Human iPSC-Derived Motor Neurons
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
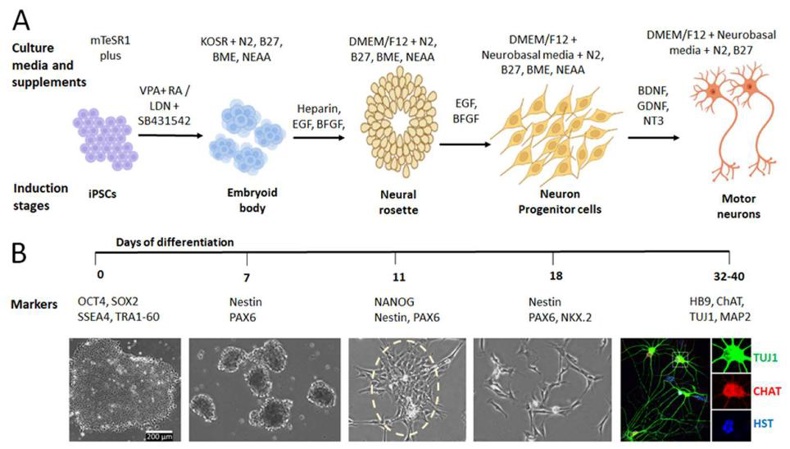
Human induced pluripotent stem cell‑derived motor neurons (hiPSC‑MNs) are a physiologically relevant in vitro model that recapitulates the native human spinal motor neuron in terms of morphology, electrophysiology and molecular identity. Starting from readily accessible somatic cells (skin fibroblasts, peripheral blood mononuclear cells, urine‑derived epithelial cells, etc. ), the Yamanaka factors reprogram the cells into iPSCs which can then be guided through a staged differentiation protocol: early neural induction (using retinoic acid (RA) and Sonic hedgehog (SHH) agonists), expansion of motor‑neuron progenitors (OLIG2⁺/NKX6.1⁺) and final maturation (using sustained RA, Purmorphamine and neurotrophic factors (BDNF, GDNF, CNTF)). HB9⁺/ISL1⁺ motor neurons emerge within 10-14 days and after 3-4 weeks they have acquired long, branched axons, express ChAT, VAChT and form functional synapses, as evidenced by action‑potential firing, calcium transients and neuromuscular junction (NMJ) formation in co‑culture with human myotubes. hiPSC‑MNs have become essential for disease modeling (ALS, SMA, etc.), gene editing, high‑throughput drug screening and transcriptomic or proteomic profiling.
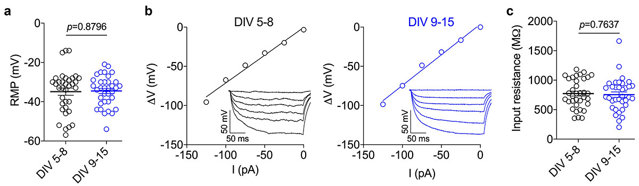
Passive Membrane Properties of iPSC-Derived Motor Neurons
Motor neuron diseases are challenging to study due to the lack of human-specific models. Induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived motor neurons offer a solution by enabling human-specific disease modeling and drug screening. However, the electrophysiological properties and maturation of commercially available iPSC-derived motor neurons need validation.
To determine the passive membrane properties of iPSC-derived motor neurons, Jurkovicova-Tarabova et al. performed patch-clamp recordings at two different time points (DIV 5-8 and DIV 9-15). Resting membrane potential (RMP) was not significantly different between the two time points (-34.9 ± 1.8 mV at DIV 5-8 and -34.5 ± 1.3 mV at DIV 9-15, p = 0.8796) (Fig. 1a). Input resistance was measured by injection of small hyperpolarizing currents to determine I/V relationship which was then fitted with linear regression. This measure was not significantly different between DIV 5-8 (772.8 ± 40.7 MΩ) and DIV 9-15 (754.0 ± 46.1 MΩ, p = 0.7637) (Fig. 1b and c). They also performed daily recordings from DIV 5 to DIV 15, and did not find any significant difference day-to-day (ANOVA, data not shown). Taken together, these data show that the passive membrane properties of iPSC-derived motor neurons do not change significantly over the culture time course.
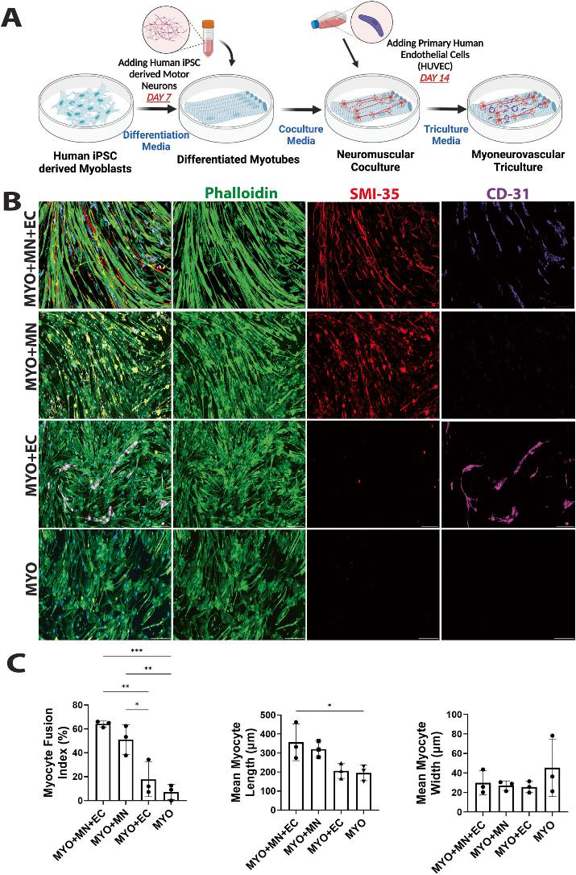
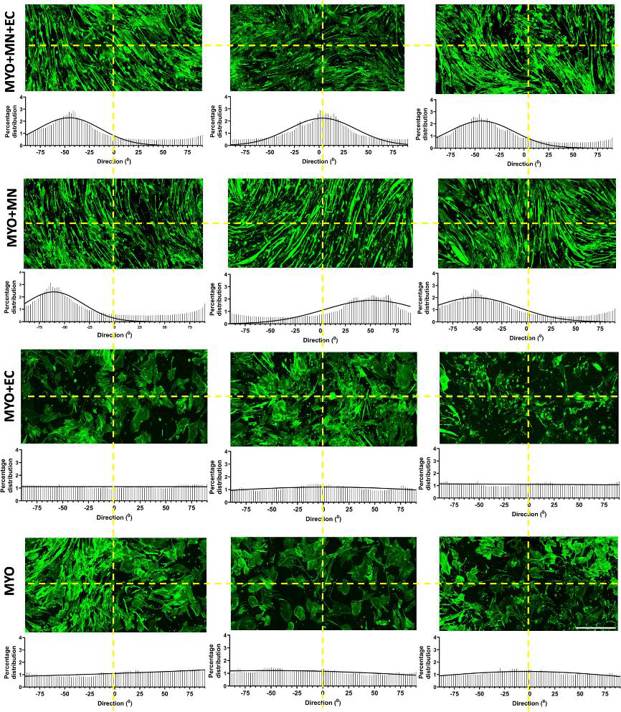
Motor Neurons and Endothelial Cells Additively Promote Development and Fusion of Human iPSC-Derived Skeletal Myocytes
Neurovascular cells significantly impact skeletal muscle biology by regulating myogenesis, maturation, and regeneration. Das et al. established an in vitro model using iPSC-derived skeletal myocytes, motor neurons, and primary endothelial cells to examine the combinatorial effects of neural and vascular cells on muscle maturation in a triculture system.
Human iPSC-derived skeletal muscle progenitor cells (SMPCs) were differentiated for 7 days and were then co-cultured with iPSC-derived motor neurons (MN). After 7 days of neuromuscular coculture, human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were added, and cells were maintained for 7 more days. Characteristic markers (F-actin, hypo-phosphorylated neurofilament, CD31) were expressed in all groups (Fig. 2A), suggesting favorable conditions for cell growth and survival. Motor neurons promoted myofiber alignment in MYO + MN and MYO + MN + EC groups (Fig. 3). Morphological parameters (length, width, polynucleation) were quantified. Motor neurons alone and in combination with endothelial cells increased myofiber fusion, length, and alignment (Fig. 2B, Fig. 3). Endothelial cells alone did not significantly affect myofiber fusion or elongation. Neither cell type affected myofiber diameter. These findings suggest that motor neurons and endothelial cells together enhance myofiber maturation.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells