Immortalized Mouse Lung Fibroblasts
Cat.No.: CSC-I2056Z
Species: Mouse
Morphology: Polygonal
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Note: Never can cells be kept at -20°C.
Mouse Lung Fibroblasts are isolated from lung tissue of mouse. Lung is one of the main respiratory organs, which is located in the thoracic cavity, is composed of five lobes and connected with larynx and nasal cavity by respiratory tract. Creative Bioarray immortalizes mouse lung fibroblasts (iMLF) by using viral vectors such as SV40 T antigen. Fibroblasts are the main cell type of loose connective tissue that differentiates from mesenchymal cells in embryo. In normal physiological function, MLFs are involved in repairing and maintaining lung tissue by synthesizing and secreting extracellular matrix (ECM) to support the structural integrity of lung tissue. In addition, MLFs are involved in lung immune responses and inflammation regulation, which are essential in infection and inflammatory diseases.
iMLFs serve as vital components in pulmonary fibrosis models used for investigating the disease's pathological mechanisms. They can also be used as in vitro models to simulate the pathological changes in lung tissue. For example, researchers found that lung fibroblasts differentiate into myofibroblasts after lung injury and promote fibrosis. Due to their ability to continuously proliferate and maintain a stable phenotype, these cells are often used in cytotoxicity testing of biomaterials.
TLR4 Signaling Has a Very Weak Effect on ER Stress-Induced SGs in Immortalized Mouse Lung Fibroblasts
Stress granules (SGs) are membraneless compartments formed in stressed cells, with roles in cellular homeostasis and chemotherapy resistance. Previous studies showed that innate immune signaling via Toll-like receptors (TLRs) inhibits SGs induced by endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in bone-marrow-derived macrophages. To test if this is generalizable, Lamichhane et al. examined TLR4 signaling effects on SGs in human lung cancer-derived A549 cells and mouse lung fibroblasts.
First, they confirmed that TLR signaling inhibits ER stress-induced SGs in BMDMs. However, TLR4 signaling had a weak effect on SGs in A549 lung cancer cells. Since A549 cells are human and BMDMs are mouse-derived, species differences might explain the discrepancy. To test this, they used immortalized mouse lung fibroblasts (iMLFs). They stimulated cells with 1 µg/mL LPS for 6 h before treating with 1 µg/mL thapsigargin for 1 h to induce ER stress and SGs. Like A549 cells, LPS had a weak effect on SGs (Fig. 1A and B) and did not significantly affect SGs induced by 500 mM sodium arsenite (Fig. 1A–C). Thus, the lack of TLR-mediated SG inhibition was not due to species differences. Since A549 cells are lung cancer cells, they likely express oncogenes that promote SG assembly. To test if oncogenes were responsible, they repeated the experiment with primary mouse lung fibroblasts (MLFs). Results showed that LPS did not significantly affect SGs induced by ER stress or sodium arsenite (Fig. 2A–C). However, TLR signaling inhibited SGs in oncogene-expressing immortalized BMDMs (iBMDMs) (Fig. 2D–G). These findings suggest that the effect is cell-intrinsic and independent of oncogene expression.
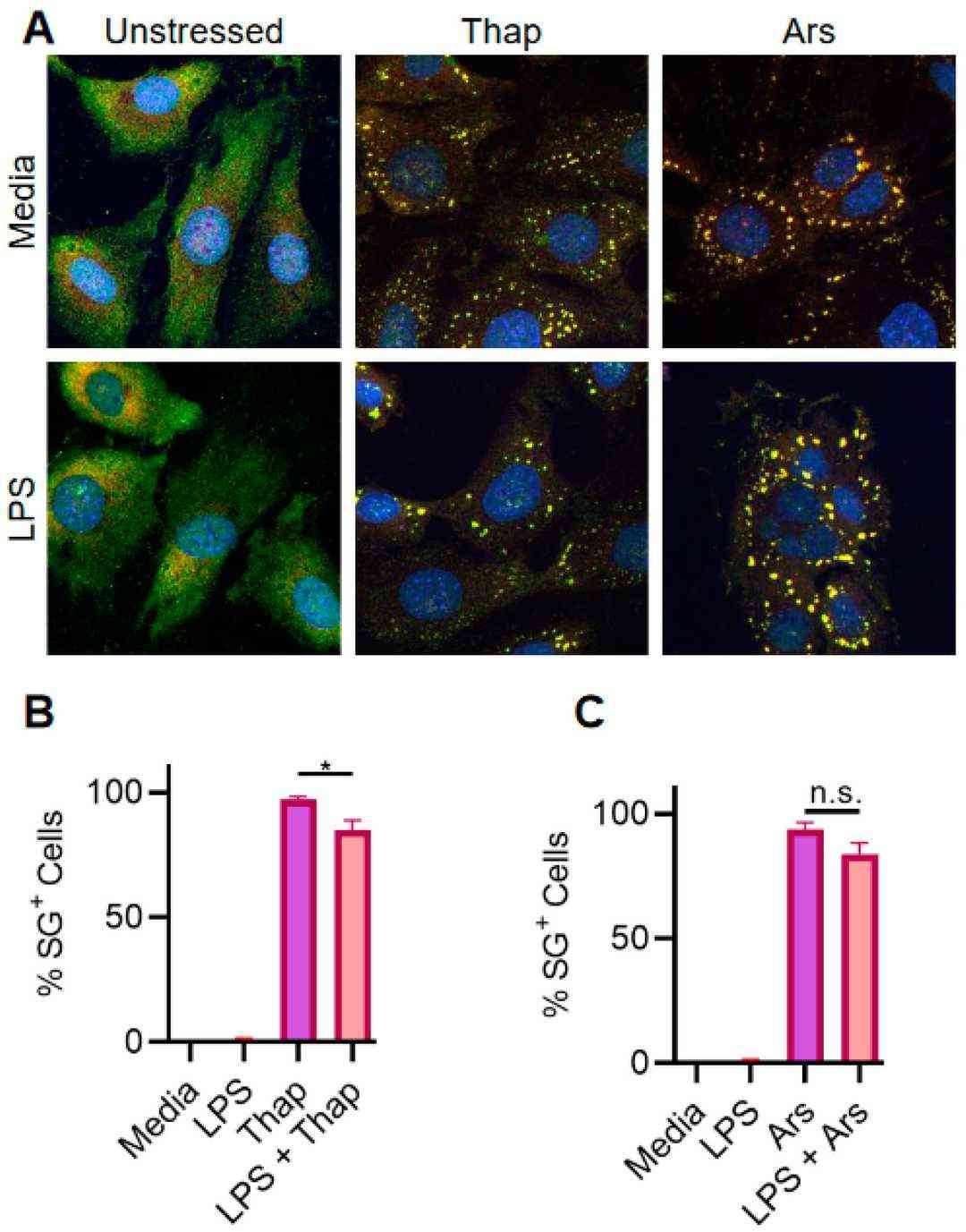 Fig. 1. TLR signaling only weakly inhibits ER stress-induced SGs in iMLFs (Lamichhane PP, Xie X, et al., 2024).
Fig. 1. TLR signaling only weakly inhibits ER stress-induced SGs in iMLFs (Lamichhane PP, Xie X, et al., 2024).
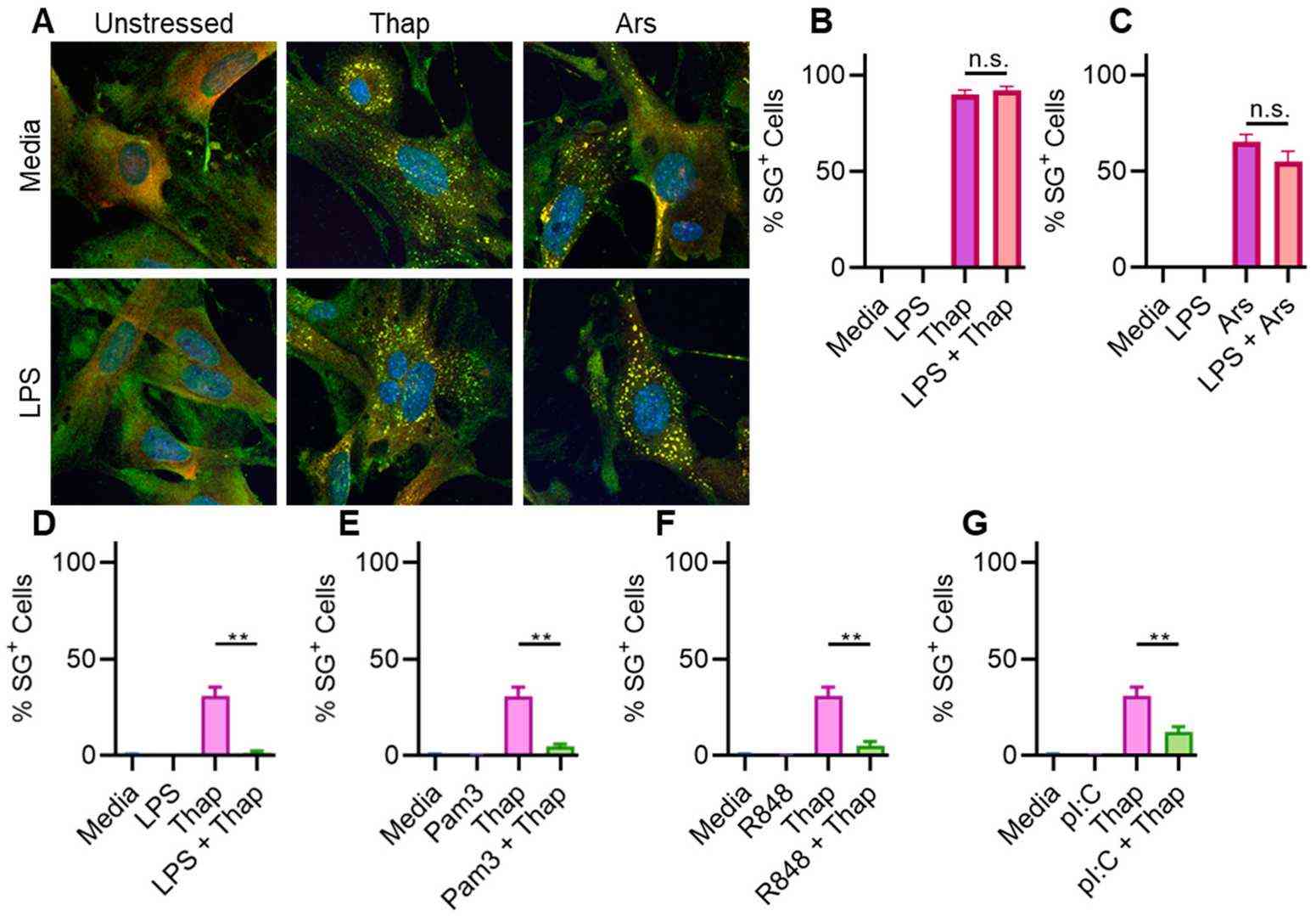 Fig. 2. TLR signaling fails to inhibit SGs in primary MLFs (Lamichhane PP, Xie X, et al., 2024).
Fig. 2. TLR signaling fails to inhibit SGs in primary MLFs (Lamichhane PP, Xie X, et al., 2024).
Cytotoxicity and Cell Adhesion Studies of Bioresorbable Ureteral Stents from Natural Origin Polymers
Ureteral stents are essential for treating urinary tract issues but often face problems like encrustation and infection. Traditional stents are non-biodegradable, leading to complications. Barros et al. developed biocompatible and bioresorbable stents using natural polysaccharides like alginate, and gelatin. These stents are produced through templated gelation and CO₂ drying, aiming to improve stent performance and reduce complications.
The cytotoxicity of six developed stents was evaluated using immortalized mouse lung fibroblasts, following ISO/EN 10,993.27. Cell viability was assessed after 72 hours of contact with the stents, compared to cells grown on a tissue culture plate (Fig. 3a). No significant differences were found between the developed stents and the commercial stent used as a negative control. Additionally, cell adhesion on the stent surfaces was tested after 1 and 3 days using the MTS viability assay (Fig. 3b). Results showed no cell adhesion on the stent surfaces, similar to the commercial stent. This is likely due to the hydrophilic nature of the biopolymers, although some literature reports cell adhesion on similar materials.
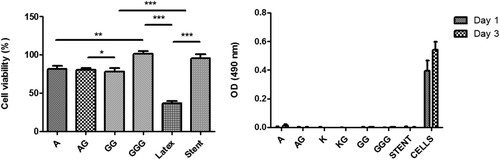 Fig. 3. Cytotoxicity and cell adhesion studies: (a) cell viability measured after 72 h and (b) cell adhesion on the surface of the different stents (Barros A A, Rita A, et al., 2014).
Fig. 3. Cytotoxicity and cell adhesion studies: (a) cell viability measured after 72 h and (b) cell adhesion on the surface of the different stents (Barros A A, Rita A, et al., 2014).
Immortalized Mouse Lung Fibroblasts are lung fibroblast cells derived from mice that have been genetically modified to go beyond 20 passages in vitro. They retain critical features of primary lung fibroblasts, making them a valuable model for respiratory and fibrotic research.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells