639-V
Cat.No.: CSC-C0456
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Ureter
Morphology: epithelial-like cells growing adherently in monolayers
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin +, cytokeratin-7 +, cytokeratin-8 +, cytokeratin-17 -, cytokeratin-18 +, cytokeratin-19 +, desmin -, endothel -, EpCAM -, GFAP -, neurofilament -,
The 639-V cell line was originally derived from malignant urinary bladder carcinoma. In short, it is an epithelial-like cell line that was first obtained from the tumor tissue and displays the general morphology and traits of cancerous cells like adherent growth and heteroploid karyotype. Functionally, 639-V cells are used as a model for pathogenesis and progression of urothelial carcinoma. They express tumorigenic properties, and therefore, they are applied in oncological research to understand the mechanisms of uncontrolled cell proliferation, apoptosis resistance, and response to stress conditions. Notably, 639-V is extensively used for chemosensitivity and cytotoxicity assays. The cell line is frequently utilized for screening and assessing the efficacy of new chemotherapeutic agents and anticancer drugs, providing valuable pre-clinical data on the tumor cell response to treatment.
In addition, 639-V can be used for research into gene expression profiles, biomarker discovery, and molecular pathways of bladder cancer, and general cancer-related conditions as well, for example, the involvement of tumor suppressor genes and oncogenes. Tumor microenvironment interactions such as angiogenesis and invasion can also be explored through this cell line.
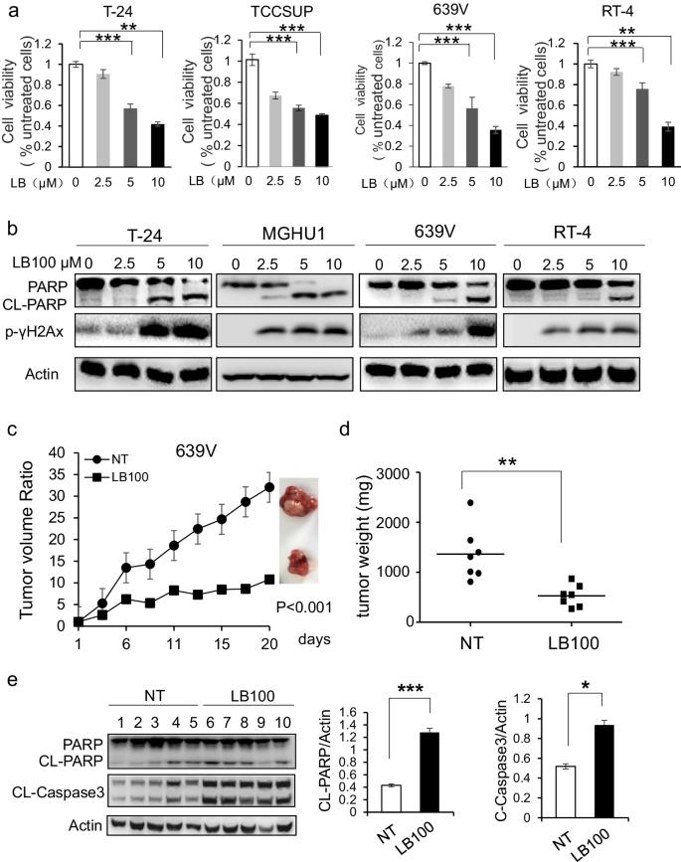
LB100 alone Induces DNA Damage and Apoptosis in BLCA Cells
Bladder carcinoma (BLCA) is a common urinary tract cancer with poor chemotherapy response. Protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) regulates cellular processes like apoptosis and DNA-damage response. LB100, a PP2A inhibitor, enhances chemotherapy in various cancers, but its effects in BLCA are unknown. Gao's team tested LB100's cytotoxicity on 7 BLCA cell lines (T24, MGHU1, TCCSUP, 639 V, RT-4, RT112 and 97-1) using a viability assay and found it reduced cell viability dose-dependently (Fig. 1a). LB100 also induced γH2AX phosphorylation and Parp1 cleavage without changing PP2A expression (Fig. 1b). In a 639 V xenograft mouse model, LB100 significantly reduced tumor volumes without weight loss (Fig. 1c, d) and increased cleaved Parp1 and Caspase3 levels (Fig. 1e). These results indicate LB100 can induce DNA damage and apoptosis in BLCA cells both in vitro and in vivo.
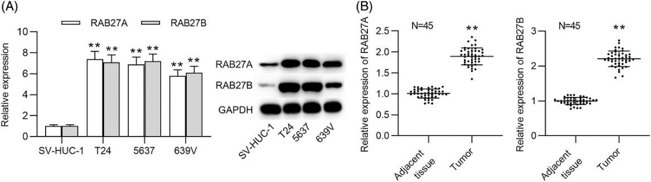
RAB27A/B Expression is Upregulated in Bca Tissues and Cells
Bladder cancer (BCa) is a common malignancy of the urinary system. RAB27A and RAB27B have been linked to tumor development, yet their functions in BCa are unknown. Zhang et al. explored the function and mechanism of RAB27A and RAB27B in BCa. They determined the mRNA expression and protein levels of RAB27A/B in BCa cells (T24, 5637 and 639 V) and urothelial cells (SV-HUC-1) utilizing RT-qPCR and western blot analyses. RAB27A/B expression levels were significantly increased in BCa cells, particularly in T24 and 5637 cells (Fig. 2A). Then, they evaluated the expression of RAB27A/B in adjacent nontumor tissues (n = 45) and BCa tissues (n = 45). RAB27A/B also had relatively high expression in tumor tissues than in nontumor tissues (Fig. 2B).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells