- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
OE21 is a human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cell line with an epithelial-like morphology, displaying typical characteristics of epithelial cells. It also shows several properties of cancer cell growth, such as rapid proliferation and responsiveness to specific growth factors and hormones. The cell line has been shown to be sensitive to androgen receptor (AR) signaling and exhibit changes in proliferation and apoptosis upon stimulation by factors like TGF-β1 and 5α-dihydrotestosterone (DHT). In vitro studies have demonstrated a response to chemerin, potentially involving chemotaxis and activation of signaling pathways. Widely used in cancer research, the OE21 cell line serves as a valuable in vitro model for investigating ESCC pathogenesis, drug screening, and gene expression profiling. It is particularly useful for studying tumor invasion, metastasis, and chemosensitivity mechanisms.
CCT6A Promoted Cell Proliferation in OE21 and TE-1 Cells
Chaperonin-containing TCP1 subunit 6A (CCT6A) has been found to be a promoter of malignancy in a variety of cancers. However, its function in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) remains unclear. Zhao's team investigated whether CCT6A regulates ESCC cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by modulating the TGF-β/Smad/c-Myc pathway, potentially identifying a novel therapeutic target.
In order to minimize the off-target effect of siRNA, three CCT6A siRNAs were transfected into OE21 and TE-1 cells. In OE21 cells (Fig. 1A) and TE-1 cells (Fig. 1B), CCT6A expression was reduced in the CCT6A-siRNA1, CCT6A-siRNA2 and CCT6A-siRNA3 groups compared with the NC-siRNA group; cell proliferation (as reflected by OD value) at 72 h was inhibited in the CCT6A-siRNA1, CCT6A-siRNA2 and CCT6A-siRNA3 groups compared with the NC-siRNA group (Fig. 1D). Meanwhile, CCT6A-encoding plasmids were transfected into OE21 cells (Fig. 1E) and TE-1 cells (Fig. 1F), and CCT6A expression was increased in the CCT6A-pEX2 group compared with the NC-pEX2 group; cell proliferation (as reflected by OD value) at 72 h was promoted in the CCT6A-pEX2 group compared with the NC-pEX2 group (Fig. 1H). Notably, since CCT6A siRNA1 had the greatest inhibitory effect on CCT6A expression, CCT6A siRNA1 (referred to as CCT6A-siRNA below) was selected for subsequent cellular experiments.
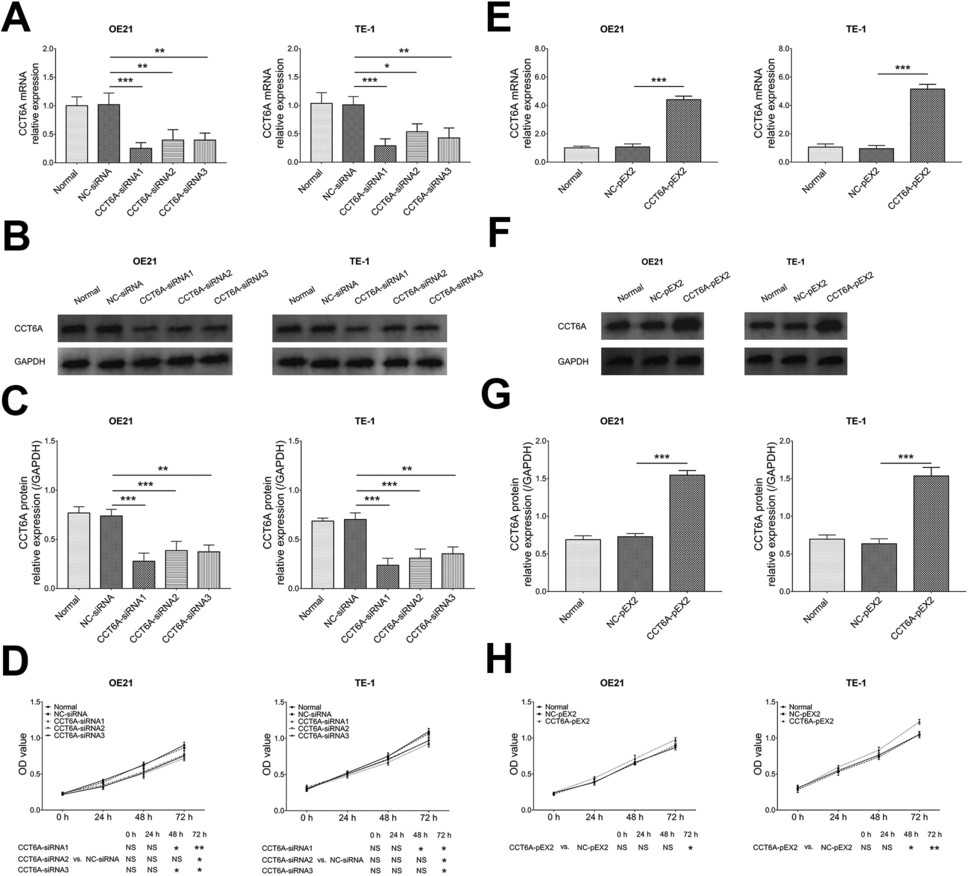 Fig. 1. CCT6A's effect on cell proliferation (Xia X L, Zhao S S, et al., 2023).
Fig. 1. CCT6A's effect on cell proliferation (Xia X L, Zhao S S, et al., 2023).
Esophageal Cancer Cell Lines have Variable Expression of Mxa and Exhibit a Range of Sensitivity to Oxaliplatin and 5-Fluorouracil
Esophageal cancer is one of the deadliest malignancies due to resistance to chemotherapy regimens. MxA expression is dysregulated in a variety of cancers and is also known to be associated with the induction of apoptosis. However, its role in determining the response to drugs in esophageal cancer was unclear. In this study, Hayers et al. measured the expression of MxA in five esophageal cancer cell lines (Fig. 2A). MxA was not expressed in KYSE450 and KYSE140 cells, while FLO-1, KYSE270, and OE21 had variable expression of MxA (Fig. 2B). MxA-expressing cancer cells were more sensitive to 5-FU and oxaliplatin, with evidence of cellular toxicity within 24 h and caspase-3-mediated apoptosis (Fig. 2B). In MxA-negative cancer cells, the onset of toxicity was delayed to 48 h, and the apoptotic response to 5-FU or oxaliplatin was significantly lower (Fig. 2B).
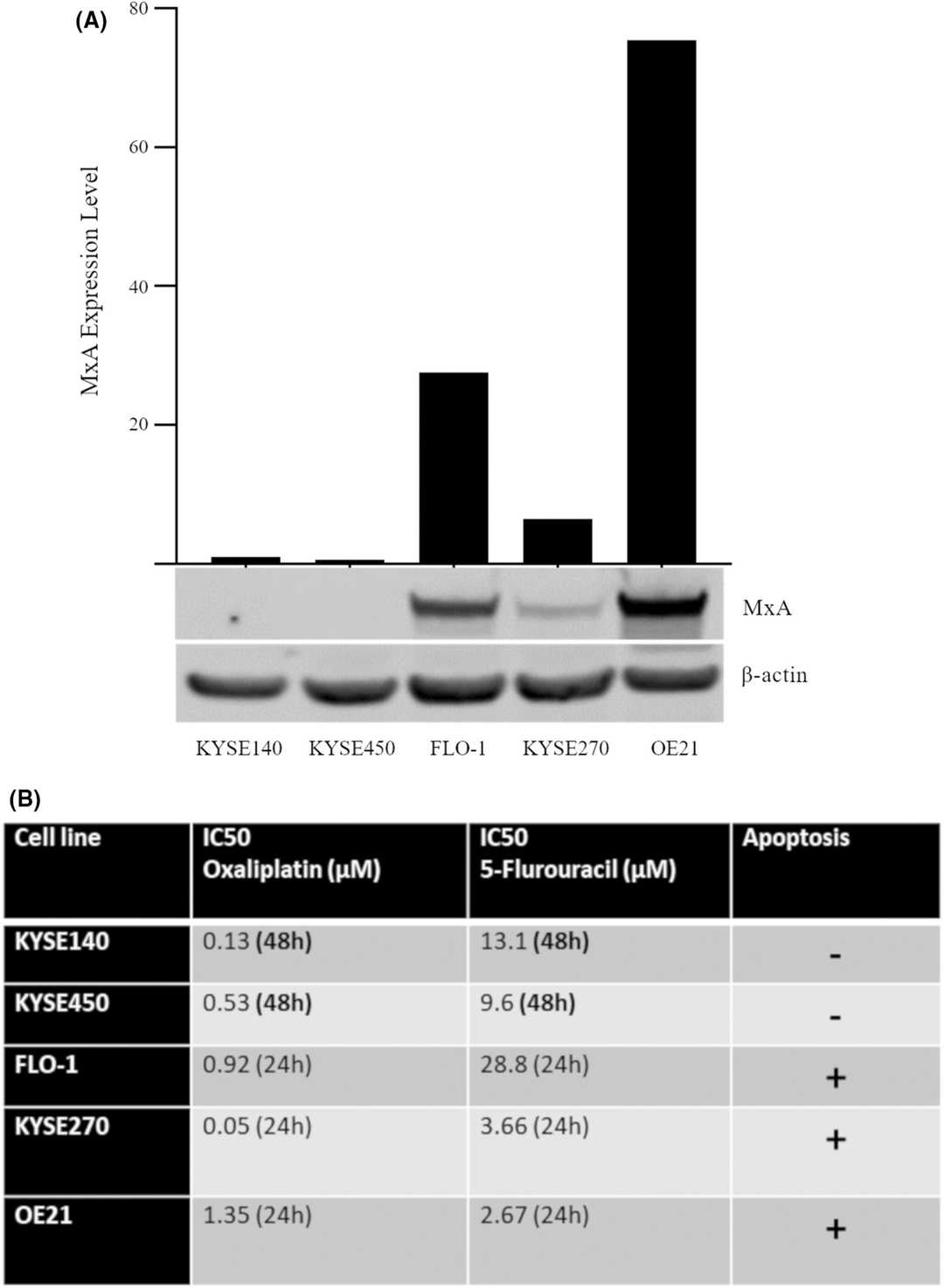 Fig. 2. MxA protein expression and apoptosis competency in a panel of esophageal cancer cell lines (Hayes RM, O'Donovan TR, et al., 2024).
Fig. 2. MxA protein expression and apoptosis competency in a panel of esophageal cancer cell lines (Hayes RM, O'Donovan TR, et al., 2024).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells





