Py230
Cat.No.: CSC-C6530J
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
Source: Breast
Morphology: Epithelial-like
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Shipping: Dry Ice, Frozen
The Py230 cell line is a well-established murine epithelial-like cell line, serving as a cornerstone model for studying triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) biology, tumor progression, and the tumor microenvironment. Isolated in 2004 from a spontaneously arising mammary adenocarcinoma in an adult female MMTV-PyMT (mouse mammary tumor virus promoter-driven Polyoma middle T-antigen) transgenic C57BL/6 mouse. This cell line faithfully recapitulates key stages of malignant progression and is widely used in preclinical breast cancer research.
Py230 cells are defined by a combination of genetic, molecular, and behavioral traits that make them particularly relevant for simulating human breast cancer.
| Feature | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Genotype | Derived from MMTV-PyMT transgenic mouse; carries the Polyoma virus middle T oncogene. | Simulate oncogene-driven tumorigenesis. |
| Immunophenotype | Triple-Negative: ER-/PR-/HER2-low. Luminal Progenitor-like: Expresses E-cadherin, cytokeratin 8, and cytokeratin 14. | Simulate aggressive, treatment-resistant TNBC and luminal progenitor biology. |
| In Vivo Behavior | Tumorigenic; forms luminal-type primary tumors and lung metastases. Exhibits locally invasive but slower, less metastatic growth compared to lines like 4T1. | Ideal for studying local invasion, immune evasion, and the metastatic cascade. |
| Differentiation Potential | Exhibits lineage plasticity; can differentiate into luminal, myoepithelial, and alveolar cells upon stimulation. | Useful for studying cell state transitions, plasticity, and therapy resistance. |
PARP7 and Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Differentially Regulate Mammary Cancer Cell Proliferation and STING-Induced Type I Interferon Signaling
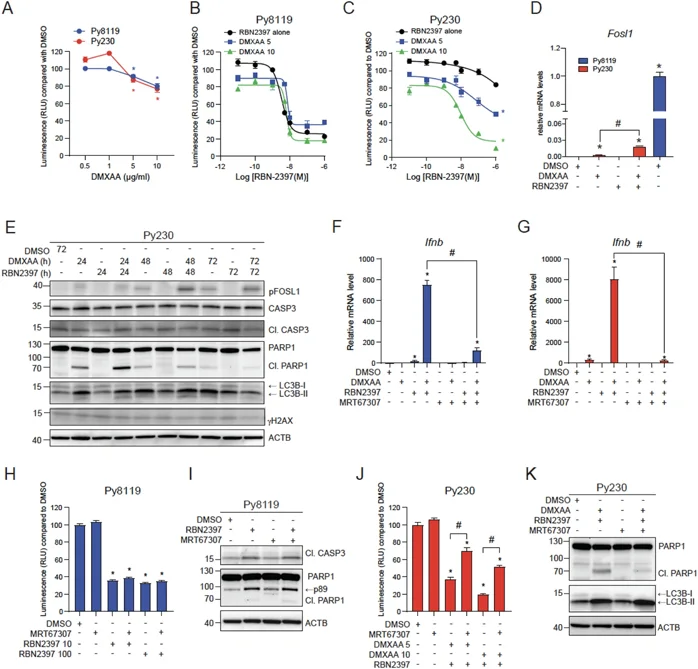
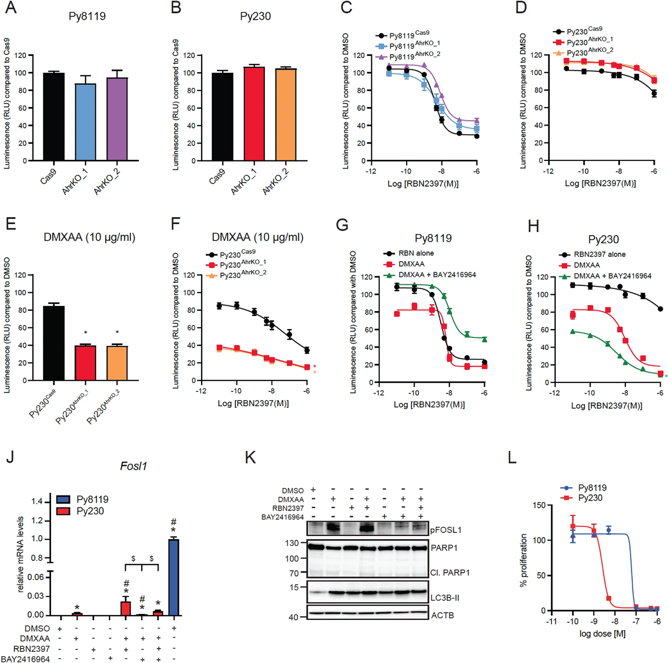
PARP7 is a negative regulator of type I interferon (IFN-I) and aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) signaling and has important roles in cell proliferation and antitumor immunity. Recently, several cancer cell lines have been reported to be sensitive to the antiproliferative effect of PARP7 inhibition by RBN2397; however, the roles of AHR and IFN-I signaling in this effect are not fully understood.
Murine mammary cancer cells were treated with AHR ligands, RBN2397 and with the stimulator of interferon genes (STING) agonist, DMXAA. The impact of ligand treatments on AHR and IFN-I signaling and cell proliferation was determined.
RBN2397 enhanced AHR ligand signaling and STING-induced IFN-I responses in both cell lines. Py8119 but not Py230, 4T1 or EO771 cells were sensitive to the antiproliferative effects of RBN2397. In agreement with FOS-related antigen 1 (FOSL1) being required for sensitivity to RBN2397, Py8119 but not Py230 cells expressed FOSL1. However, RBN2397 insensitive 4T1 and EO771 cell lines also expressed FOSL1, suggesting that the role of FOSL1 in RBN2397-mediated growth inhibition exhibits cell line specificity. In Py8119 cells, RBN2397 induced apoptosis which was independent of AHR ligand treatment and DMXAA-induced STING activation. Although Py230 cells were resistant to the antiproliferative effects RBN2397 alone, combined treatment of DMXAA with RBN2397 reduced their proliferation, which was further reduced by AHR loss or its inhibition.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells