Immortalized Mouse Lung Epithelial Cells (MLE-12)
Cat.No.: CSC-I2116Z
Species: mouse
Morphology: Polygonal
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
free from contaminations (bacteria incl. mycoplasma, fungi, HIV, HAV, HBV, HCV, Parvo-B19) and cross-contaminations
Note: Never can cells be kept at -20°C.
MLE-12 is a murine lung epithelial cell line derived from the distal respiratory epithelium. This cell line was established using transgenic mice expressing the simian virus 40 (SV40) large tumor antigen, under the control of the human surfactant protein C (SP-C) promoter. MLE-12 possesses the ability to maintain certain properties of alveolar type II cells, such as the expression of surfactant proteins SP-B and SP-C, which are crucial for the synthesis of pulmonary surfactant and lung function. MLE-12 cells also exhibit key morphological features of alveolar type II cells, including microvilli and multivesicular bodies, although some features like lamellar bodies are lacking in subsequent passages.
The MLE-12 cell line is widely used to study the regulation and secretion of surfactant proteins and their pulmonary response to stimulation. It secretes phospholipids in response to various secretagogues such as ATP and phorbol esters, mimicking aspects of type II alveolar cell function. While this secretion is robust in early passages, it diminishes in subsequent passages, along with changes in receptor-mediated responses. This model is of particular value for exploring mechanisms underlying respiratory distress syndrome and surfactant deficiency. Furthermore, the cell line offers insights into pulmonary carcinogenesis, given its derivation from SV40-driven tumorigenesis.
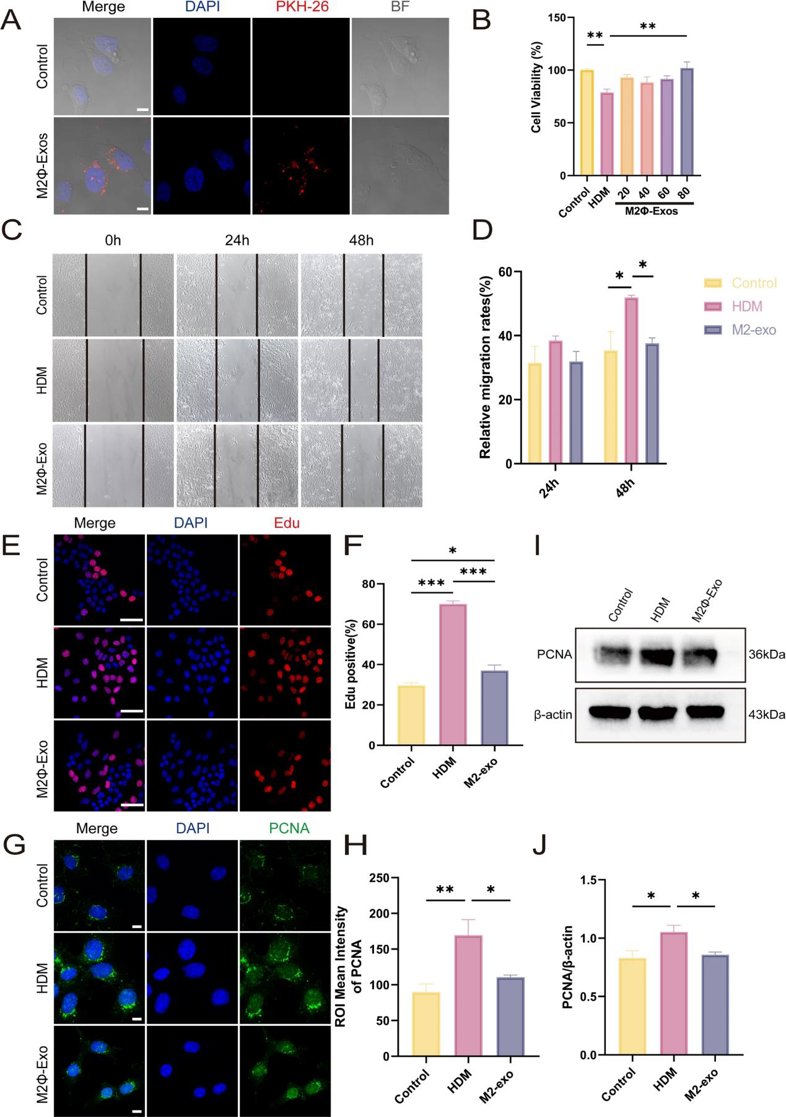
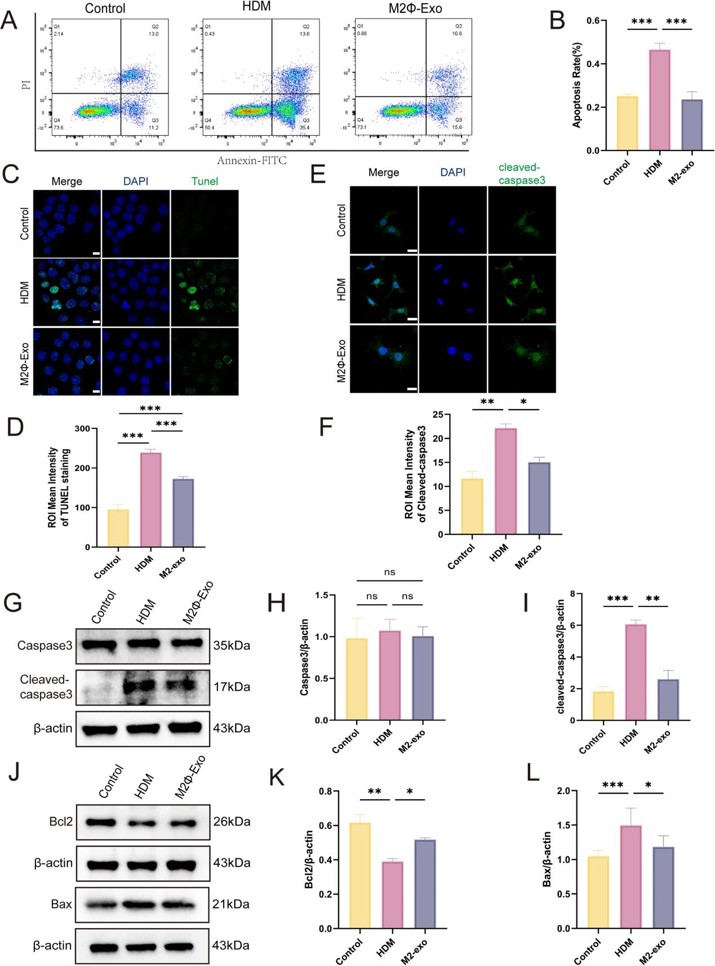
Exosomes Derived from M2 Macrophages Regulate Airway Inflammation by Modulating Epithelial Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by airway remodeling and immune dysregulation. This study aimed to explore the mechanisms by which M2 macrophage-derived exosomes (M2Φ-Exos) regulate airway inflammation in asthma by modulating epithelial cell proliferation and apoptosis.
M2Φ-Exos were extracted and characterized by morphology, size, and marker protein expression. In vitro, the effects of M2Φ-Exos on House Dust Mites (HDM)-stimulated mouse lung epithelial cells (MLE-12s) were evaluated using western blotting to analyze Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen (PCNA), B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2), Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax), and cleaved caspase-3 expression.
The results showed that MLE-12 cells internalized M2Φ-Exos, leading to reduced abnormal proliferation and apoptosis in HDM-stimulated cells.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells