LAN-1
Cat.No.: CSC-C0637
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Bone Marrow Metastasis
Morphology: cells are growing adherently and in clumps in suspension
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
LAN-1 is a chemotherapy-resistant human cell line which was established from the neuroblastoma tissue of a patient. Neuroblastoma is the most common primary malignant tumor in children, and its main site is adrenal medulla, which is mostly caused by immature neuroblasts. LAN-1 is an important cell line for neuroblastoma study. Analysis found that high expression of MYCN gene is significantly associated with the occurrence and development of neuroblastoma and that the inhibition of MYCN gene expression could greatly enhance the apoptosis of LAN-1 cells. Study also found that LAN-1 cells have M1 and M3 subtypes of muscarinic receptors, and the M1 and M3 muscarinic receptors can regulate the physiological functions of the cells by increasing the intracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i). In addition, LAN-1 cell line has been used to observe the effects of heavy ion radiation on tumor cells. It was found that heavy ion radiation has a high sensitivity to LAN-1 cells, with an RBE of 2.3-2.6. This shows that LAN-1 cell lines have certain application value in evaluating the effectiveness of new radiotherapy methods.
Laser Power and PBNP Concentration Controls PBNP-PTT Thermal Dose
Photothermal therapy (PTT) is successful for tumor ablation and has been applied in conjunction with immunotherapy; however, the immunogenic outcome of PTT is unclear. Sekhri et al.delivered defined thermal doses using Prussian-blue-nanoparticle PBNP-PTT to SH-SY5Y and LAN-1 neuroblastoma cells. ICD markers, costimulatory/immune-checkpoint molecules, MHC, NK ligands, and T-cell cytotoxicity were measured. Determine dose-dependent immunogenicity profiles to predict PTT efficacy for neuroblastoma immunotherapy.
PBNP-PTT dosing was adjusted in vitro by altering the PBNP concentration and near-infrared laser power. They synthesized PBNPs with a mean diameter of 55 nm and a surface charge of −39 mV. SH-SY5Y and LAN-1 cells were exposed to PBNP-PTT under varying conditions. The temperature increase during the heating phase was higher at greater laser power in SH-SY5Y cells (Fig. 1A). These temperature profiles were converted to cumulative equivalent minutes at 43 °C (∑CEM43) to determine that thermal dose is dependent on both PBNP concentration and laser power (Fig. 1B). Increasing the thermal dose decreased SH-SY5Y cell viability. We observed 96% killing of SH-SY5Y cells at a thermal dose of 11.3 log(∑CEM43). A similar trend was observed in LAN-1 cells, with increasing temperature, thermal dose, and PBNP concentration leading to decreasing cell viability. We achieved 98% killing of LAN-1 cells at 11.3 log(∑CEM43) (Fig. 1D and E).
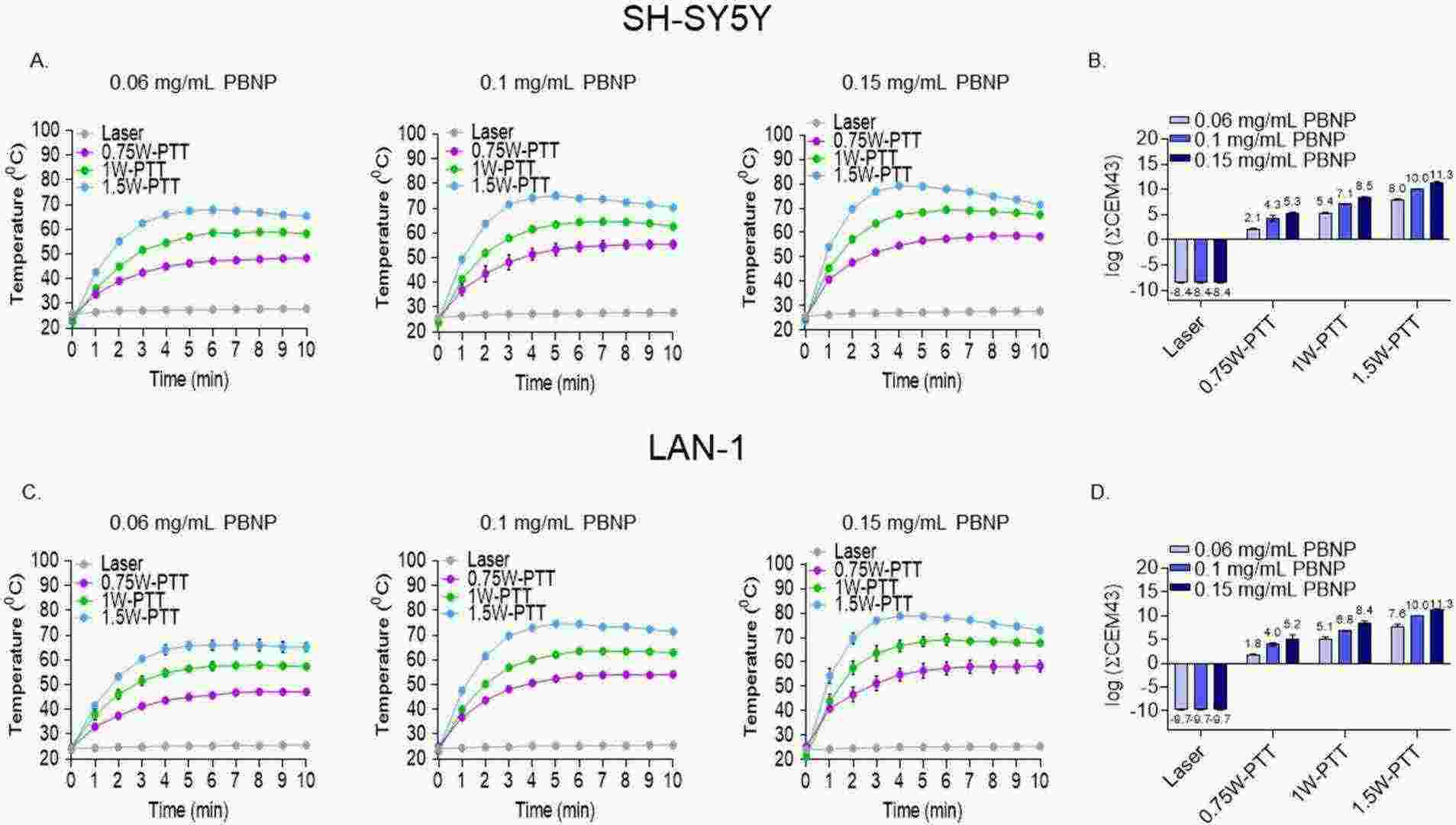 Fig. 1. PBNP-PTT-administered thermal dose is controlled by PBNP concentration and laser power (Sekhri P, Ledezma DK, et al., 2022).
Fig. 1. PBNP-PTT-administered thermal dose is controlled by PBNP concentration and laser power (Sekhri P, Ledezma DK, et al., 2022).
CDKi Treatment Triggers NB Cell Differentiation and Impairs Viability
Neuroblastoma (NB) is not characterized by recurrent somatic mutations which limits therapeutic approaches. Inducing NB differentiation through differentiation therapy by agents such as cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors (CDKis) is emerging as a promising strategy. Retinoic acid (RA) is a known differentiation agent, but RA resistance is often observed. In this study, Shokraie et al. assessed 3 CDKis (abemaciclib, fadraciclib, dinaciclib) alone or in combination with RA, on NB cells to determine their ability to drive cell differentiation, growth, gene expression, and immunogenic cell death in MYCN amplified (LAN-1, CHLA-90) and non-amplified (CHLA-172) cell lines.
NB cell lines (LAN-1, CHLA-90, and CHLA-172) were exposed to increasing doses of CDKi and cell metabolic activity was determined at 72h and 2×72h time points (Fig. 2). Exposure to low doses of abemaciclib (0.1µM) was sufficient to drive stromal-like morphology (flattened cytoplasm and enhanced cell to cell adhesion) indicative of glial differentiation and higher cytotoxicity for dinaciclib/fadraciclib (Fig. 2A). Dose response curves for these CDKis confirmed these results and 2×72h exposures amplified the effects (Fig. 2B). Chromosome 12 polysomy (CDK4 amplification) was observed in all three cell lines. Partial deletion of CDKN2A was observed in LAN-1 and CHLA-172 lines, while amplification of CHKN2A was observed in CHLA-90 (Fig. 2C).
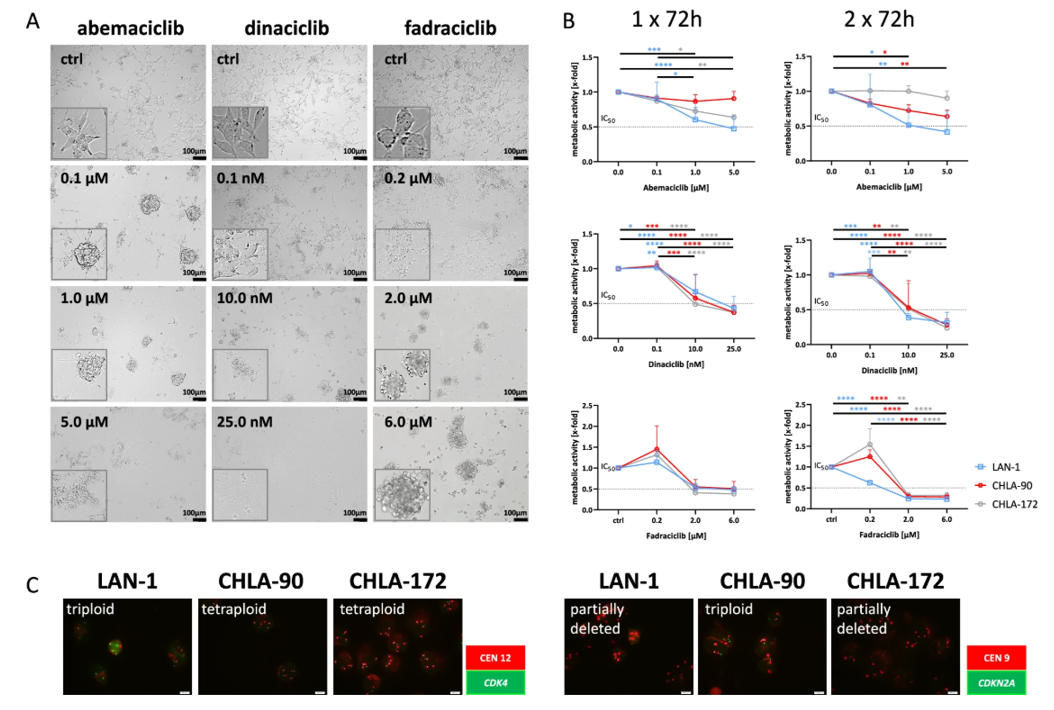 Fig. 2. Dose response curve and molecular analysis (Shokraie F, Lechermeier L, et al., 2025).
Fig. 2. Dose response curve and molecular analysis (Shokraie F, Lechermeier L, et al., 2025).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells