MKN-7
Cat.No.: CSC-C6250J
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Lymph Node Metastasis
Morphology: epithelial-like
Culture Properties: Adherent cells
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Store in liquid nitrogen.
MKN-7 cell line is a well-characterized human gastric carcinoma cell line established from a well-differentiated tubular adenocarcinoma. This cell line is part of a broader panel of gastric cancer cell lines that have been developed to study various histological and biological behaviors of gastric cancer.
MKN-7 cells are known to exhibit morphological features indicative of intestinal differentiation, such as cell polarity and the presence of microvilli with core filaments. These features are generally observed in both in vitro cultures and in xenografts in nude mice, although the degree of differentiation may diminish over time with prolonged culture conditions. In terms of functional characteristics, MKN-7 cells exhibit low fibrinolytic activity, which is primarily dependent to plasminogen. This activity is significantly lower compared to other gastric cancer cell lines, such as MKN-1 and MKN-28, which have higher fibrinolytic activities. The low fibrinolytic activity of MKN-7 cells may be relevant to studying the role of fibrinolysis in cancer progression, particularly with respect to the invasive and metastatic potential of gastric tumors. In addition, the MKN-7 cell line, as well as other gastric cancer cell lines, has been used in studies examining thromboplastic activity, although MKN-7 is noted for its relatively low levels of this activity as well. This suggests a more limited role in the hypercoagulable states often associated with the aggressive tumor phenotype.
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Entinostat Mediates HER2 Downregulation in Gastric Cancer
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) inhibition represents a therapeutic approach with proven clinical efficacy in gastric cancer. However, resistance against HER2-directed therapeutics highlights the need for alternative approaches or drug combinations. Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) display a broad spectrum of antitumor properties, which may include effects on receptor tyrosine kinases. We describe the downregulation of HER2 in gastric carcinoma cells upon HDACi treatment. Concomitantly, cells with high basal or treatment-induced HER2 expression showed most profound sensitivities towards HDACi. These findings may thus provide the basis for HDACi treatment as a therapeutic option particularly valuable in HER2-amplified gastric cancer and particularly useful in combination therapies with HER2 inhibitors.
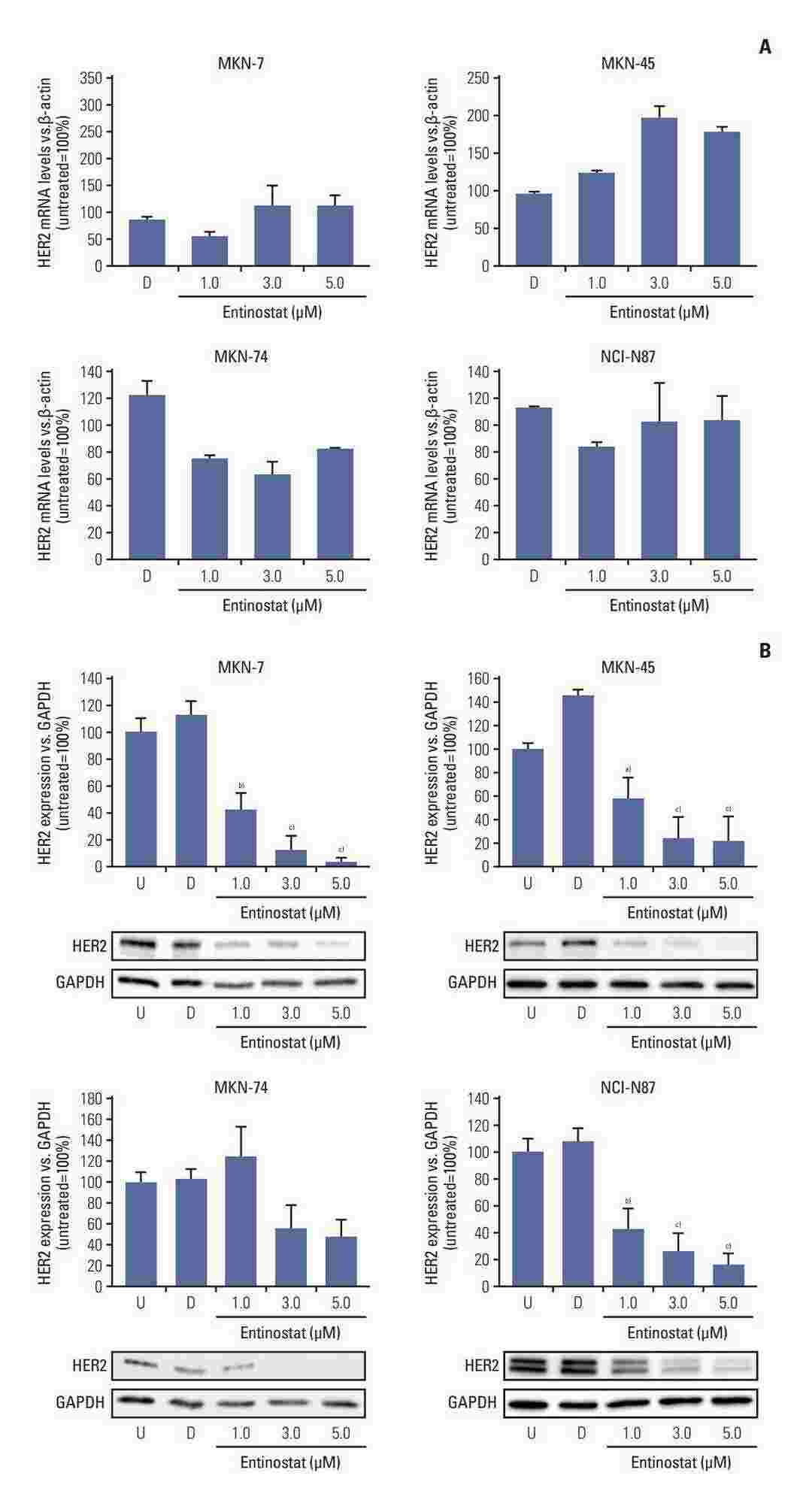 Fig. 1. Effect of entinostat treatment on HER2 mRNA levels and HER2 protein expression in NCI-N87, MKN-7, MKN-74, and MKN-45 cells (Zenz, Tamara, et al. 2024).
Fig. 1. Effect of entinostat treatment on HER2 mRNA levels and HER2 protein expression in NCI-N87, MKN-7, MKN-74, and MKN-45 cells (Zenz, Tamara, et al. 2024).
PMEPA1 Promotes Gastric Cancer Cell Proliferation by Regulating the Ubiquitin-Mediated Degradation of 14-3-3σ and Promoting Cell Cycle Progression
Treatment for advanced gastric cancer (GC) often requires chemotherapy, whose effects are closely associated with the cell cycle. This association highlights the critical need to understand cell cycle regulators that can influence the effectiveness of chemotherapy.
Bioinformatics analyses were performed on transcriptome data from a hospital cohort and on a publicly available database. Flow cytometry was used for cell cycle analysis. The interaction of PMEPA1 with 14-3-3σwas confirmed by coimmunoprecipitation and immunofluorescence staining. 14-3-3σ was identified as a downstream target of PMEPA1. PMEPA1 binds to 14-3-3σ and promoted its degradation by facilitating its ubiquitination. Overexpression of PMEPA1 increased its interactions with TTC3 and 14-3-3σ, increased 14-3-3σ ubiquitination, and reduced 14-3-3σ stability, and the opposite effects were observed after PMEPA1 knockdown. PMEPA1 recruited TTC3, allowing the ubiquitination of 14-3-3σ and leading to its degradation, thus promoting cell cycle progression in GC.
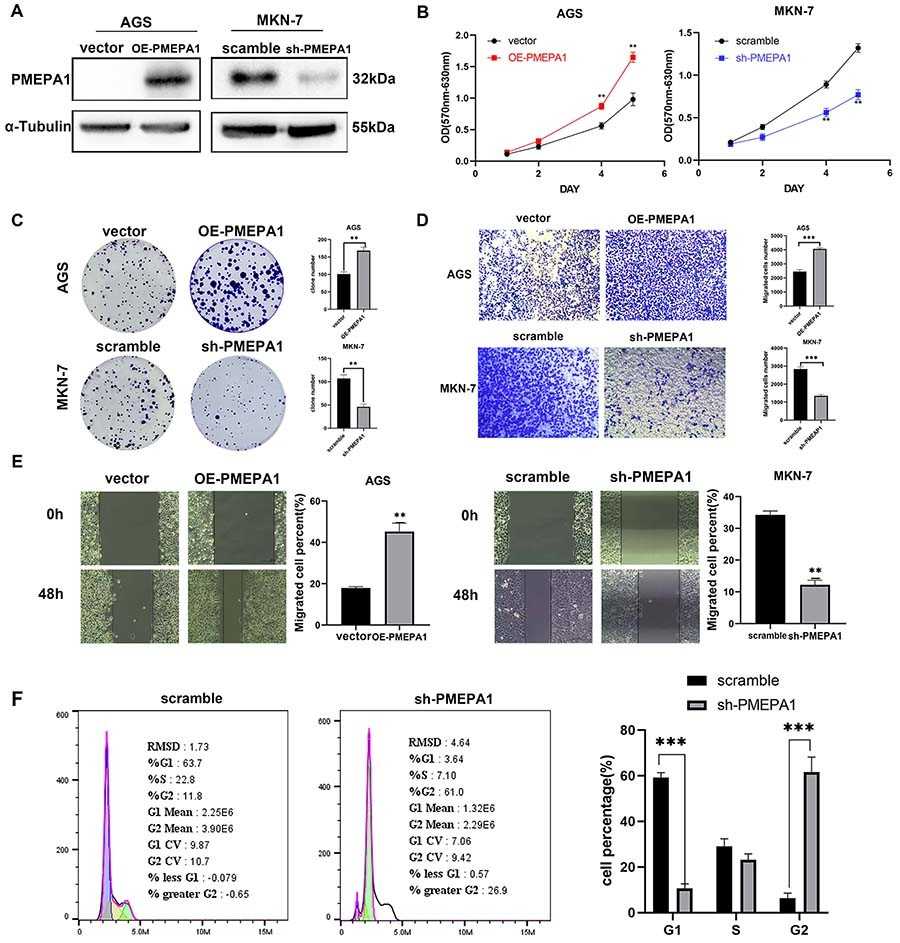 Fig. 2. In vitro cellular functional experiments of PMEPA1 overexpression and knockdown (Huang, Heyuan, et al. 2024).
Fig. 2. In vitro cellular functional experiments of PMEPA1 overexpression and knockdown (Huang, Heyuan, et al. 2024).
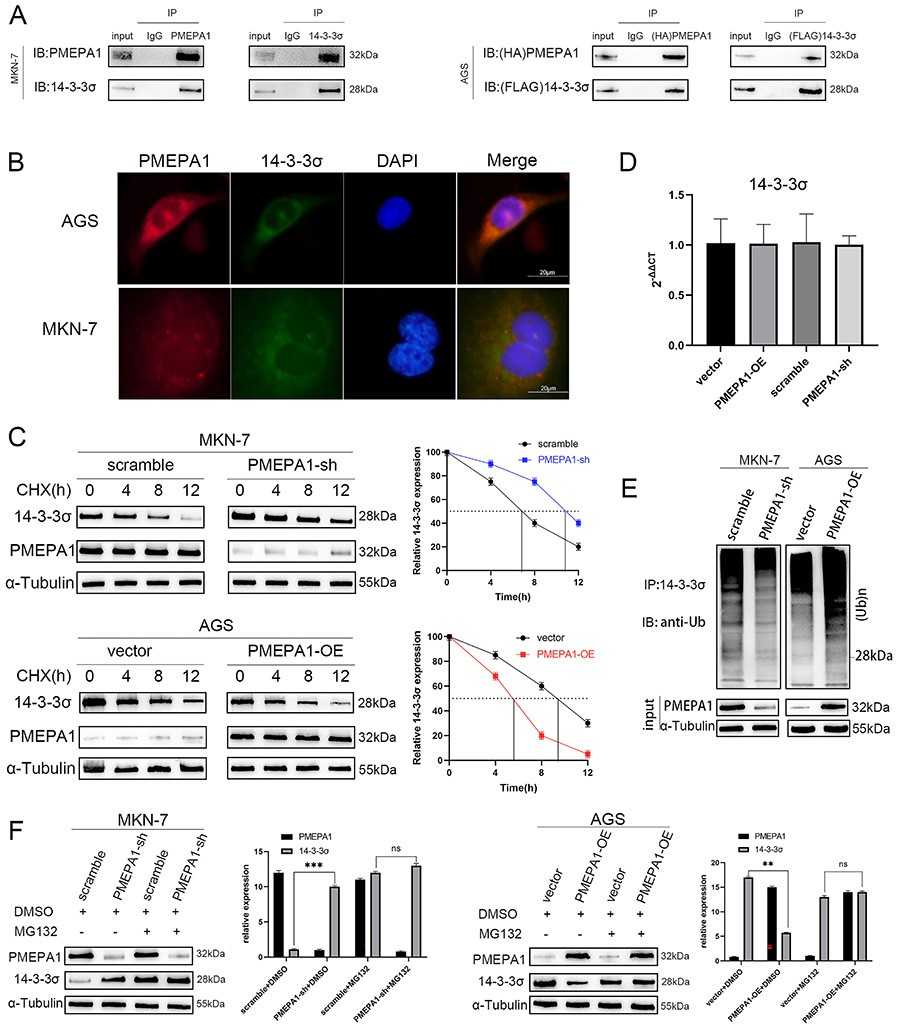 Fig. 3. PMEPA1 bound to 14-3-3σ and promoted its degradation by facilitating its ubiquitination (Huang, Heyuan, et al. 2024).
Fig. 3. PMEPA1 bound to 14-3-3σ and promoted its degradation by facilitating its ubiquitination (Huang, Heyuan, et al. 2024).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells