CTX TNA2
Cat.No.: CSC-C9174W
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
Source: Brain
Morphology: fibroblast
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
CTX-TNA2 is an immortalized type I astrocyte cell line derived from primary cultures of astrocytes from the frontal cortex of 1-day-old Sprague-Dawley rat pups. After three days in primary culture, cells were transfected with an SV40 large T antigen expression construct under the control of a human GFAP promoter and murine PGK-neo promoter. Clonal expansion under G418 selection produced a stable cell line in which >95% of cells express the SV40 T antigen. Immortalized CTX-TNA2 cells maintain many of the phenotypic and biochemical properties characteristic of astrocytes.
Morphologically, the cells are polygonal or spindle-shaped. About 20% of the cells in culture are immunoreactive for GFAP, a major marker of astrocytes. Functionally, CTX-TNA2 cells synthesize α₂-macroglobulin at levels similar to primary astrocytes and have a β-alanine-inhibitable high affinity uptake system for GABA. They also lack markers characteristic of type II astrocytes and do not synthesize proenkephalin A or galactocerebroside. The above properties make CTX-TNA2 a convenient in vitro model of type I astrocytes.
CTX-TNA2 is widely used in neuroscience research to model aspects of glial biology, mechanisms of neurotoxicity, and neuroprotection. They have been used to construct functional in vitro blood-brain barrier (BBB) models in co-culture with brain endothelial cells with resultant high transendothelial electrical resistance and expression of tight junction proteins, efflux transporter activity, and receptor-mediated transferrin uptake. CTX-TNA2 also provides a stable and reproducible in vitro model for the study of oxidative stress responses, mitochondrial dysfunction, excitotoxicity-induced apoptosis and autophagy, and other astrocyte-mediated mechanisms of relevance to neurodegenerative disease and brain injury.
Characterization of Exosomes of Hypoxic Preconditioned CTX-TNA2 Cells
Exosomes are influenced by donor cell conditions, including hypoxia. Here, Tseng et al. exposed CTX-TNA2 astrocytes to different hypoxic durations followed by normoxia and assessed the effects of resulting exosomes on primary cortical neurons treated with hemin.
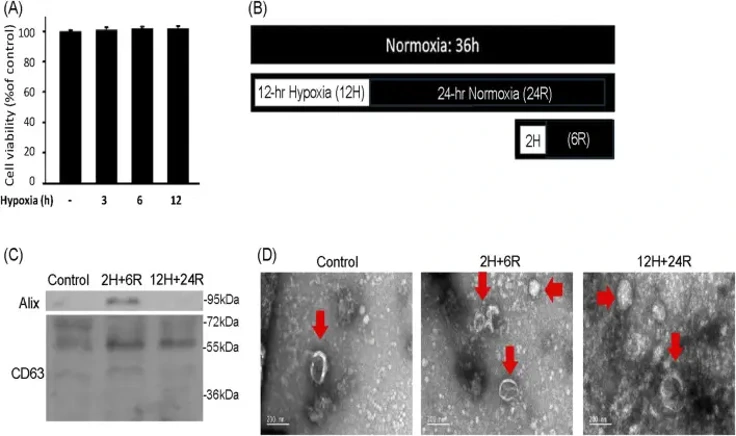
To understand the effect of hypoxic preconditioning on exosome secretion, CTX-TNA2 astrocyte cells were treated with 3 hours, 6 hours, and 12 hours of hypoxia. The SRB assay indicated that CTX-TNA2 cells did not suffer significant cell loss after 3, 6 or 12 hours of hypoxia (1% oxygen) (Fig. 1A). Therefore, two hypoxic preconditioning protocols, 2 hours of hypoxia and 6 hours of normoxia (2H/6R) and 12 hours of hypoxia and 24 hours of normoxia (12H/24R), were used for exosome harvest (Fig. 1B). Western blot analysis of the exosomes demonstrated increased levels of Alix and CD63 in both 2H/6R and 12H/24R treatments compared to the control (Fig. 1C). TEM of exosomes from all three groups showed spherical morphology with an intact lipid bilayer membrane (Fig. 1D). NTA results indicated that sizes of 2H/6R and 12H/24R exosomes were slightly larger than the control exosomes, but not statistically different, at 89.8 ± 9.9 nm for control exosomes, 99.4 ± 12.7 nm for 2H/6R exosomes and 105.1 ± 22.3 nm for 12H/24R exosomes. The exosome concentrations and zeta potentials were also not statistically different between the three groups.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells