KKU-055
Cat.No.: CSC-C6854J
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Liver; Bile Duct
Morphology: Epithelial-Like
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
The KKU-055 cell line is a cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) cell line derived from Thailand. Liver fluke infection is one of the main etiological factors for CCA, which causes malignant transformation of bile duct epithelial cells through chronic inflammation and DNA oxidative damage. KKU-055 was established during liver fluke infection studies and serves as an essential model for researching cholangiocarcinoma associated with liver fluke infections. This cell line can be used to study how liver fluke infection induces chronic inflammation and DNA damage in bile duct epithelial cells and how these two mechanisms contribute to malignant transformation. Moreover, it can also be used to study how liver fluke eggs in bile affect tumor growth and metastasis.
KKU-055 cell line shows stem cell-like properties, which form spheroids under ultra-low attachment culture condition and exhibit higher expression of stem cell markers (SOX2, CD44, CD147, and EpCAM) in stem cell culture medium. KKU-055 cells also showed higher proliferative activity but lower sensitivity to some chemotherapeutic agents under stem cell culture condition. Consequently, this cell line could be used for cancer stem-like cell related studies, such as tumor initiation, progression, and metastasis, and development of novel therapies against stem cell-like properties regulation.
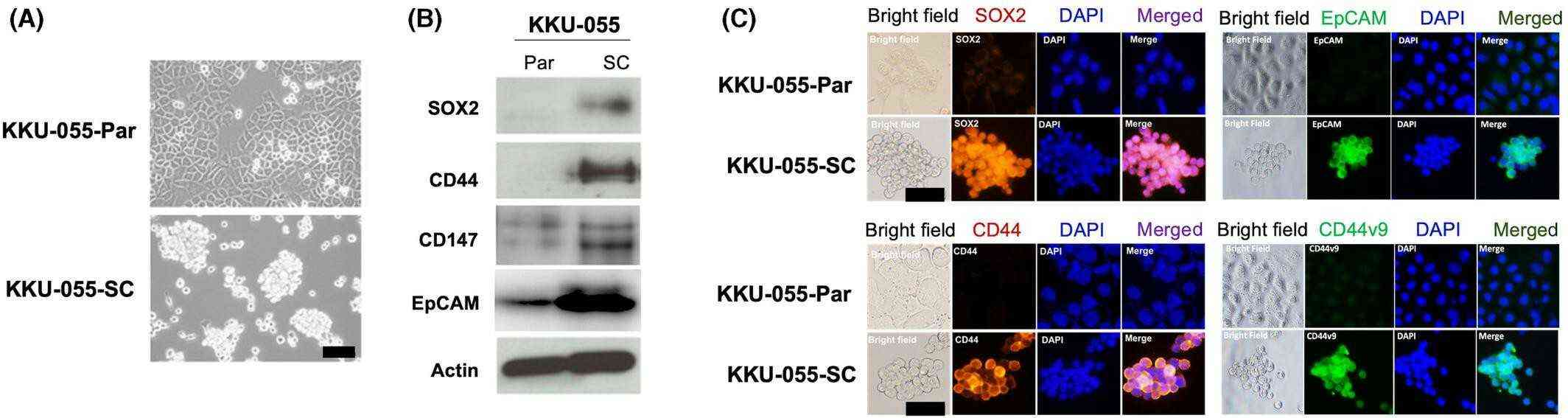 Fig. 1. Morphology and stem cell marker expression of parental KKU-055 cells (KKU-055-Par) and KKU-055 sphere cells (KKU-055-SC; 50th passage) (Panawan O, Silsirivanit A, et al., 2023).
Fig. 1. Morphology and stem cell marker expression of parental KKU-055 cells (KKU-055-Par) and KKU-055 sphere cells (KKU-055-SC; 50th passage) (Panawan O, Silsirivanit A, et al., 2023).
IL4RPep-1 Preferentially Binds to IL-4R-High CCA Cells
Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) has a poor prognosis and high chemoresistance. Interleukin-4 receptor (IL-4R) is overexpressed in several cancer cells and plays a crucial role in tumor progression and drug resistance. IL4RPep-1, an IL-4R-binding peptide, has been identified by phage display and used for tumor targeting. In this study, Permpoon et al. exploited IL4RPep-1 to guide the tumor-specific delivery of a proapoptotic peptide to chemoresistant CCA, thereby inhibiting tumor growth.
They used two CCA cell lines, KKU-213 and KKU-055, that are derived from liver fluke-associated intrahepatic CCA for examining the binding of IL4RPep-1 to CCA cells. Flow cytometric analysis showed that KKU-213 cells expressed IL-4R at higher levels than KKU-055 cells (Fig. 1A). Accordingly, FITC-labeled IL4RPep-1 preferentially bound to IL-4R-high KKU-213 cells over IL-4R-low KKU-055 cells (Fig. 1B). Immunofluorescence microscopy also showed that IL-4R was highly expressed on the KKU-213 cell membrane compared with KKU-055 cells, and IL4RPep-1, but not the control peptide, bound to KKU-213 cells and was colocalized with IL-4R at the cell membrane (Fig. 1C). Next, we determined IL4RPep-1 binding affinity (KD) to CCA cells using LigandTracer Green to analyze the real-time binding kinetics of living cells. The KD values of IL4RPep-1 binding to KKU-213 and KKU-055 cells were 3.5 ± 1.9 × 10–6 and 3.2 ± 1.8 × 10–1 M, respectively (Fig. 1D). To further examine the specificity of peptide binding, we competed for the binding of IL4RPep-1 with the anti-IL-4R antibody. The binding of IL4RPep-1 was inhibited in a dose-dependent manner by the anti-IL-4R antibody (Fig. 1E).
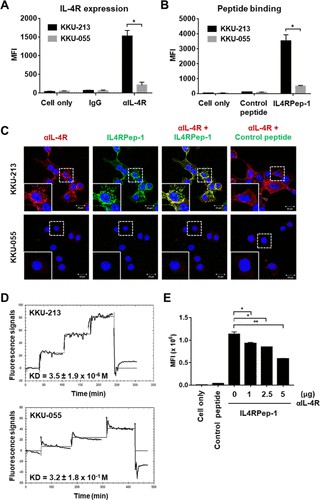 Fig. 1. IL-4R expression and IL4RPep-1 binding to CCA cell lines (Permpoon U, Khan F, et al., 2020).
Fig. 1. IL-4R expression and IL4RPep-1 binding to CCA cell lines (Permpoon U, Khan F, et al., 2020).
Liraglutide Reduced Migration Ability of iCCA Cells
The effect of GLP-1R agonist on risk and progression of cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is uncertain. The present study was designed to investigate the roles of GLP-1R and its agonists on intrahepatic CCA (iCCA) progression. To investigate the effect of GLP-1R agonists on iCCA cell proliferation, we performed in vitro experiments with iCCA cell lines. The expression of GLP-1R protein was confirmed in all iCCA cell lines examined by western blotting, with no statistically significant difference in the expression levels between four iCCA cell lines (Fig. 2a, b). Two iCCA cell lines with different histological grades (KKU-055 and KKU-213A) were selected for further study. The effects of two GLP-1R agonists, exendin-4 and liraglutide, on iCCA cell proliferation were investigated. Neither of the two agonists significantly affected iCCA cell proliferation at concentrations up to 1000 nM (Fig. 2c). As lagirlutide is more structurally similar to native GLP-1 and its effect on iCCA has not been studied previously, it was selected for further study as a representative GLP-1R agonist. Although GLP-1R agonist did not affect iCCA cell proliferation in vitro, another study showed that exendin-4 could significantly inhibit the migration of non-Ov-associated CCA cells. The effect of liraglutide on iCCA cell migration was further investigated. Liraglutide significantly inhibited the migration of both KKU-055 and KKU-213A iCCA cells at the same rate (Fig. 3a, b).
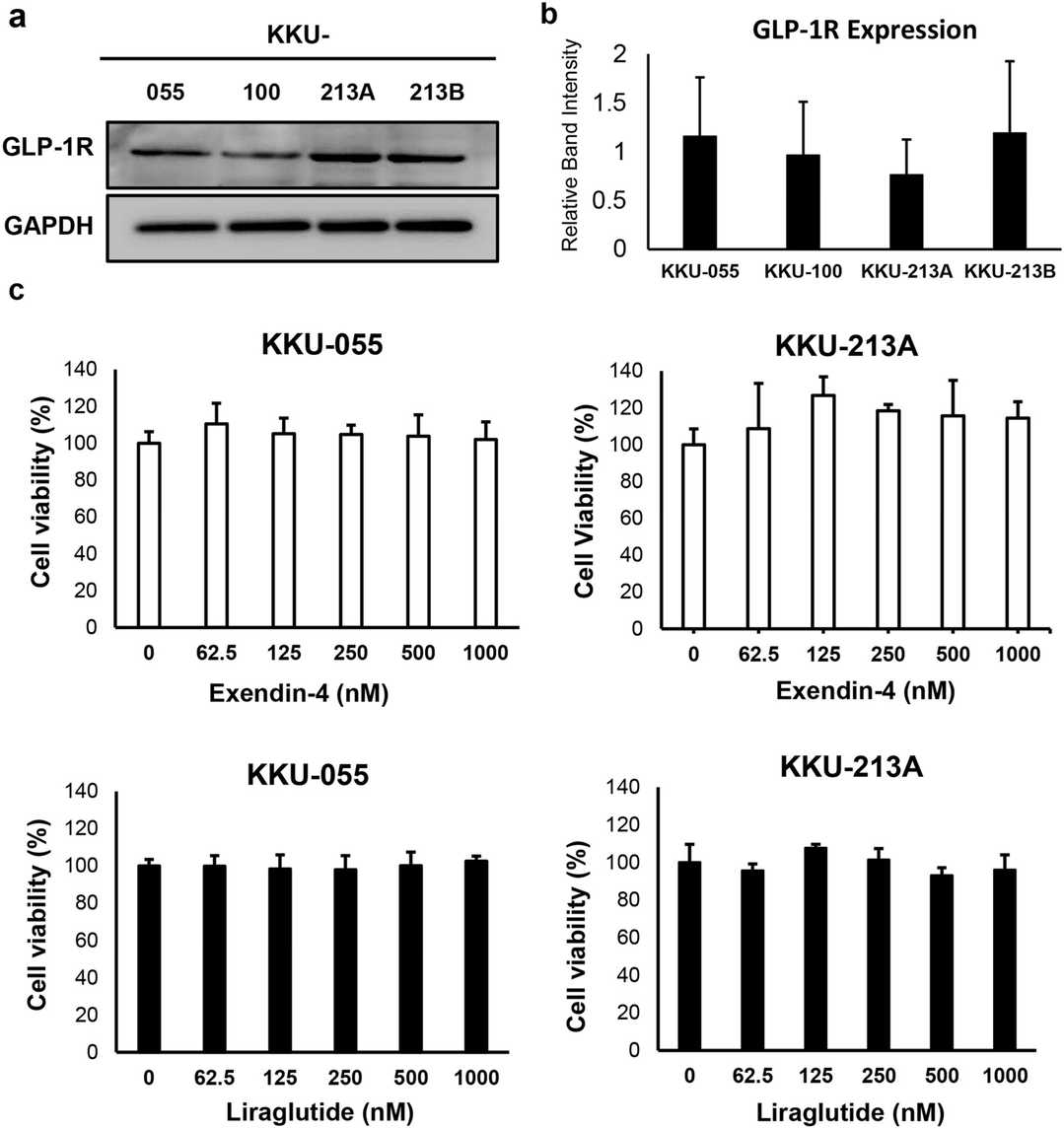 Fig. 2. Liraglutide inhibits Akt and STAT3 pathways in CCA cells (Trakoonsenathong R, Kunprom W, et al., 2024).
Fig. 2. Liraglutide inhibits Akt and STAT3 pathways in CCA cells (Trakoonsenathong R, Kunprom W, et al., 2024).
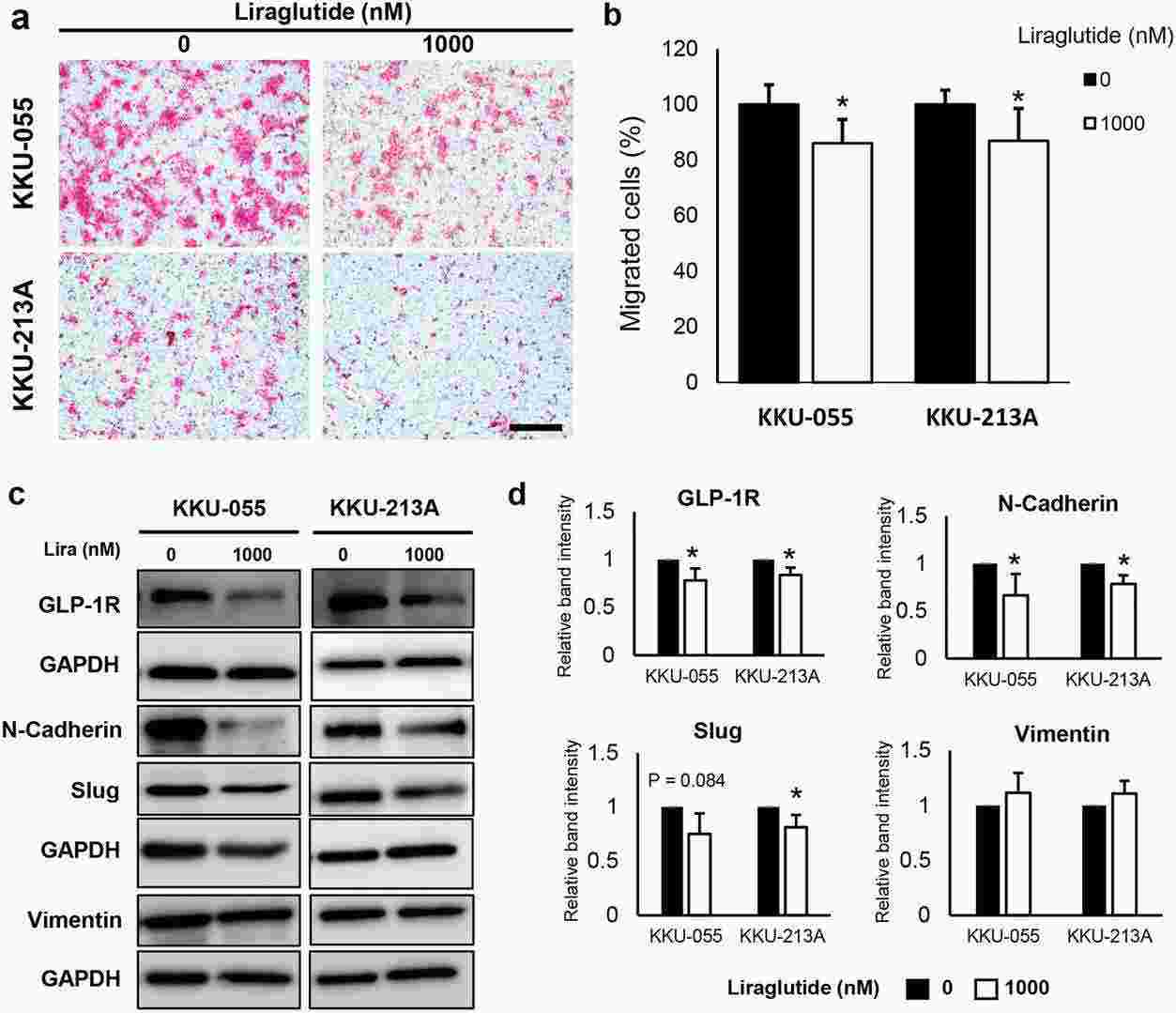 Fig. 3. Liraglutide suppresses the migration of CCA cells by suppressing the expression of GLP-1R and epithelial-mesenchymal (EMT) markers (Trakoonsenathong R, Kunprom W, et al., 2024).
Fig. 3. Liraglutide suppresses the migration of CCA cells by suppressing the expression of GLP-1R and epithelial-mesenchymal (EMT) markers (Trakoonsenathong R, Kunprom W, et al., 2024).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells





