Okadaic Acid Induced Model
Neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) containing hyperphosphorylated aggregates of the protein tau, a widely known pathological hallmarker of Alzheimer's disease, closely related with the severity of dementia in AD patients. Okadaic acid (OKA) is a selective and potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase that was used to induce dementia in rats by microinjecting it into the dorsal lateral hippocampal region.
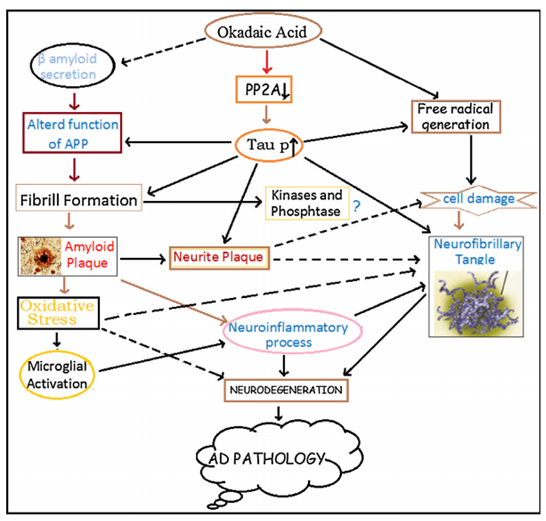 Figure. 1. Schematic diagram showing the involvement of OKA in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease.
Figure. 1. Schematic diagram showing the involvement of OKA in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease.
Our capabilities
- We can provide comprehensive behavioral and cognitive testing on AD model and the drug screening.
- We can utilize LTP (long-term potentiation) assay to evaluate your preclinical drug candidates against the synaptic impairments in animals.
- We can evaluate anti-oxidative stress in the hippocampus of animals treated with drug candidates.
- We can evaluate various biomarkers through WB, IHC, ELISA, sequencing, etc.
Assays available
- Learning and memory deficits tests
- Synaptic impairment
- Oxidative stress
- Neuroinflammation
- Phosphorylated tau
- Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3β)
- Neurofilament Light Chain levels
- Neuronal loss
- β-AP level
- Plaque load
- β-sheet load
- pE(3)-Aβ load
- Enzyme activity related to cholinergic system
- NMDA receptor function and excitotoxicity
- Mitochondrial dysfunction
- Brain slice staining and synaptic electrophysiology
- Blood brain barrier homeostasis
- Cerebral vascular angiopathy (CAA)
With 10 years of hard working and continuous development, as a senior leader specialize in AD research with enormous industrial experience, Creative Bioarray is exceptional to be worked with for you. We will make our best efforts to meet your unique requires by providing individually customized service.
Study examples
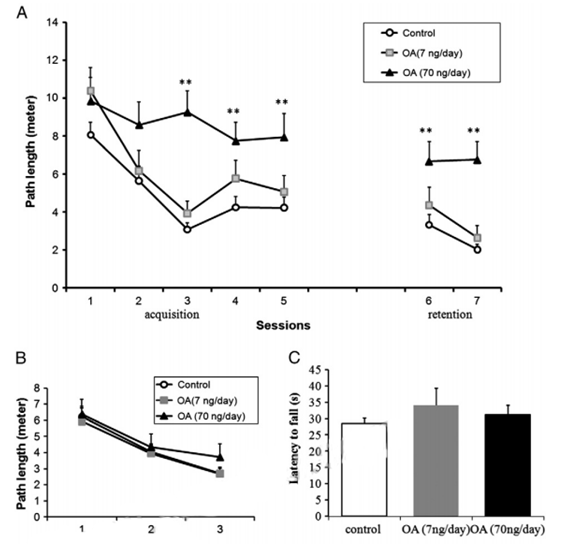 Figure. 2. MWM performance of rats infused with OA for 14 days. (A) The behavior test in the MWM started after 14 days of microinfusion of OA or vehicle into the dorsal hippocampus of the rats. The swimming path length to the escape platform was recorded to assess learning ability (acquisition test) and memory ability (retention test). After regular MWM, a visible MWM test (B) was performed and followed by rotarod tests (C). Control: 1% DMSO in artificial spinal–cerebral fluid, n= 20. Treatment groups: OA (7 or 70 ng/day) was microinfused into unilateral dorsal hippocampal area for 14 days, n= 10/group. Data were represented in mean±SEM. **p< 0.01 between control and OA (70 ng/day) groups.
Figure. 2. MWM performance of rats infused with OA for 14 days. (A) The behavior test in the MWM started after 14 days of microinfusion of OA or vehicle into the dorsal hippocampus of the rats. The swimming path length to the escape platform was recorded to assess learning ability (acquisition test) and memory ability (retention test). After regular MWM, a visible MWM test (B) was performed and followed by rotarod tests (C). Control: 1% DMSO in artificial spinal–cerebral fluid, n= 20. Treatment groups: OA (7 or 70 ng/day) was microinfused into unilateral dorsal hippocampal area for 14 days, n= 10/group. Data were represented in mean±SEM. **p< 0.01 between control and OA (70 ng/day) groups.
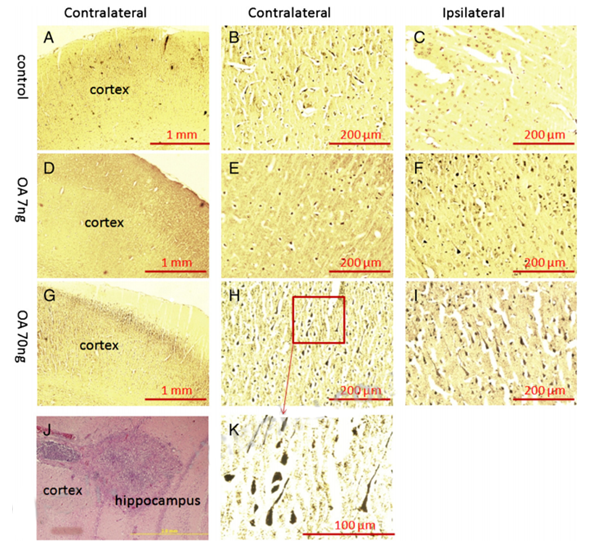 Figure. 3. Bielschowsky silver staining of the cortex in OA-treated rats. After the behavioral tests, half of rats received transcardiac perfusion with 4% formaldehyde in PBS, followed by immersion fixation of the removed brain. Then brain tissue was processed for paraffin sectioning, and 10-μm slides were prepared for silver staining. There was no positive staining found in either contralateral (A, B) or ipsilateral (C) cortex of control group. A few silver positive staining was found in the ipsilateral side of the cortex received low-dose OA (7 ng) infusion (F) but was not seen in the contralateral cortex (D, E). Much more silver positive staining was found in the both sides of cortex in high-dose OA group (G, H, I, K). The brain infusion cannula terminal was verified by H&E staining (J).
Figure. 3. Bielschowsky silver staining of the cortex in OA-treated rats. After the behavioral tests, half of rats received transcardiac perfusion with 4% formaldehyde in PBS, followed by immersion fixation of the removed brain. Then brain tissue was processed for paraffin sectioning, and 10-μm slides were prepared for silver staining. There was no positive staining found in either contralateral (A, B) or ipsilateral (C) cortex of control group. A few silver positive staining was found in the ipsilateral side of the cortex received low-dose OA (7 ng) infusion (F) but was not seen in the contralateral cortex (D, E). Much more silver positive staining was found in the both sides of cortex in high-dose OA group (G, H, I, K). The brain infusion cannula terminal was verified by H&E staining (J).
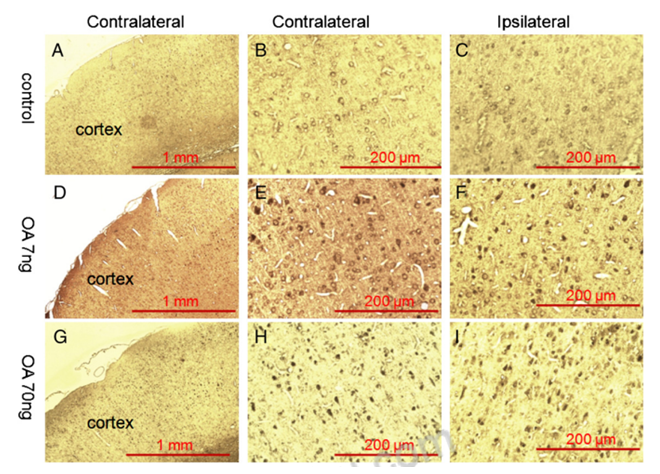 Figure. 4. Immunohistochemistry staining of the cortex in OA-treated rats. Fourteen days after microinfusion of OA into dorsal hippocampus unilaterally, rats were subjected to paraffin section preparation for immunohistochemistry staining and probed with antibody raised against phospho-tau (p-Thr205). There was no positive staining found in either side of the cortex in the control group (A, B, C). A few anti-p-Thr205 immunoreactivity positive staining was found on both side of the cortex in the rats that received low-dose OA infusion (D, E, F) and more positive staining was found in high-dose OA group (G, H, I).
Figure. 4. Immunohistochemistry staining of the cortex in OA-treated rats. Fourteen days after microinfusion of OA into dorsal hippocampus unilaterally, rats were subjected to paraffin section preparation for immunohistochemistry staining and probed with antibody raised against phospho-tau (p-Thr205). There was no positive staining found in either side of the cortex in the control group (A, B, C). A few anti-p-Thr205 immunoreactivity positive staining was found on both side of the cortex in the rats that received low-dose OA infusion (D, E, F) and more positive staining was found in high-dose OA group (G, H, I).
Quotation and ordering
If you have any special needs or questions regarding our services, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to cooperating with you in the future.
References
- Kamat P K et al. Okadaic acid induced neurotoxicity: An emerging tool to study Alzheimer's disease pathology[J]. NeuroToxicology, 2013, 37:163-172.
- Zhang Z et al. An okadaic acid-induced model of tauopathy and cognitive deficiency[J]. Brain Research, 2010, 1359(none):233-246.