- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Histopathology: adenocarcinoma, tubular
Differentiation: moderately differentiated
Note: Mycoplasma-eliminated cells by MC-210
vWA: 16,20
FGA: 23
Amelogenin: X
TH01: 6
TPOX: 8,11
CSF1P0: 12
D5S818: 11
D13S317: 11
D7S820: 9
Shipping Condition: Room Temperature
MKN-28 cell line was isolated from a 70-year-old female's tumor tissue with gastric cancer. Studies have shown that MKN-28 cell line had a strong proliferation in vitro, and the side population (SP) cells from MKN-28 showed a higher proliferation and colony forming potential, suggesting the stemness of SP cells. Also, MKN-28 cells had a high proliferative activity and migratory potential under in vitro culture condition.
The MKN-28 cell line is commonly used to evaluate the cytotoxic effects of drugs on gastric cancer cells, such as studies on the cytotoxicity and apoptosis-inducing effects of paclitaxel and oxaliplatin. They also widely used to study various signaling pathway in gastric cancer such as mTOR, PI3K/AKT and RASSF1A signaling pathways. In addition, MKN-28 cells were used to study the role of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), microRNAs (miRNAs) and other regulators in gastric cancer.
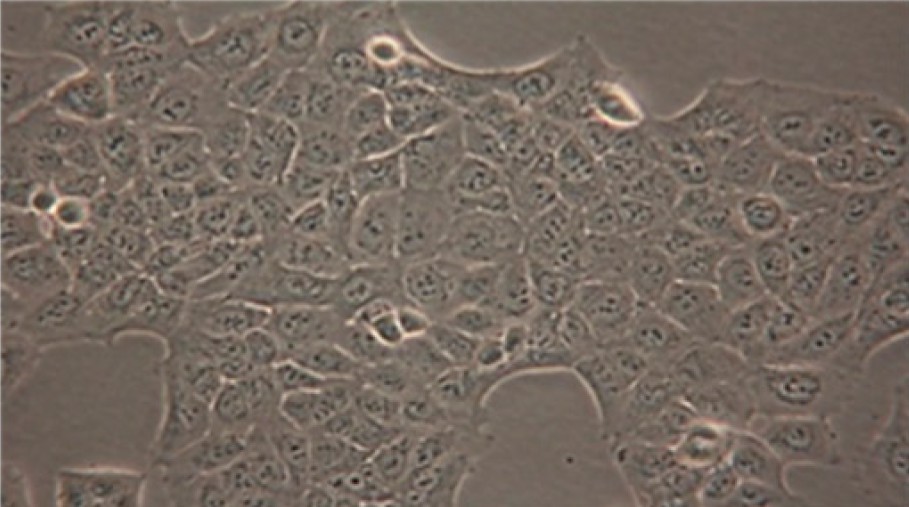 Fig. 1. Morphology of MKN28 cells under light microscopy (×400) (Lee HJ, Venkatarame Gowda Saralamma V, et al., 2018).
Fig. 1. Morphology of MKN28 cells under light microscopy (×400) (Lee HJ, Venkatarame Gowda Saralamma V, et al., 2018).
Response to CDDP-Induced Cell Death in Both Parental and CDDP-Resistant GC Cell Lines
Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the most common causes of cancer-related death in the world and cisplatin (CDDP) is one of the important chemotherapeutic agents. CDDP resistance is the major challenge that dramatically decreases the chemotherapeutic efficiency and patient survival rate of advanced GC. Therefore, Mora-Lagos et al. aimed to develop and characterize CDDP-resistant GC cell lines (AGS R-CDDP and MKN-28 R-CDDP) by stepwise drug selection and investigate the underlying molecular mechanism of CDDP chemoresistance to identify novel chemotherapeutic targets.
As shown in Fig 1, flow cytometry data (annexin V/PI staining) showed significantly lower cell death rate in CDDP-resistant cells than that in parental cell lines. Cell death rate of AGS R-CDDP was 14.5% in comparison to 47.5% in AGS cells (Fig 1A). AGS R-CDDP cells exhibited lower live cell population compared to that of AGS cells (Fig 1B vs. 1C). The representative controls are in Fig 1D (AGS WT) and 1E (AGS R-CDDP). Cell death rate of MKN-28 R-CDDP was 40.8% in comparison to 59.2% in parental cells (P<0.01; Fig 1F). MKN-28 R-CDDP cells also showed lower live cell population compared to that of MKN-28 cells (Fig 1G vs. 1H). The representative controls are in Fig 1I (MKN-28 WT) and 2J (MKN-28 R-CDDP).
 Fig. 1. Cell death analysis through flow cytometry with annexin-V and PI) staining of AGS and MKN28 cells treated with cisplatin (Mora-Lagos B, Cartas-Espinel I, et al., 2020).
Fig. 1. Cell death analysis through flow cytometry with annexin-V and PI) staining of AGS and MKN28 cells treated with cisplatin (Mora-Lagos B, Cartas-Espinel I, et al., 2020).
MSLN-CAR NK Cells Specifically Targeted MSLN-Positive Cancer Cell Lines In Vitro
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) NK cell therapy faces challenges in solid tumors due to limited tumor-specific targets and low efficacy. Mesothelin (MSLN) has been considered as a candidate target for gastric cancer immunotherapy. However, the anti-tumor activity of anti-MSLN CAR NK cells has not been investigated. In this study, Cao's team engineered and characterized MSLN-targeted CAR NK-92 cells (MSLN-CAR NK) for their cytotoxic potential to specifically target MSLN-positive gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo.
First, to test the cytotoxicity of CAR NK cells, they generated luciferase/GFP-labeled gastric cancer cell lines (N87 GL, MKN-28 GL, AGS GL, Huh-7 GL; Fig. 2A). In 6-hour killing assays, MSLN-CAR NK cells displayed significantly stronger cytotoxic activity against MSLN-positive (N87 GL, MKN-28 GL, AGS GL) compared to CD19-CAR NK or parental NK-92 cells at high effector:target ratios. This effect was not observed in MSLN-negative Huh-7 GL cells (Fig. 2B). ELISA analysis further demonstrated that MSLN-CAR NK cells secreted increased amounts of IFN-γ, GM-CSF, Granzyme B and perforin when co-cultured with MSLN-positive gastric cancer cells, which was consistent with the qPCR data. The target-dependent degranulation and cytokine production observed were not observed in control cells (Fig. 2C). Taken together, these data show that MSLN-CAR NK cells have the potential to specifically kill MSLN-expressing gastric cancer cells.
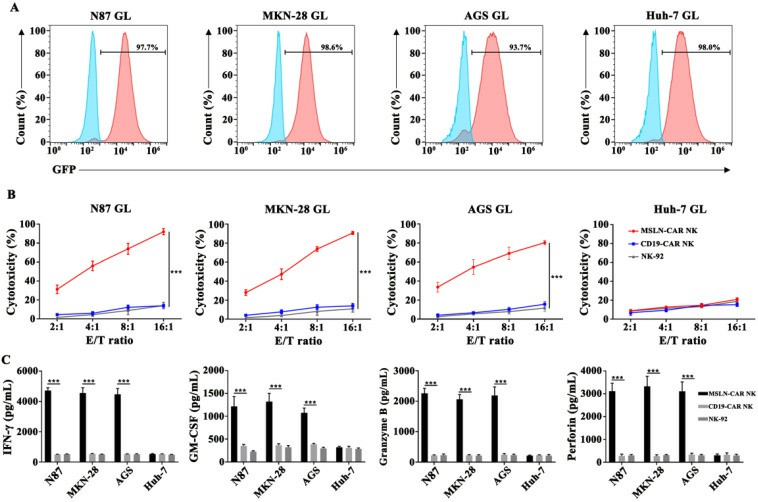 Fig. 2. MSLN-CAR NK cells showed strong antitumor activity against MSLN-positive gastric cancer cell lines in vitro (Cao B H, Liu M T, et al., 2021).
Fig. 2. MSLN-CAR NK cells showed strong antitumor activity against MSLN-positive gastric cancer cell lines in vitro (Cao B H, Liu M T, et al., 2021).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells