KYSE-70
Cat.No.: CSC-C0414
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Esophagus
Morphology: epitheloid cells growing adherently in monolayers
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin +, cytokeratin-7 -, cytokeratin-8 +, cytokeratin-17 -, cytokeratin-18 +, cytoker
KYSE-70 is a human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cell line that is derived from tumor tissue from a Japanese female. The KYSE-70 cell line represents one of the esophageal cancer cell lines in the KYSE series established by Kyoto University's research team. It has adherent growth characteristics in vitro, and a typical epithelial-like or polygonal cell morphology, which demonstrates the features of squamous carcinoma cells such as cobblestone-like appearance.
Molecularly, KYSE-70 has TP53 gene mutation, EGFR expression, and is positive for cytokeratins (CK5/6, CK14) and is usually HPV-negative, which matches the epidemiological characteristics of ESCC in Asian populations. Because of its stable growth characteristics and known genetic background, KYSE-70 is often used in the study of esophageal cancer pathogenesis, drug sensitivity assays, and tumor metastasis model research.
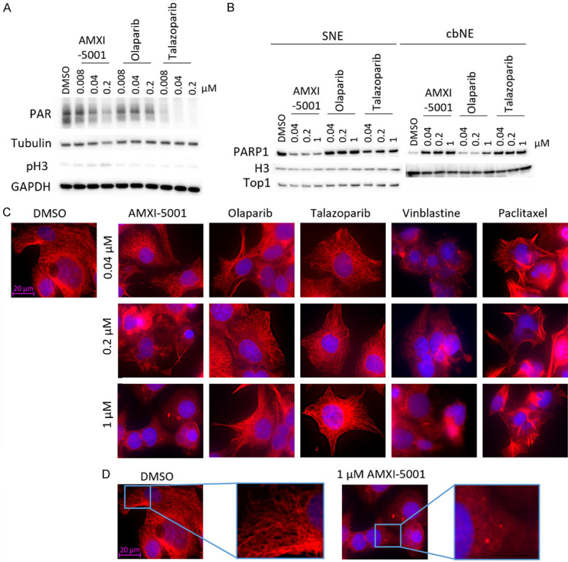
AMXI-5001 Inhibits both PARP and Microtubule Polymerization
Esophageal cancer is associated with high mortality and poor survival despite standard care. Brand et al. explored the potential of AMXI-5001, a novel dual-action PARP and microtubule polymerization inhibitor, to inhibit esophageal carcinoma growth.
AMXI-5001 has been shown to be an effective inhibitor of parp1/2 and microtubule polymerization. In order to further confirm the mechanism of action in esophageal cancer cells, KYSE-70 cells were treated with AMXI-5001, Olaparib, or Talazoparib for 24 hours. Western blot analysis confirmed that while Olaparib and Talazoparib are capable of PARP inhibition, but not tubulin (Fig. 1A), AMXI-5001 is able to abrogate both PARP and tubulin (Fig. 1A). Furthermore, by immunofluorescence, they confirmed that AMXI-5001 disrupted microtubule networks in a dose dependent manner, while both Olaparib and Talazoparib, do not (Fig. 1C and D). To control for inhibitor and enhancer of microtubule polymerization, they used Vinblastine and paclitaxel, respectively. We conclude that AMXI-5001 can potently inhibit microtubule polymerization in KYSE-70 cells.
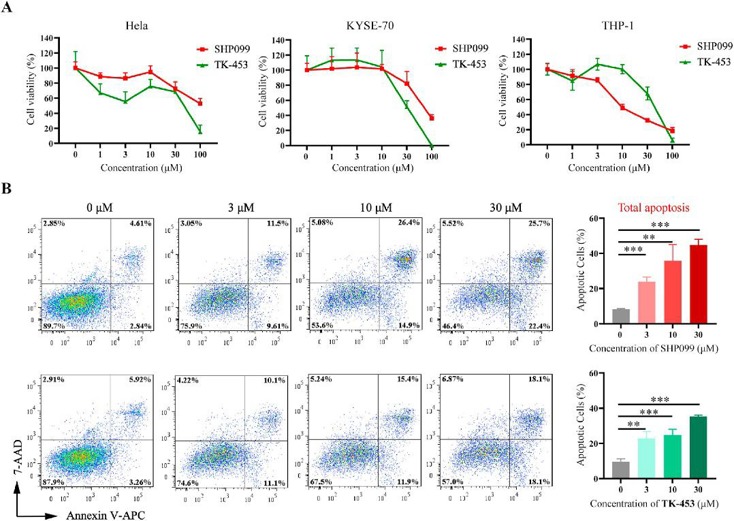
TK-453 Inhibited Cell Proliferation and Induced Apoptosis of Cancer Cells In Vitro
SHP2, encoded by PTPN11, is a non-receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase that has been implicated in a variety of cancers. Dysregulation of SHP2 signaling has been shown to play a role in cancer pathogenesis, and SHP2 is a promising therapeutic target. Tang et al. developed a potent, selective and active SHP2 inhibitor through structure-based design and extensive SAR studies. They also evaluated the impact of SHP2 inhibitors on the proliferation and apoptosis of tumor cells. Hela, KYSE-140 and THP-1 cell lines were selected as paper reported. As shown in Fig. 2A, similar to the control compound SHP099, TK-453 had moderate inhibitory effects on the proliferation of KYSE-70, Hela and THP-1 cells at concentrations of 30 and 100 μM. These findings suggested that these small-molecule compounds might not exert their effects by significantly affecting tumor cell proliferation. TK-453 induced apoptosis in Hela cells in a concentration-dependent manner (Fig. 2B).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells





