NMB
Cat.No.: CSC-C0639
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Bone Marrow Metastasis
Morphology: polymorphic cells (mostly epithelial with short neurites) growing adherently in monolayers
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin -, cytokeratin-7 -, cytokeratin-8 -, cytokeratin-17 -, cytokeratin-18 -, desmin -, endothel -, EpCAM -, GFAP
NMB refers to an established cell line that is typically used for experimentation. Originating from a neuroectodermal tumor, NMB cells are thought to be a neuroblastoma cell line for the most part. NMB has been used in cancer biology and neuroscience studies. NMB cells grow and behave in a consistent manner when maintained in typical cell culture conditions. As with most tumor cell lines, they can proliferate indefinitely and are useful for experimentation that spans longer time periods or requires understanding of mechanism. Morphologically, NMB cells usually resemble typical neuroblastoma cells in that they will grow as adherent cells with a polygonal shape. Depending on how they are maintained, they can take on an elongated phenotype as well. Molecularly, NMB cells express proteins related to neuronal development as well as proteins involved in promoting cell growth typical of cancer cells. This allows them to be used to study neural differentiation as well as mechanisms of transformation and apoptosis. NMB cells will react to certain growth factors, stress signals and pharmacological agents in a reproducible fashion allowing for pathway elucidation. Because of this, NMB cells have been used to study tumor cell growth, apoptosis, migration and signal transduction. This cell line can also be used to screen for potential cancer therapeutic agents, study drug resistance as well as for basic transfection or gene silencing experiments.
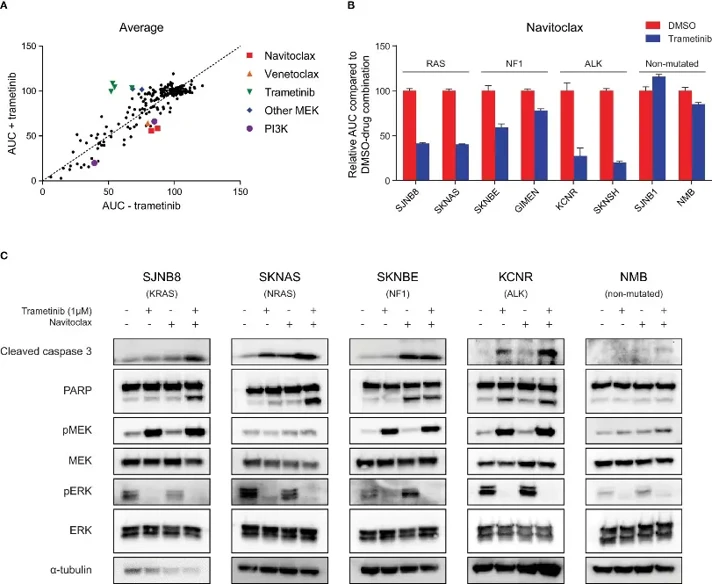
Combination of Trametinib with Navitoclax Enhances Apoptosis in RAS-MAPK-Mutated Cell Lines
Neuroblastoma is a pediatric tumor with variable prognosis. Relapsed tumors often have mutations in the RAS-MAPK pathway and are sensitive to MEK inhibitors in vitro, but these inhibitors alone do not lead to tumor regression in vivo. Eleveld et al. investigated the potential of combining MEK inhibitors with BCL-2 family inhibitors to improve therapeutic outcomes for neuroblastoma patients with RAS-MAPK mutations.
MEK inhibition typically reduces pERK and increases pMEK due to feedback loops. Trametinib, a MEK inhibitor, effectively decreased pERK in neuroblastoma cell lines, confirming on-target activity (Fig. 1C). However, increased levels of pMEK were observed with trametinib treatment in all cell lines except for NRAS-mutant SKNAS cells and wildtype NMB cells. Trametinib did not significantly kill RAS-MAPK-mutated neuroblastoma cells and mostly caused a plateau at higher concentrations. Treatment of trametinib with navitoclax significantly increased apoptosis. This was demonstrated by increased levels of cleaved caspase 3 and cleaved PARP (Fig. 1C). Bliss independence scores were calculated and showed synergy. Average bliss scores were 0.33 for RAS-mutated lines, 0.15 for NF1-mutated lines, and 0.34 for ALK-mutated lines. As controls, wildtype cell lines were used as they lack mutations in the RAS-MAPK pathway. Cell viability had no change with no cleaved caspase 3 or PARP detected and had a bliss score of 0.08 (Fig. 1C). This demonstrates that this combination is working better in cells with increased activity of the RAS-MAPK pathway.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells