TCMK-1
Cat.No.: CSC-C9735L
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
Source: Kidney
Morphology: epithelial
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Strain: C3H/Mai
Virus Susceptibility: vesicular stomatitis (Indiana)
Tumorigenecity: no
Histocompatibility: H-2k
Histopathology: normal
Note: the cells ar5e SV40 transformed and are positive for SV40 T-antigen; about 2% of the cells are positive for SV40 viral antigen, but virus is not recoverable; tested and found negative for ectromelia virus (mousepox)
Shipping Condition: Room Temperature
TCMK-1 is a mouse renal tubular epithelial cell line originally isolated from kidney tissue of a transgenic mouse expressing the simian virus 40 (SV40) large T antigen. The cells are non-tumorigenic kidney epithelial cells and have been used extensively as an in vitro model for renal tubular cell biology, kidney injury and nephrotoxicity. Due to its stable growth and well-defined epithelial characteristics, TCMK-1 provides a reliable alternative to primary renal cells for mechanistic and pharmacological studies.
Morphologically, TCMK-1 cells are epithelial with cobblestone-like appearance and grow as an adherent monolayer. The cells have been shown to have robust cell-cell junctions and also express markers of epithelial cells. In addition, these cells exhibit contact inhibition under standard culture conditions (typically DMEM + fetal bovine serum). TCMK-1 express renal epithelial markers in a pattern that is consistent with proximal tubular origin.
Functionally, the cells have also retained many of the characteristics expected of renal epithelial cells. TCMK-1 cells are sensitive to nephrotoxic insults and will respond to inflammatory and oxidative stress stimuli. As such, the cells are used commonly for mechanistic studies of acute kidney injury, renal inflammation and fibrosis-related signaling, as well as the cellular response to drugs or environmental toxins. TCMK-1 cells have also been used in studies of renal metabolism, apoptosis and protective signaling.
CircVmn2r1 Promotes TCMK-1 Cell Senescence In Vitro
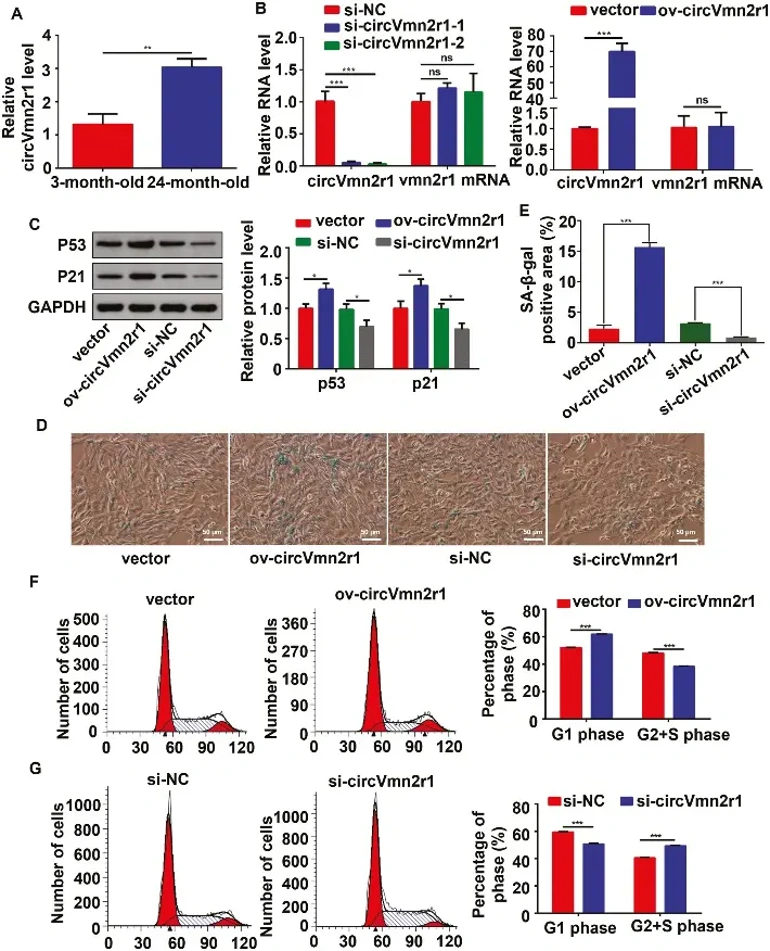
Kidney aging exacerbates kidney diseases and affects other organs. CircRNAs are crucial in aging, but their roles in kidney aging are unknown. Here, Gao's team identified circVmn2r1 as a highly expressed circRNA in mouse kidneys, significantly upregulated in 24-month-old mice compared to 3-month-old mice. They demonstrated that circVmn2r1 overexpression promotes kidney aging in senescence-accelerated mice.
To explore the function of circVmn2r1 in TCMK-1 cells, two siRNAs targeting the junction site of circVmn2r1 and an overexpression vector were designed. qRT-PCR confirmed that circVmn2r1 expression was significantly downregulated or upregulated in TCMK-1 cells transfected with the respective siRNA or vector. Among the siRNAs, si-circVmn2r1-2 had the highest silencing efficiency and was selected for further study. Importantly, neither overexpression nor knockdown of circVmn2r1 affected the linear Vmn2r1 transcript levels (Fig. 1B), making these reagents suitable for functional studies. To demonstrate that circVmn2r1 regulates the senescence of TCMK-1 cells, Gao's team conducted western blot experiments to determine the protein levels of P53 and P21 after circVmn2r1 was overexpressed or knocked down. They found that overexpression of circVmn2r1 increased the expression of P53 and P21, while knockdown of circVmn2r1 decreased the expression of P53 and P21 (Fig. 1C). SA-β-gal staining showed that SA-β-gal activity was increased by overexpression of circVmn2r1 and reduced by knockdown of circVmn2r1 (Fig. 1D and E). Flow cytometry was used to determine DNA content by staining with PI. Gao's team found that upregulation of circVmn2r1 increased the G1 phase and reduced the G2 + S phase, while downregulation of circVmn2r1 had the opposite effects (Fig. 1F and G). In summary, these results suggest that circVmn2r1 promotes ageing and inhibits proliferation of TCMK-1 cells in vitro.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells