BALB/3T3 clone A31
Cat.No.: CSC-C9339L
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
Source: Embryo
Morphology: fibroblast
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Strain: BALB/c
Virus Susceptibility: Herpes simples; vesicular stomatitis (Indiana)
Tumorigenecity: no
BALB/3T3 clone A31 is a well-known murine embryonic fibroblast cell line of BALB/c origin, initiated from mouse embryo tissue in 1963 by Todaro and Green in a 3T3 (subculture every 3 days at 3×105 cells/dish) manner. BALB/3T3 clone A31 cells are a continuous passage cell line that display adherent growth and classic fibroblast morphology (spindle-shaped or polygonal), with a high degree of contact inhibition when cultured as a monolayer. The cells have sensitivity to growth factors and are frequently used as a cell line to determine the cytotoxicity of chemicals or biomaterials thus it is one of the reference cell lines recommended in the international standard for biocompatibility testing ISO 10993-5. In the biomedical field, the BALB/3T3 clone A31 cell line is not only employed for material safety assessment but also widely utilized in carcinogenicity studies (such as soft agar colony formation assays), growth factor functional analysis, and drug screening.
Graphene Monolayer's Impact on Focal Cell Morphology and Size in BALB/3T3 Fibroblasts
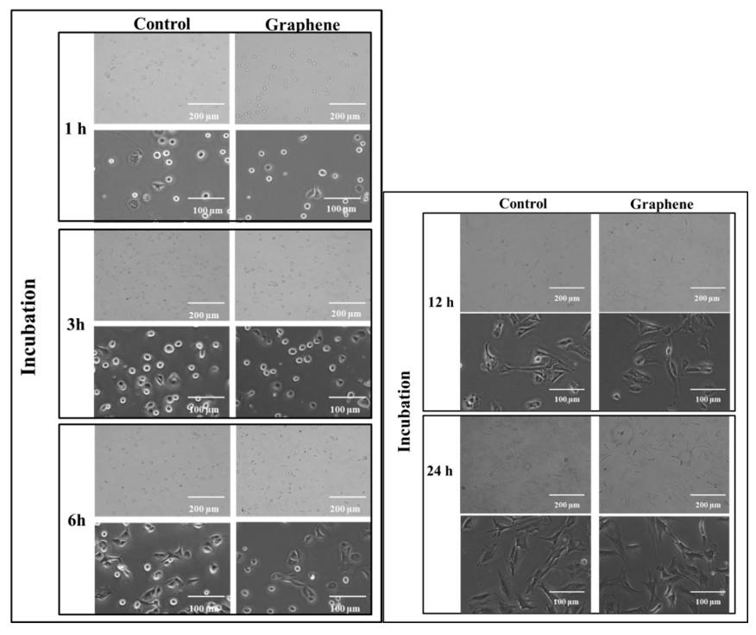
Lasocka et al. investigated the effect of graphene scaffold on morphology and size in BALB/3T3 clone A31 fibroblasts and provides new data on biocompatibility of the "graphene-family nanomaterials".
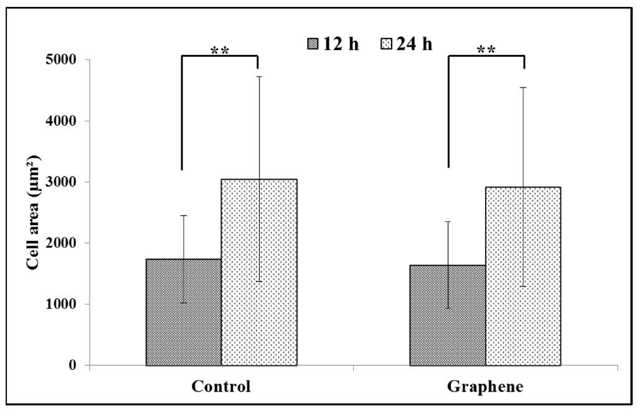
The 24-hour cytotoxicity test with BALB/3T3 mouse fibroblasts showed comparable cell attachment and growth on graphene scaffolds and control substrates. Within the first 3 hours, cells adhered and flattened on both graphene and glass. Morphological changes began at 6 hours (Fig. 1), with cells transitioning to spindle shapes and extending pseudopods. By 12 hours, most cells became spindle-shaped with multiple pseudopods (Fig. 1), exhibiting intact nuclei and nucleoli. After 24 hours, pseudopods merged into thin lamellae. Cells grew normally on graphene without damage, detachment, or morphological differences versus controls (Fig. 1). BALB/3T3 cells exhibit contact inhibition, also known as contact paralysis, where cells avoid overlapping upon contact and change direction. Therefore, culturing them at the correct density (3 × 10⁴ cells/cm²) is crucial for proper morphology and size. After 12 hours, cells on graphene and control substrates measured 1638.6 ± 709.5 µm² and 1732.8 ± 711.2 µm², respectively (Fig. 2). Over the next 12 hours, their area increased by nearly half (Fig. 2), with no significant difference between graphene and glass.
Evaluation of Cytotoxicity of Hyaluronic Acid/Chitosan/Bacterial Cellulose-Based Membrane
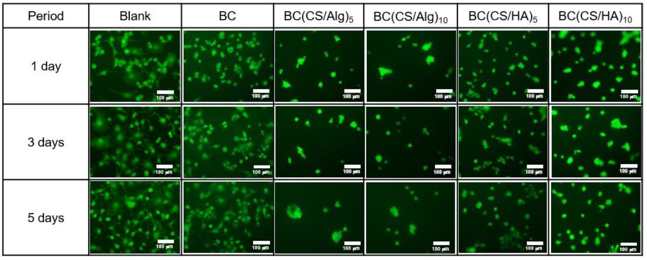
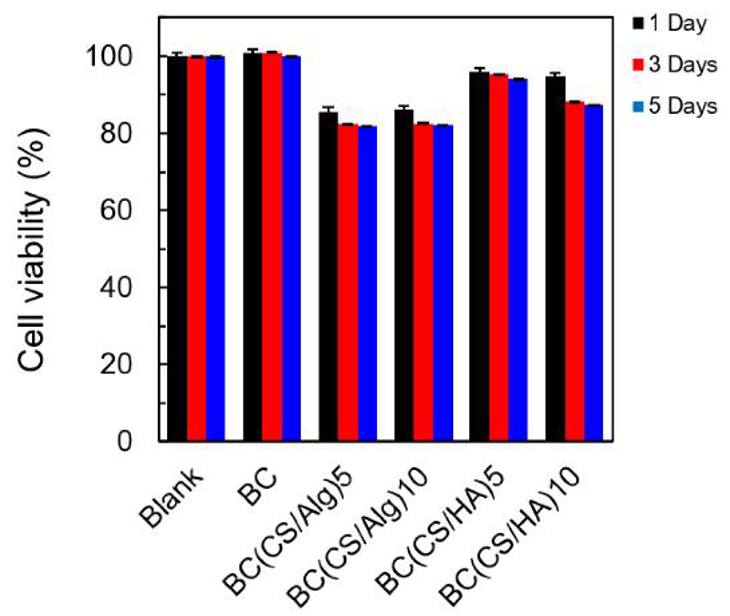
Novel wound dressings must exhibit non-cytotoxic properties with cell viability exceeding 92%. In this study, Dechojarassri et al. compared the cytotoxicity of hyaluronic acid/chitosan/bacterial cellulose (BC(CS/HA)) membranes with alginate/chitosan/bacterial cellulose (BC(CS/Alg)) membranes.
BALB-3T3 clone A31 fibroblasts were initially grown at 1×10⁴ cells/well in a T75 flask for seven days before transferring them to 96-well plates for further incubation at 1, 3, and 5 days. Figure 3 is a fluorescence microscopy image of the live cells, while figure 4 shows a graph with the viability data. The blank (0% no membrane) and BC control showed 100% viability throughout the entire experiment. The BC(CS/Alg)5 and BC(CS/Alg)10 had decreased viability (around 82% at 5 days), while BC(CS/HA)5 and BC(CS/HA)10 had higher viability (94 and 87%, respectively). It was reported that the reason BC(CS/HA) has a greater biocompatibility was due to the HA being able to overcome CS caused cell damage. This was in-line with previously published data for the same CS/HA-based materials, which had 93-94% viability. In terms of wound dressing development, it was noted that BC(CS/HA)5 had 94% viability after 5 days, which is above the safety limit of 92% for wound dressings. Thus, the BC(CS/HA)5 membrane is a possible future development with antibiotics to improve wound healing.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells