AC-1M88
Cat.No.: CSC-C0486
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Morphology: epitheloid cells growing adherently in monolayers
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin +, desmin -, endothel -, GFAP -, neurofilament -, vimentin +
Viruses: PCR: EBV -, HBV -,
The AC-1M88 cell line is a human trophoblast cell line, which was originated from a hybridoma between primary extravillous trophoblasts (EVT) isolated from term placenta and a selectable mutant of the choriocarcinoma JEG-3 cell line. Cells have an epithelial morphology and a doubling time of 30-50 hours. They are cultured in DMEM/F12 medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin at 37°C and 5% CO₂.
AC-1M88 cells are used as a model for studying various aspects of trophoblast behavior, including adhesion, migration, and invasion. They have been used to study the mechanisms underlying trophoblast function and placental development. The AC-1M88 cell line has also been used in studies of trophoblast-endometrial stromal cell interactions.
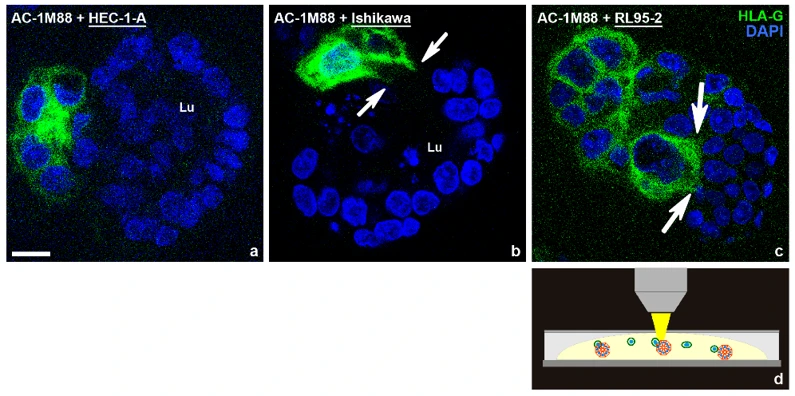
Confrontation of Endometrial Epithelial Spheroids with Trophoblast Cells from the Basal Cell Pole
Endometrial tissue remodeling is essential for embryo implantation during the menstrual cycle. Here, Classen-Linke et al. review the changes in human endometrial epithelium that facilitate implantation, focusing on polarity, adhesion, cytoskeletal organization, and extracellular matrix.
To prove the concept that differently polarized spheroids are more or less permissive for invasion of trophoblast cells, an invasion assay was established. As a model for extravillous trophoblast cells invading endometrial glands from the basal side, the AC-1M88 trophoblast cell line was used, which is a hybridoma of primary extravillous trophoblast cells and the JEG-3 choriocarcinoma cell line. They were confronted with the differently polarized endometrial cell-line derived spheroids. As depicted in Figure 1, trophoblast cells were found to be barely attached to the highly polarized HEC-1-A cells, extended cell protrusions into Ishikawa spheroids and completely invaded RL95-2 spheroids.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells