KB-V1
Cat.No.: CSC-C6212X
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Uterus; Cervix
Morphology: epitheloid-like, sometimes round cells growing in loosely adherent monolayers when vinblastine is present
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin +, desmin -, endothel -, GFAP -, neurofilament -, vimentin +
Viruses: ELISA: reverse transcriptase negative; PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HHV-8 -, H
KB-V1 is a cell line of human cervical cancer cells and a subline of HeLa cells. The "V" in KB-V1 is the abbreviation of Vincristine, "1" means that it is a cell line developed after the first round of drug resistance screening. The drug resistance of KB-V1 cell line was induced by stepwise increase of drug concentration. This cell line is resistant to multiple chemotherapeutic drugs, such as Doxorubicin, Vincristine, Paclitaxel. The main reason for drug resistance of KB-V1 cells is the overexpression of P-glycoprotein (P-gp). P-gp is an ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter on the cell membrane which can transport a variety of chemotherapeutic drugs out of the cells, reducing their cytotoxicity.
KB-V1 cells can be used as a research tool for studying the multidrug resistance mechanism of P-glycoprotein. Using KB-V1 cells, the structure, function, and regulatory mechanism of P-gp can be further studied. Because of the drug-resistant characteristic of KB-V1 cells, they are often used for screening and optimizing novel anti-tumor drugs, especially those drugs with anti-resistance effects. KB-V1 cells are also used to test the reversal effect of natural products (such as plant extracts and the component of traditional Chinese medicine) on multidrug resistance. For example, Epimedium extract has shown a good anti-resistance effect in KB-V1 cells.
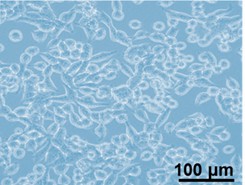 Fig. 1. Microscopic images of KB-V1 cells (Siwowska K, Schmid R M, et al., 2017).
Fig. 1. Microscopic images of KB-V1 cells (Siwowska K, Schmid R M, et al., 2017).
Identification of Compounds that can Overcome MDR through High-Throughput Screening
Multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancer cells, driven by overexpression of ABC transporters such as P-glycoprotein (Pgp), limits the efficacy of chemotherapy. In order to identify compounds with the ability to overcome Pgp-mediated MDR, Zahra et al. screened 1,127 inhibitors (Selleckchem library) in KB-3-1 cells and their Pgp-overexpressing multidrug-resistant derivative KB-V1 cells (Fig. 1A). The majority of compounds were more potent in KB-3-1 cells compared to KB-V1 cells. They retested 118 of the top hit compounds from the primary screen in two pairs of parental and resistant cell lines (KB-3-1/KB-V1 and A2780/A2780-Pac-Res) at 1 μM in a 3-day SRB proliferation assay (Fig. 1A, 1B). Fifteen compounds (out of 118) retained similar potency in sensitive and resistant cells at 1 μM (Fig. 2A, 2B), and are thus able to overcome Pgp-mediated MDR. Paclitaxel was used as a resistance control in Pgp-overexpressing cell lines (Fig. 2C).
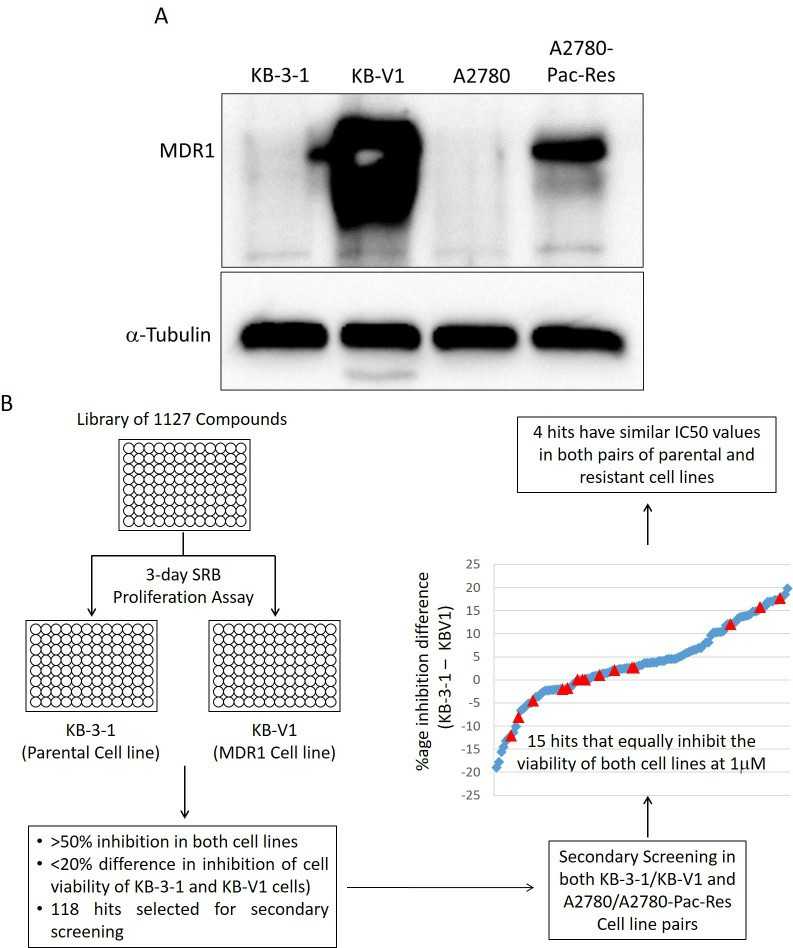 Fig. 1. Screening for compounds with the ability to overcome Pgp-mediated MDR (Zahra R, Furqan M, et al. 2020).
Fig. 1. Screening for compounds with the ability to overcome Pgp-mediated MDR (Zahra R, Furqan M, et al. 2020).
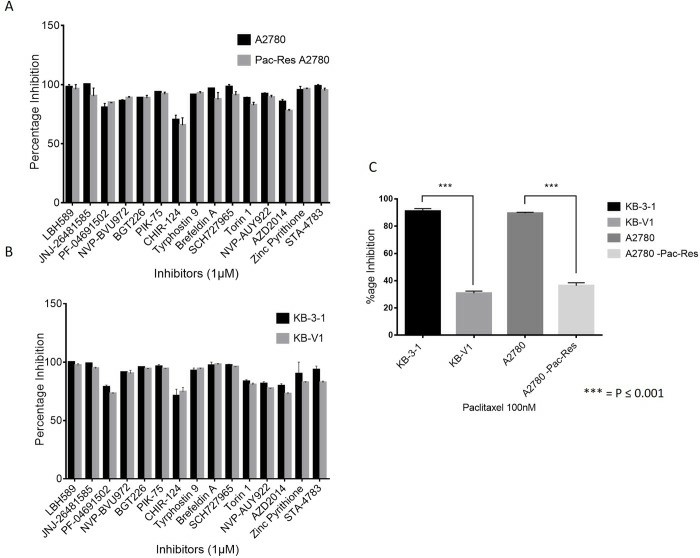 Fig. 2. Secondary screening with 118 compounds in both pairs of parental and resistant cell lines (Zahra R, Furqan M, et al. 2020).
Fig. 2. Secondary screening with 118 compounds in both pairs of parental and resistant cell lines (Zahra R, Furqan M, et al. 2020).
Highly Cytotoxic Cryptophycin Derivatives with Modification in Unit D for Conjugation
Cryptophycins are highly potent cyclodepsipeptides, making them ideal candidates for drug conjugates for tumor therapy. Functionalization for conjugation of this class of compounds often comes at the cost of a toxicity penalty. Using a modular and scalable synthetic methodology, Dessin et al. have modified unit D of cryptophycins to diversify this class, and introduce a number of new analogues with functional groups amenable to conjugation.
All synthesized cryptophycins were assayed for cytotoxicity in KB-3-1, a human cervix carcinoma cell line, and the most active were further tested in the MDR subclone KB-V144 (Fig. 3A). The Dap-derived cryptophycins 33a (Dap), 33b (Dap(Me)) and 34a (Dap(Me2)) had the highest activity and picomolar cytotoxicity with the 34a having the lowest IC50 of 2.91 pM. The Dab-derived analogues 33c (Dab), 33d (Dab(Me)) and 34c (Dab(Me2)) were significantly less active but maintained the same trend: increased cytotoxicity with methylation of the amine and 34c having the highest toxicity (38.3 pM). The diethylated amine 34b and the allylmethylamine 33k had picomolar activity. Most of the amines had resistance factors (FR) in the range 103–104 against KB-V1 cells, but 33k had a low FR of 40.4 and triple-digit picomolar activity against KB-V1 cells.
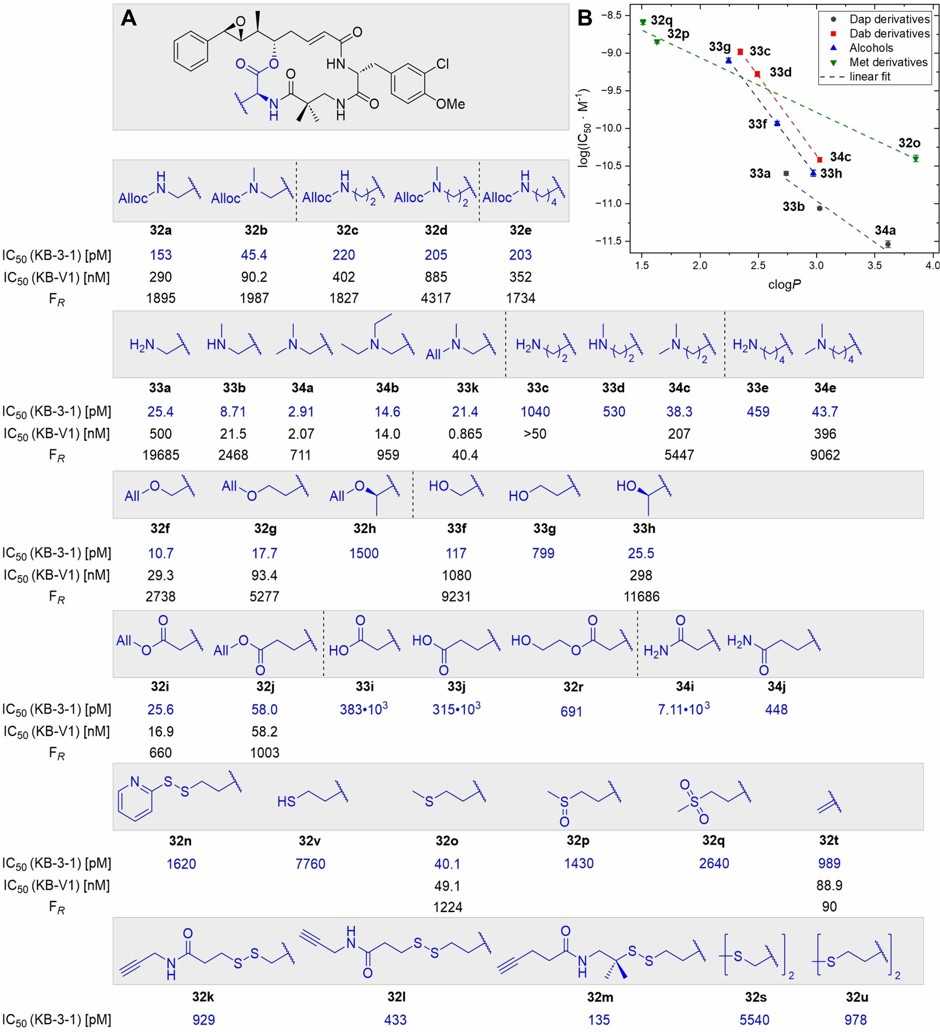 Fig. 3. Cytotoxic profile of synthesized cryptophycins (Dessin C, Schachtsiek T, et al., 2024).
Fig. 3. Cytotoxic profile of synthesized cryptophycins (Dessin C, Schachtsiek T, et al., 2024).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells