M-07e
Cat.No.: CSC-C0249
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Blood; Peripheral Blood
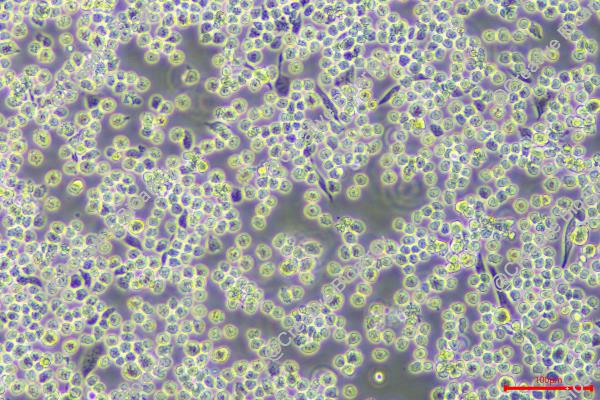
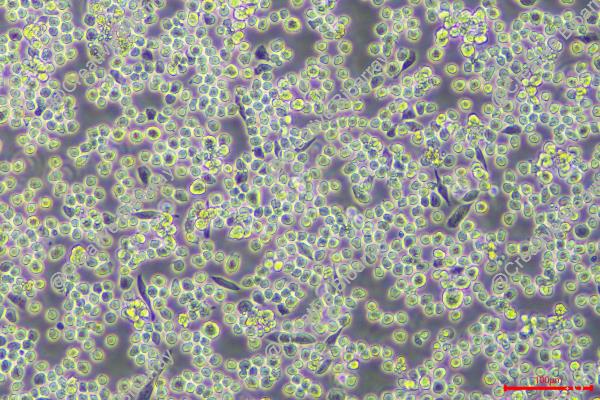
Morphology: single round cells in suspension, a few cells are lightly adherent
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: CD3 -, CD13 +, CD14 -, CD19 -, CD33 +, HLA-DR -
Viruses: ELISA: reverse transcriptase negative; PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HHV-8 -, HIV -, HTLV-I/II -, SMRV -
The M-07e cell line is a highly significant and well-characterized model system in the field of acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AML M7) research. This cell line was established in 1987 from the peripheral blood of a 6-month-old girl who was diagnosed with AML M7 at the time of disease presentation.
One of the defining characteristics of the M-07e cell line is its responsiveness to a wide range of cytokines and growth factors, including GM-CSF, interferons, interleukins, nerve growth factor, stem cell factor, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. This broad cytokine sensitivity reflects the diverse signaling requirements of the underlying megakaryoblastic leukemia. Importantly, the researchers have observed that the M-07e cell line can rapidly become cytokine-independent, potentially due to the outgrowth of cells that have acquired autonomous growth capabilities.
The ability to maintain the M-07e cell line in vitro and study its cytokine responsiveness and transition to cytokine independence has been instrumental in advancing the understanding of the pathogenesis of AML. Researchers have utilized this model system to elucidate the signaling cascades, genetic alterations, and cellular mechanisms that contribute to the development and progression of this rare and challenging leukemic subtype.
M-07e Cell Line as a Bioassay for the Human Cytokines GM-CSF and IL-3
M-07e cell line requires either interleukin-3 (IL-3) or granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) for growth, even in the presence of fetal calf serum. This cell line will not grow long-term in any other cytokine although it responds slightly to IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-9, and interferon-gamma. The M-07e subline was used to develop a quantitative bioassay for the measurement of levels of either GM-CSF or IL-3.
To estimate the level of activity of either GM-CSF or IL-3 in samples containing both, the alternate cytokine activity must be neutralized and the residual activity compared to the activity obtained after both factors have been neutralized. This procedure is illustrated in Fig. 1. Neutralization of both factors is required to demonstrate that no other cytokines present in the sample contribute to the measured activity. In this case, IL-3 levels are estimated from the difference between the activity of the conditioned medium after the GM-CSF has been neutralized and the activity after both the IL-3 and GM-CSF have been inactivated. Simple inhibition of the IL-3 with anti-IL-3 does not accurately reflect IL-3 levels because residual GM-CSF in the sample can compensate for the decrease in incorporation expected from inactivation of the IL-3.
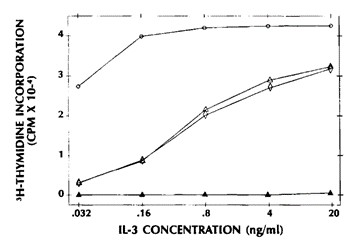 Fig. 1 Measurement of IL-3 in the presence of GM-CSF in the M-07e proliferation assay. (Avanzi GC, et al., 1990)
Fig. 1 Measurement of IL-3 in the presence of GM-CSF in the M-07e proliferation assay. (Avanzi GC, et al., 1990)
Downregulation of MIR100HG Induces Apoptosis in M-07e Cells
Long noncoding ribonucleic acids (lncRNAs) are RNA molecules longer than 200 nucleotides without protein-coding capacity. Several studies have shown that lncRNAs play a pivotal role in the initiation, maintenance, and progression of AML, which could make them a promising candidate in the diagnosis and treatment of leukemia.
MIR100HG was downregulated in a human AML cell line (M-07e) using Antisense LNA GapmeRs. The transfection efficiency of M-07e cells was determined based on fluorochrome-conjugated oligonucleotides with fluorescence microscopy. The optimized transfection of M-07e cells was assessed to be about 90% (Fig. 2). The expression level of lncRNA MIR100HG in M-07e cells, transfected by Antisense LNA GapmeRs, was measured at different time points (24, 48, and 72 h post-transfection) by qRT-PCR. A significant decrease was observed in the expression level of lncRNA MIR100HG in the Antisense LNA GapmeRs group compared to the other groups (Antisense LNA GapmeRs Negative Control (ALGNC group), control and Mock control (untreated groups)) (Fig. 3).
The effect of lncRNA MIR100 HG suppression on apoptosis and necrosis was assessed by flow cytometry. LncRNA MIR100 HG suppression by Antisense LNA GapmeRs considerably increased the apoptotic ratio in the Antisense LNA GapmeRs group at three different times compared to ALGNC transfected cells and untreated control groups (Fig. 4). No significant differences were observed between ALGNC and untreated control groups by flow cytometric assays.
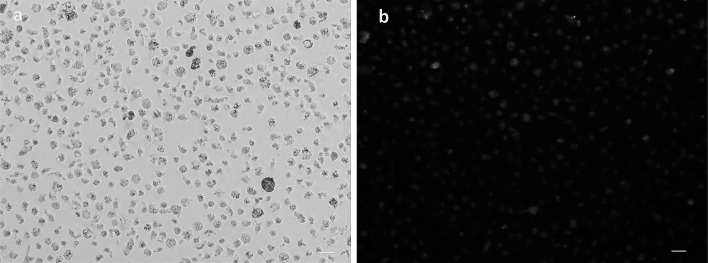 Fig. 2 Represents the evaluation transfection efficiency of M-07e cells with a fluorescent microscope. (Bagheri P, et al., 2021)
Fig. 2 Represents the evaluation transfection efficiency of M-07e cells with a fluorescent microscope. (Bagheri P, et al., 2021)
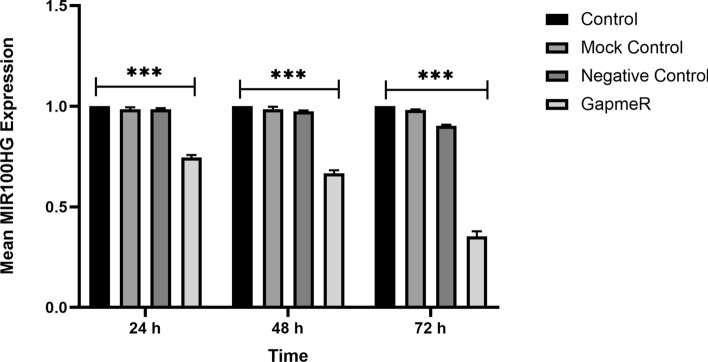 Fig. 3 Indicates the evaluation of the MIR100HG level by qRT-PCR assay at 24, 48, and 72 h after the transfection. (Bagheri P, et al., 2021)
Fig. 3 Indicates the evaluation of the MIR100HG level by qRT-PCR assay at 24, 48, and 72 h after the transfection. (Bagheri P, et al., 2021)
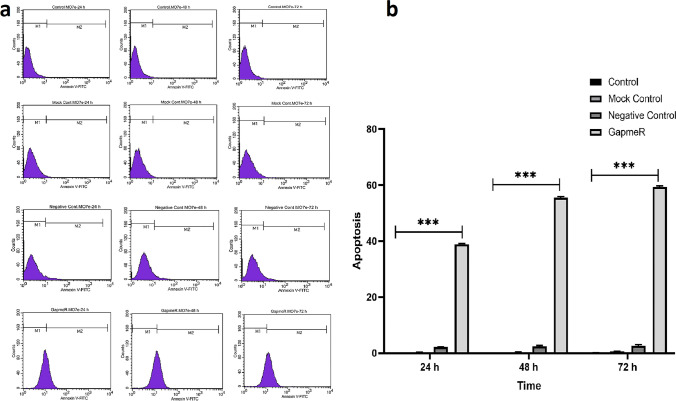 Fig. 4 Implies the evaluation of apoptosis utilizing the Annexin-V staining performed at 24, 48, and 72 h after the transfection. (Bagheri P, et al., 2021)
Fig. 4 Implies the evaluation of apoptosis utilizing the Annexin-V staining performed at 24, 48, and 72 h after the transfection. (Bagheri P, et al., 2021)
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells