Morphology: adherent epithelial-like cells growing as monolayers
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Cell type: kidney epithelial-like cells
Origin: cell line was cloned from a mixed culture of normal rat kidney cells as was NRK-49F; the two cell lines were described to be distinct in growth properties and in transforming abilities; NRK-52E is supposed to be much more stable
NRK-52E cells are an epithelial cell line, originally isolated from the proximal tubule of a rat kidney. NRK-52E cells are often used in renal studies as a model of normal kidney function. Cells are polygonal and cobblestone in appearance, and grow as an adherent monolayer in normal media. As NRK-52E cells originate from the reabsorptive portion of the nephron, they maintain many functional attributes such as electrolyte transport, hormone responsiveness and xenobiotic metabolism. This makes them a model of renal physiology which is used in a variety of different research and pharmacological studies to determine the effects of substances on kidney cells.
NRK-52E cells are often used in experiments to test for nephrotoxicity, drug metabolism and models of disease in the kidney, as they are a good representation of normal kidney cell morphology and are a robust cell line to work with. They are also used to study renal disease mechanisms such as fibrosis and oxidative stress. As they can be infected by certain viruses (such as hantaviruses) they are also used in virology studies. The cell line can also be used in toxicology screenings, such as the nephrotoxic effects of cisplatin on the kidney, as well as analyses of different molecular pathways. NRK-52E cells were first isolated in the 1970s, but are still used to this day as a gold-standard in vitro model as they grow well, are easy to culture and maintain, and display many features associated with renal epithelial cells.
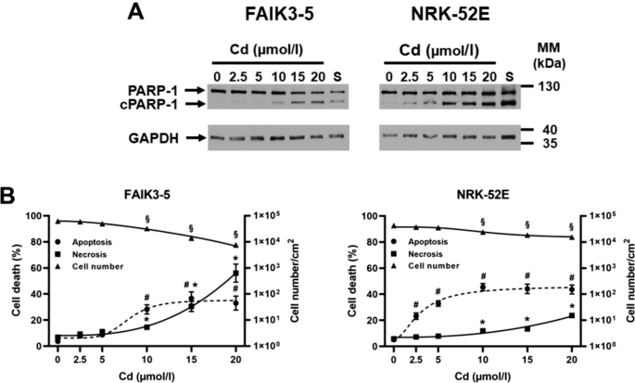
FAIK3-5 Cells Die Mostly by Necrosis at High Cd Concentrations Whereas NRK-52E Cells Die by Apoptosis at All Cd Concentrations Tested
Cadmium (Cd) disrupts renal hypoxia-PHD-HIFα (HPH) signaling and promotes chronic kidney disease (CKD), yet its molecular impact on renal cells remains unclear. Schreiber et al. examined how Cd interferes with HPH signaling in two kidney-derived cell lines and tests whether hypoxic preconditioning can mitigate Cd toxicity. Using NRK-52E proximal-tubule and FAIK3-5 EPO-producing renal cells, they exposed them to Cd²⁺ (2.5-20 µM) under chemical (DMOG) or hypoxic (1% O₂) HPH activation.
To determine Cd toxicity, both apoptosis and necrosis were investigated. Apoptosis was measured by immunoblotting for PARP-1 cleavage and quantifying the ratio of cleaved PARP-1 over total PARP-1, while necrosis was measured by quantifying trypan blue uptake. As shown in Figure 1, after 24 h of Cd exposure, the cell lines behaved differently. FAIK3-5 cells were insensitive to <5 µM Cd, died mainly by necrosis at 15-20 µM Cd (~60%), and ~30% died by apoptosis at 10-20 µM Cd. In contrast, NRK-52E cells showed increased apoptosis (about 30%) at 2.5-5 µM Cd, which remained elevated (~40%) up to the highest Cd concentration tested, consistent with previous studies. Trypan blue uptake was elevated at 20 µM Cd but was still ~100-fold lower than in FAIK3-5 cells, also reflected by more live NRK-52E cells at 20 µM Cd. In summary, both cell lines are sensitive to Cd, but FAIK3-5 cells mainly die by necrosis at high Cd concentrations, while NRK-52E cells largely die by apoptosis at all tested Cd concentrations.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells