Immortalized Human Aortic Endothelial Cells-SV40
Cat.No.: CSC-I9140L
Species: Homo sapiens
Source: Aorta
Morphology: Polygonal
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Note: Never can cells be kept at -20 °C.
CIK-HT013 HT® Lenti-hTERT Immortalization Kit
CIK-HT003 HT® Lenti-SV40T Immortalization Kit
Human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) originate from the human aorta which serves as the main artery for transporting oxygenated blood from the heart to every part of the body. The SV40 large T antigen immortalizes these cells through transfection by disrupting tumor suppressor pathways that allow for infinite cell division. HAECs embedded in the innermost layer of the aortic wall experience direct hemodynamic shear stress from blood flow. These cells release both vasoactive mediators and anti-coagulant factors which serve to maintain vascular stability and control blood pressure and thrombus formation.
HAECs produce angiogenesis-related cytokines such as VEGF and PAF and form tubular structures that mimic natural blood vessel development under appropriate conditions. The presence of external stimuli including TNF-α induces these cells to produce more inflammation-related molecules such as adhesion proteins ICAM-1 and VCAM-1. These special properties make them a widely used model in vascular disease research to understand pathogenesis processes of diseases like atherosclerosis and hypertension as well as thrombosis. HAECs maintain their endothelial-specific functions which makes them perfect models for testing anticancer drugs' cytotoxic effects and their ability to fight tumors.
β-Toxin Targets the Production of Angiogenic Proteins Involved in Proliferation and Migration
Staphylococcus aureus causes serious infections such as infective endocarditis and releases multiple virulence factors including β-toxin which exhibits sphingomyelinase and biofilm ligase functions. The production of these activities leads to endothelial dysfunction and impaired wound healing through their adverse effects on endothelial cells' growth and movement capabilities.
Tran et al. explored how S. aureus β-toxin impacts the release of proteins associated with angiogenesis in cultured immortalized human aortic endothelial cells (iHAECs). The researchers analyzed 48 proteins in iHAECs exposed to proangiogenic, antiangiogenic, and toxin treatments using a proteome array. The primary proteins released by endothelial cells in growth medium included serpin E1, endothelial growth factor (EGF), and thrombospondin-1 as shown in Figure 1. These proteins enable matrix breakdown and cell growth along with migration, which are characteristic of angiogenic environments. VEGF increased IL-8 production by 1.5-fold (Fig. 2), validating proangiogenic settings. Axitinib demonstrated antiangiogenic activity through the reduction of multiple protein secretions which matched its inhibitory function (Fig. 2). β-toxin demonstrated inhibitory properties at sublethal levels by reducing the levels of essential proteins needed for cell growth and movement which indicates its potential as an antiangiogenic agent (Fig. 2).
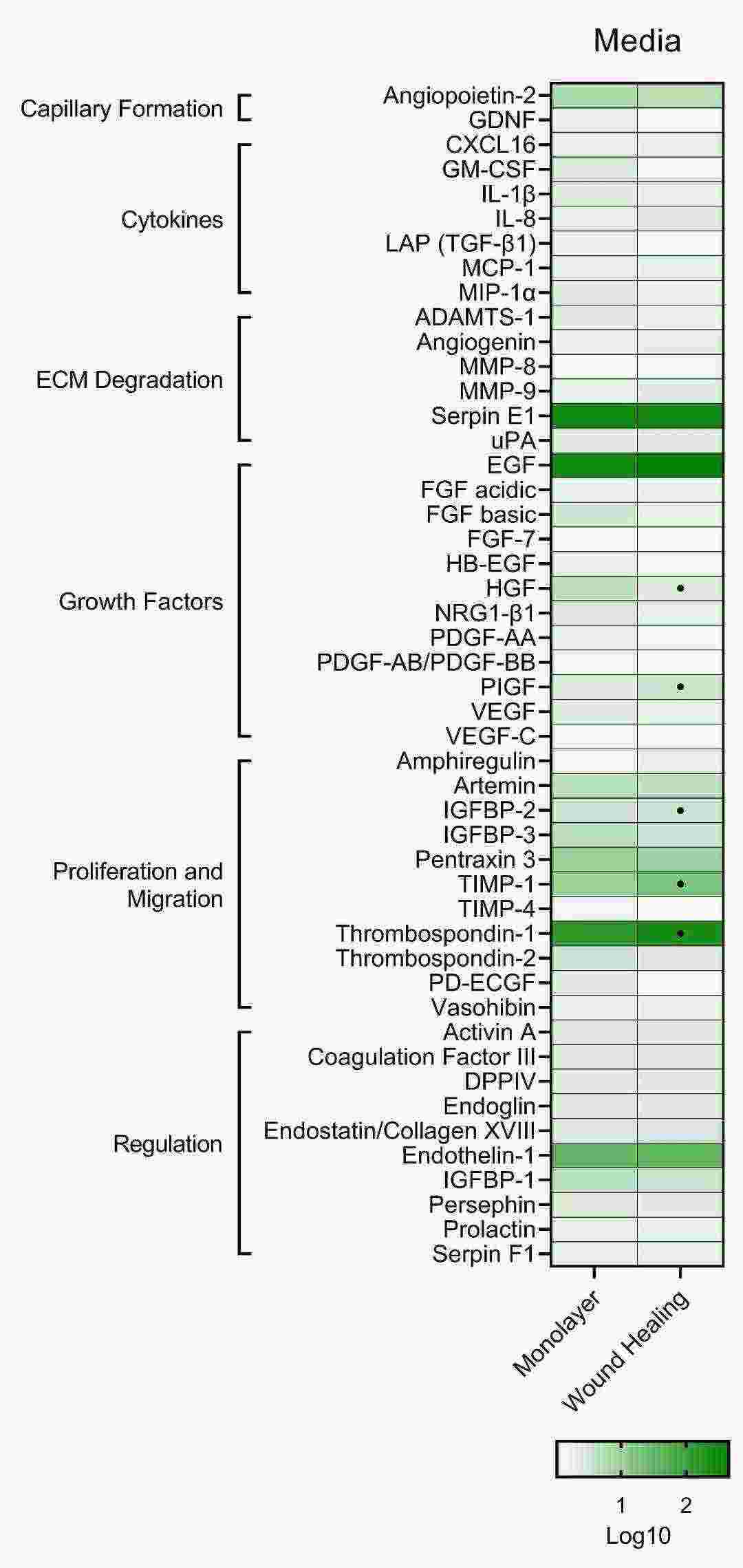 Fig. 1. Proteome analysis of untreated iHAECs grown to confluency on 1% gelatin-coated plates (Tran PM, Tang SS, et al., 2022).
Fig. 1. Proteome analysis of untreated iHAECs grown to confluency on 1% gelatin-coated plates (Tran PM, Tang SS, et al., 2022).
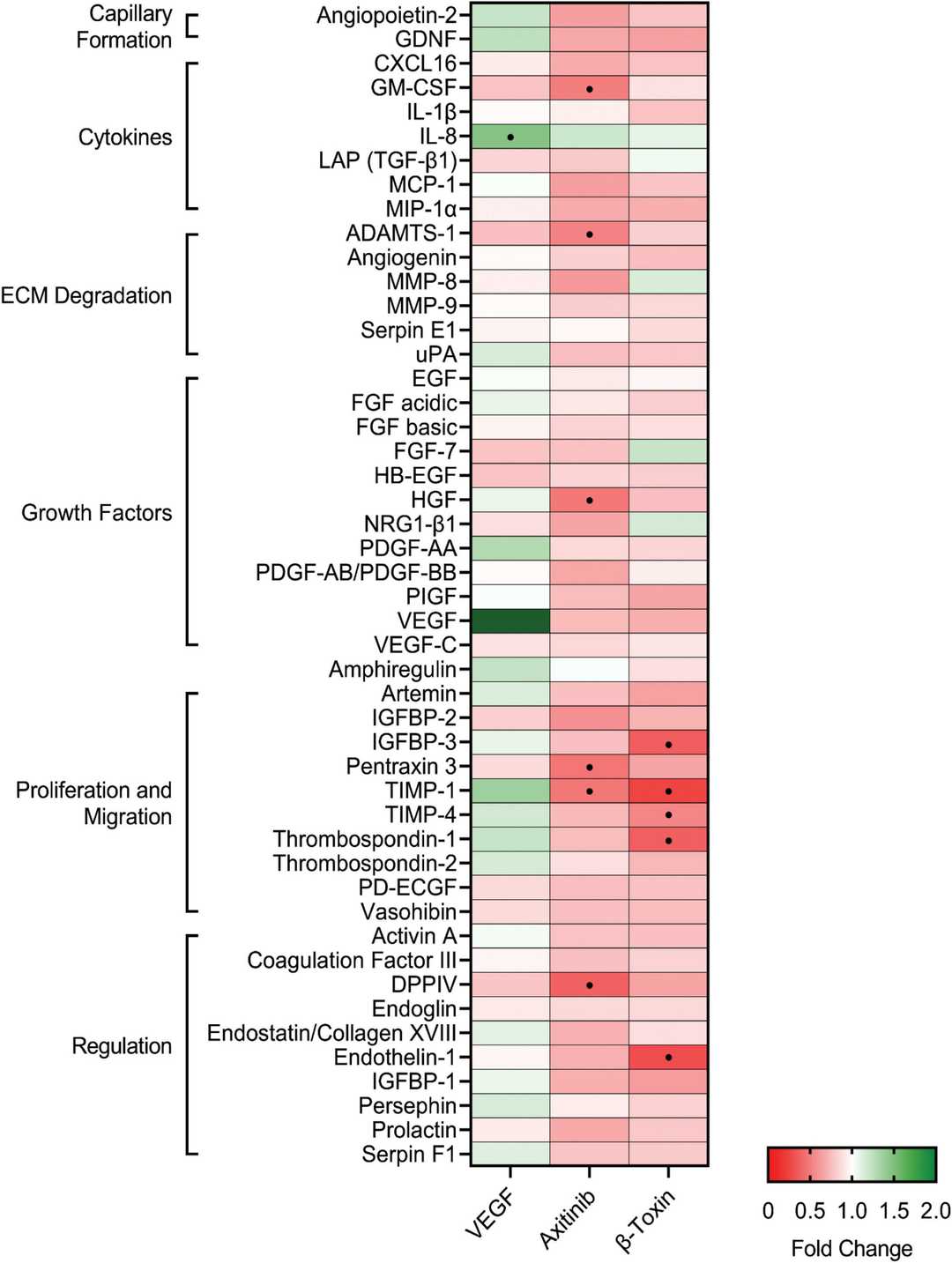 Fig. 2. β-toxin inhibits production of angiogenic proteins from human aortic endothelial cells in monolayer growth (Tran PM, Tang SS, et al., 2022).
Fig. 2. β-toxin inhibits production of angiogenic proteins from human aortic endothelial cells in monolayer growth (Tran PM, Tang SS, et al., 2022).
miR-31 Targets HIF1AN to Promote the Proliferation of Injured HAECs in vitro
Type 2 diabetes stands as a widespread metabolic disease that frequently results in serious health complications. VEGF and HIF molecules have essential functions in the formation of new blood vessels as well as vascular complications in diabetes. Current research highlights microRNAs such as miR-31 as potential targets for diabetes treatment because they regulate gene expression. Fu's team investigates how miR-31 affects type 2 diabetes and vascular damage by studying its connection with HIF-1α and VEGF-A in vitro and in vivo.
In order to imitate the high blood sugar environment in vivo, immortalized human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) was induced with high-fat and high-sugar to establish a cell damage model. Then the cells were transfected with miR-31 agomir to observe the effect of high expression of miR-31. The final concentration of miR-31 agomir used in the experiments was 50?nM as explored by immunofluorescence experiments (Fig. 3). The results showed that the proliferation ability of the cells in the DM group was weakened, and miR-31 could improve this effect, possibly because miR-31 targets HIF1AN and up-regulates the expression of HIF-1α and VEGF-A (Fig. 3).
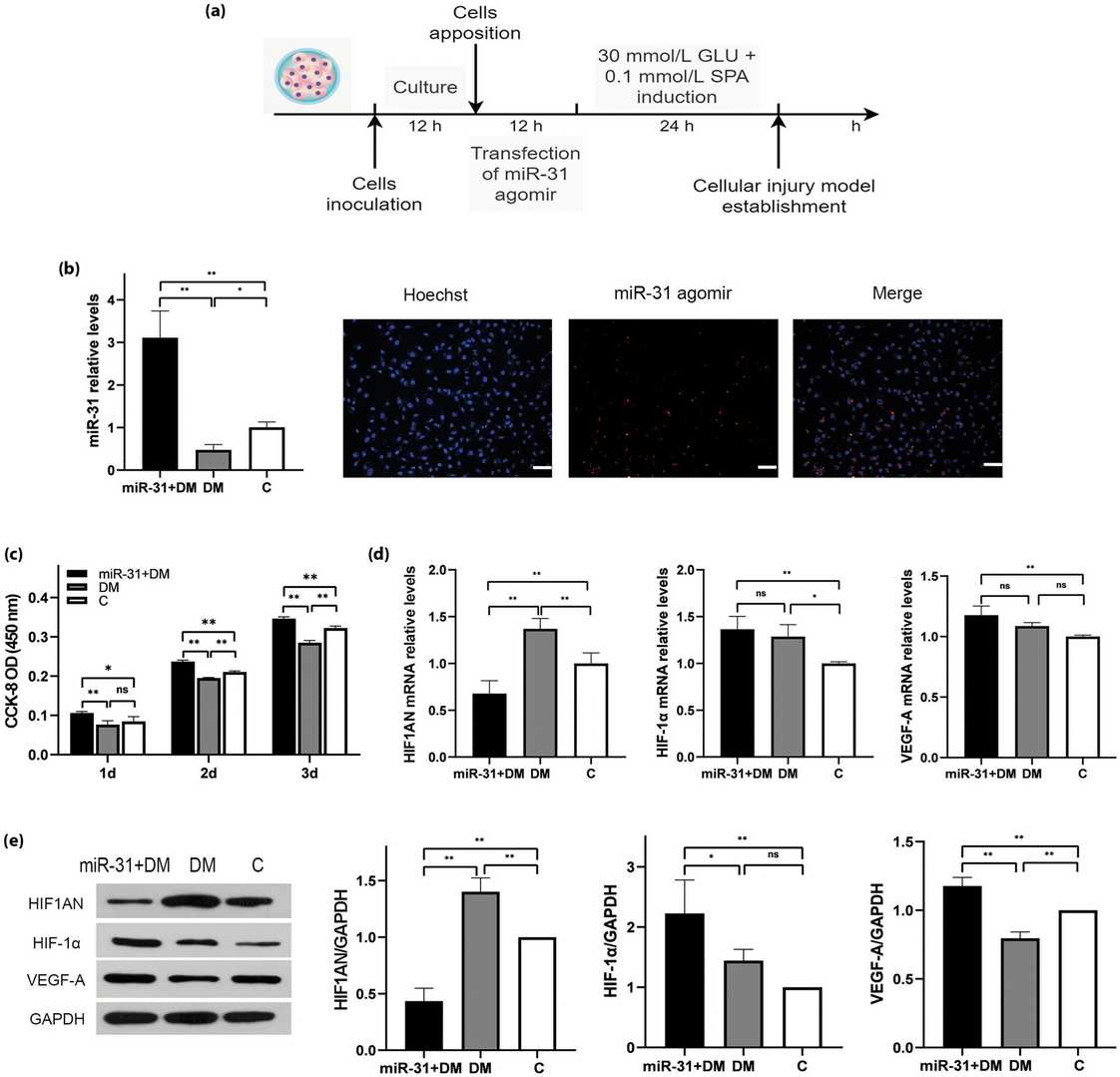 Fig. 3. miR-31 promotes the restoration of proliferation of damaged HAEC by targeting HIF1AN (Fu Y, Du R, et al., 2023).
Fig. 3. miR-31 promotes the restoration of proliferation of damaged HAEC by targeting HIF1AN (Fu Y, Du R, et al., 2023).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells
